Unveiling the Power of Treemaps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data Hierarchies
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Treemaps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data Hierarchies
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Treemaps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data Hierarchies. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Treemaps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data Hierarchies

In the realm of data visualization, where information is transformed into comprehensible and insightful visuals, treemaps emerge as a powerful tool for representing hierarchical data. They provide a unique and effective way to showcase the relative size and composition of various elements within a complex structure, enabling users to quickly grasp relationships and identify key patterns.
This comprehensive guide explores the essence of treemaps, delving into their fundamental principles, diverse applications, and the benefits they offer in various domains.
Understanding the Essence of Treemaps
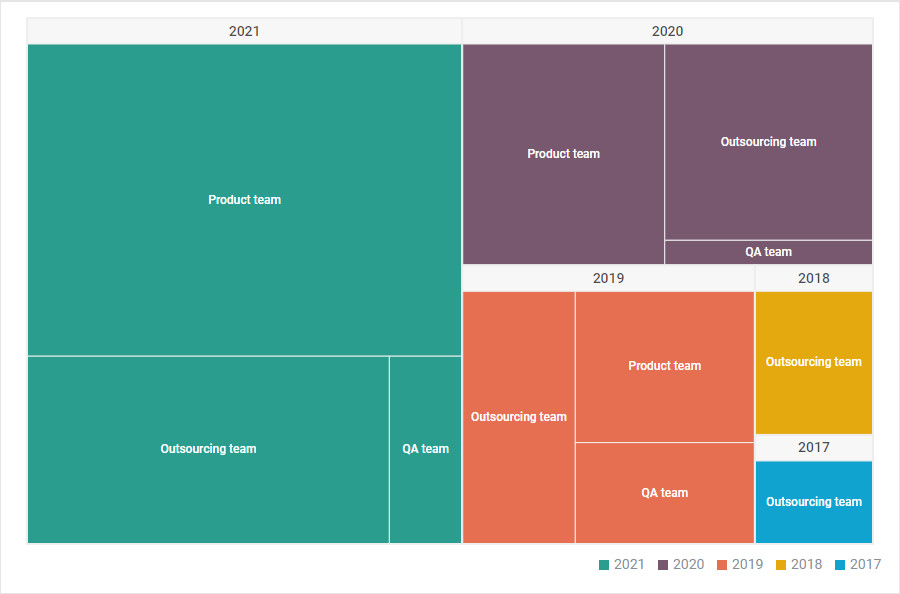
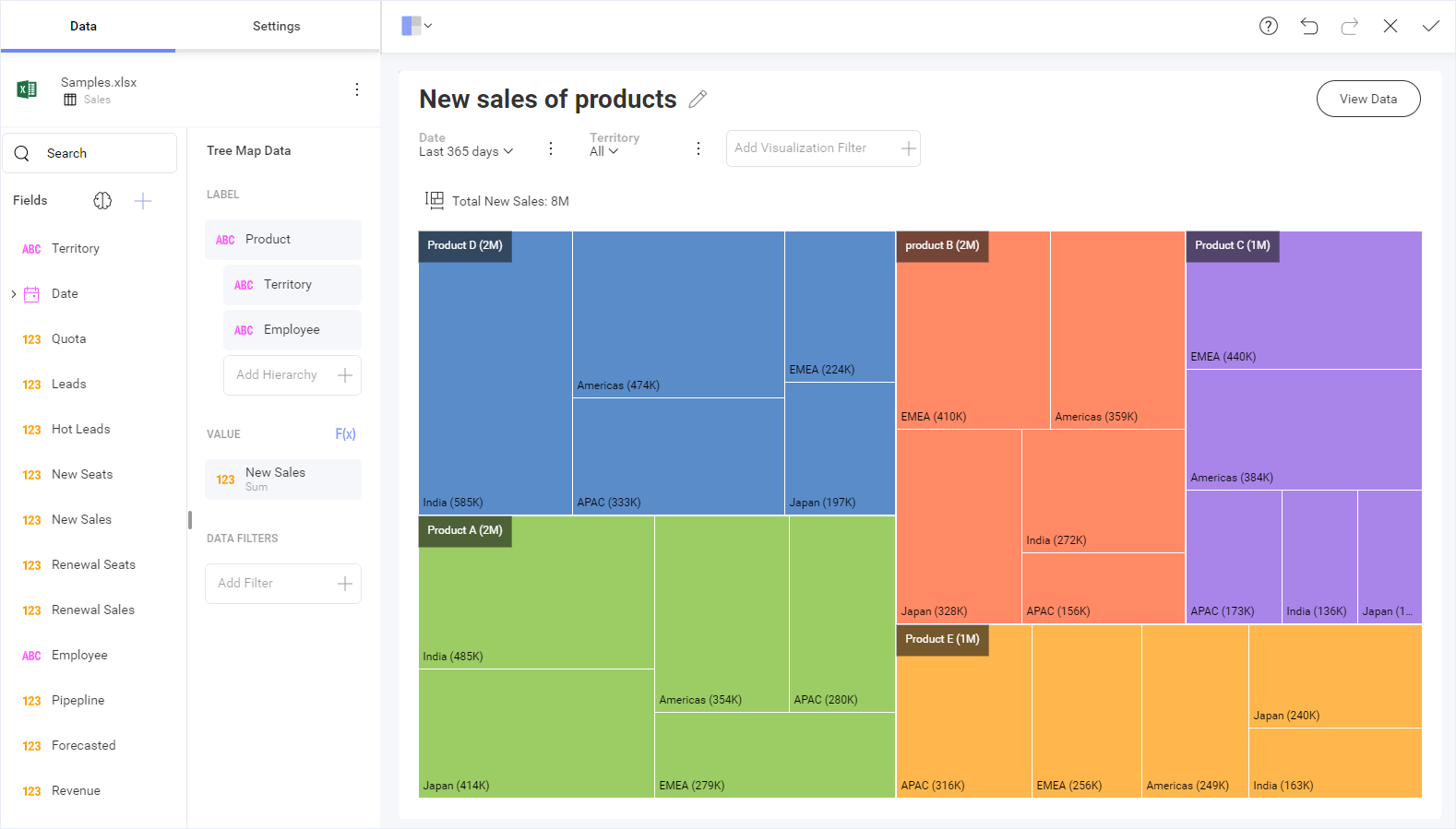
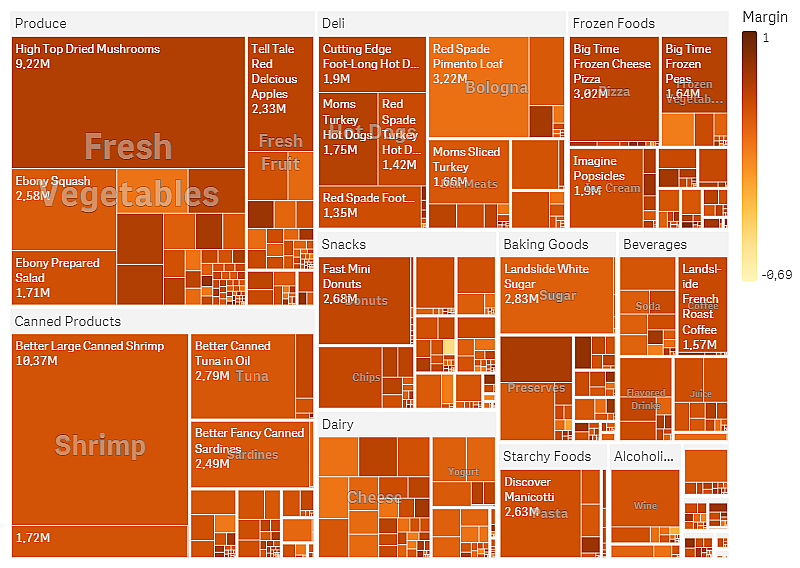
At its core, a treemap is a visualization technique that represents hierarchical data using nested rectangles. Each rectangle corresponds to a specific data element, with its area proportional to its value. The rectangles are arranged in a hierarchical structure, forming a nested arrangement that visually reflects the parent-child relationships within the data.
Imagine a company’s sales data, where each region has multiple departments, and each department contains various products. A treemap would visually represent this hierarchy by:
- Top Level: A large rectangle representing the total sales of the company.
- Region Level: Sub-rectangles within the company rectangle, each representing a specific region and sized proportionally to its sales contribution.
- Department Level: Further sub-rectangles within each region rectangle, representing departments and sized proportionally to their sales within that region.
- Product Level: Finally, sub-rectangles within each department rectangle, representing individual products and sized proportionally to their sales within that department.
This nested structure, with rectangles of varying sizes, offers a clear visual representation of the relative contribution of each element within the hierarchy, highlighting key trends and outliers.
The Benefits of Treemaps: A Visual Exploration of Data Hierarchies
Treemaps excel in showcasing hierarchical data due to their inherent advantages:
- Space Efficiency: Treemaps effectively utilize space, allowing the display of a large amount of data in a compact format. This is particularly useful when dealing with complex hierarchies containing numerous elements.
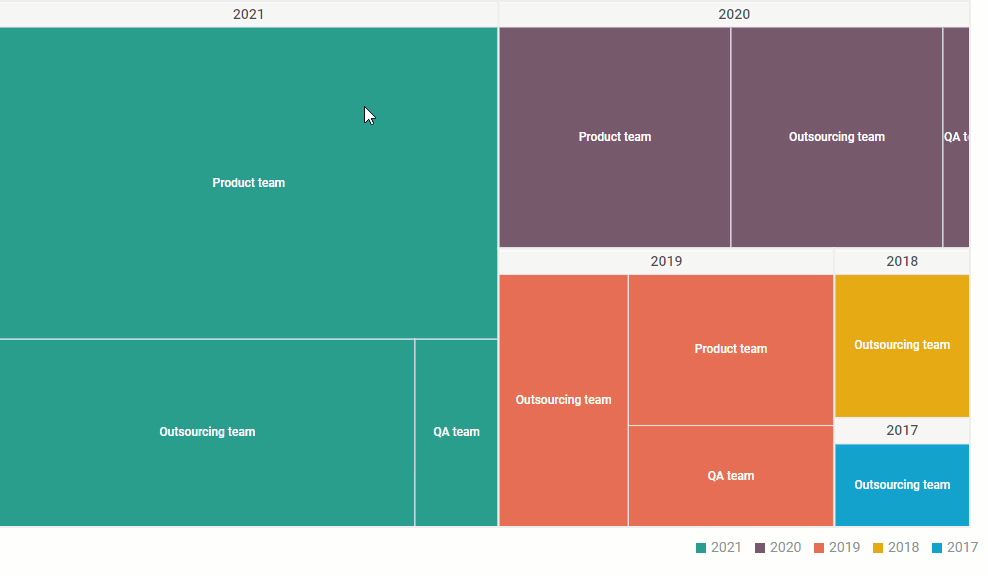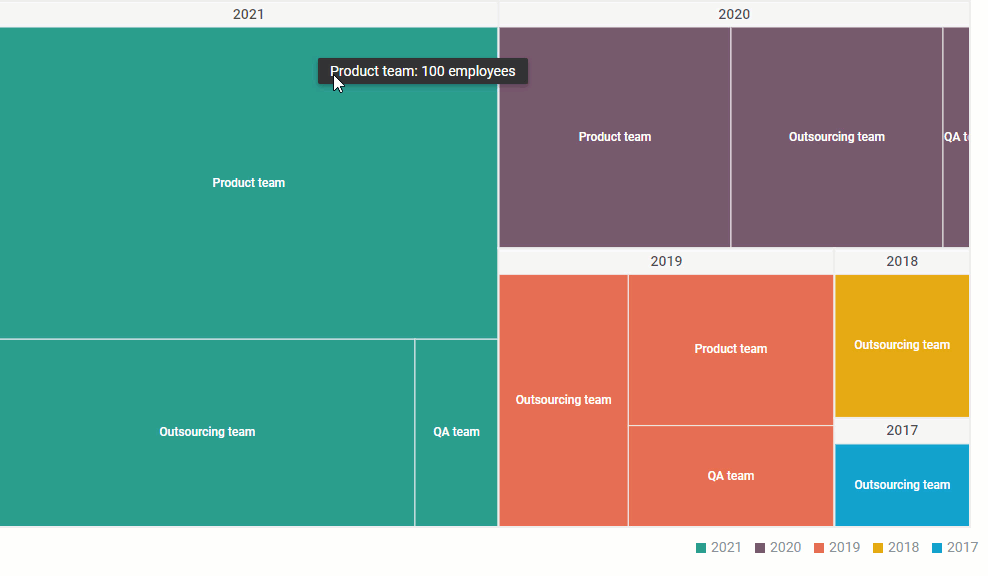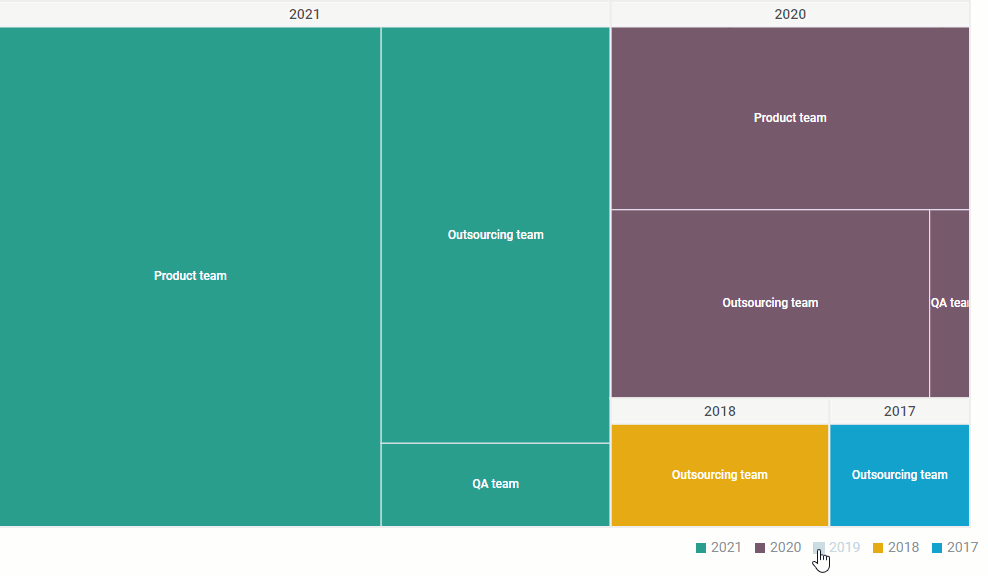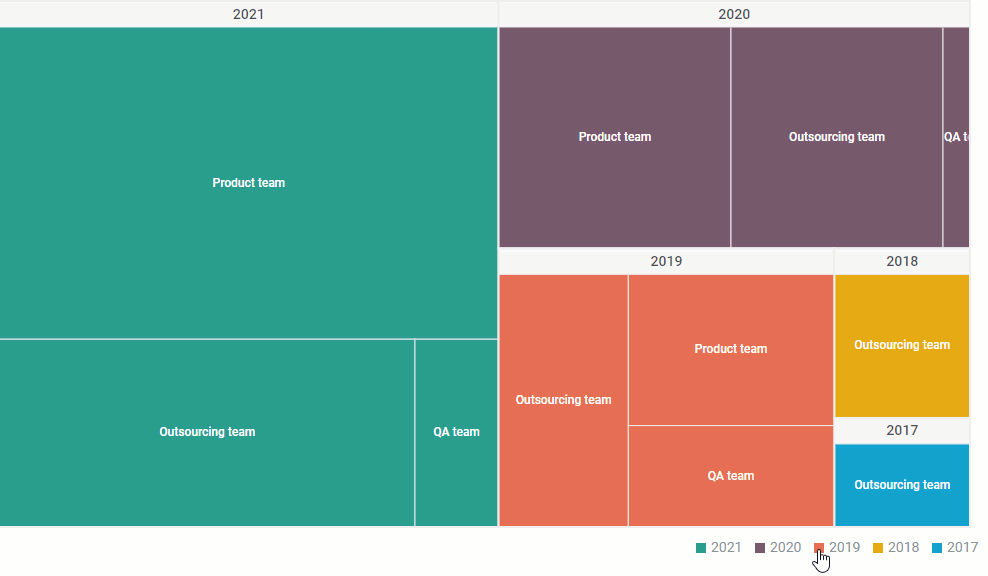
- Relative Size Representation: The area of each rectangle directly corresponds to its value, providing a quick and intuitive understanding of the relative contribution of each element within the hierarchy.
- Hierarchical Visualization: The nested structure clearly depicts the parent-child relationships, enabling users to easily navigate and understand the complex interconnections within the data.
- Outlier Identification: Significant deviations in size are easily noticeable, highlighting outliers and potentially significant trends that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Dynamic Exploration: Interactive treemaps allow users to drill down into specific branches of the hierarchy, exploring individual elements and their relationships in greater detail.
Applications of Treemaps: A Diverse Spectrum of Use Cases
Treemaps find their application in a wide range of domains, including:
- Business Analytics: Analyzing sales data, market share, customer segmentation, and resource allocation.
- Finance: Visualizing portfolio performance, asset allocation, and investment returns.
- Marketing: Understanding website traffic, campaign performance, and customer demographics.
- Healthcare: Tracking patient demographics, disease prevalence, and resource utilization.
- Education: Analyzing student performance, course enrollment, and resource allocation.
- Software Engineering: Visualizing code complexity, function call hierarchies, and software dependencies.
- Environmental Monitoring: Analyzing data on deforestation, pollution levels, and resource consumption.
Types of Treemaps: Expanding the Visual Landscape
While the fundamental principle of nested rectangles remains consistent, various treemap variations cater to different data characteristics and visualization goals:
- Squarified Treemaps: Prioritize the creation of nearly square rectangles, minimizing wasted space and improving visual clarity.
- Slice-and-Dice Treemaps: Divide the main rectangle into slices, further subdividing each slice into smaller rectangles, allowing for the visualization of multiple dimensions within the data.
- Treemap with Color Encoding: Utilize color to further differentiate data elements, highlighting specific trends or categories within the hierarchy.
- Interactive Treemaps: Enable users to drill down into specific branches of the hierarchy, exploring individual elements and their relationships in greater detail.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Treemaps
1. What are the limitations of treemaps?
While powerful, treemaps have limitations:
- Label Placement: Labeling individual rectangles can be challenging, especially when dealing with a large number of elements.
- Data Density: Treemaps can become visually cluttered with a high volume of data, potentially obscuring key insights.
- Visual Distortion: The relative size representation can be distorted when dealing with data that spans several orders of magnitude.
2. How can I choose the right treemap variation?
The selection of a specific treemap variation depends on the nature of the data and the visualization goals.
- Squarified treemaps are suitable for general hierarchical data visualization.
- Slice-and-dice treemaps are ideal for showcasing multiple dimensions within the data.
- Treemaps with color encoding enhance visual clarity and highlight specific trends.
- Interactive treemaps provide a dynamic and explorative approach to data analysis.
3. What software tools support treemap creation?
Numerous software tools support treemap creation, including:
- Excel: Provides basic treemap functionality through its charting tools.
- Tableau: Offers advanced treemap creation capabilities with interactive features.
- Power BI: Provides comprehensive treemap features with data exploration and visualization tools.
- R: Offers extensive libraries for creating custom treemaps with advanced customization options.
- Python: Provides libraries like "matplotlib" and "plotly" for creating treemaps with flexible design and interactivity.
Tips for Creating Effective Treemaps
- Clear Hierarchy: Define a clear and logical hierarchical structure to guide the visual representation.
- Appropriate Data: Choose data suitable for hierarchical visualization, where elements can be grouped and categorized.
- Color Palette: Select a color palette that enhances visual clarity and differentiates elements effectively.
- Labeling: Consider using labels strategically to highlight key elements and avoid visual clutter.
- Interactivity: Utilize interactive features to enable users to explore the data in greater detail.
Conclusion: The Power of Visualizing Hierarchies
Treemaps serve as a powerful tool for visualizing hierarchical data, offering a unique and effective approach to understanding complex relationships and identifying key patterns. Their space efficiency, relative size representation, and hierarchical visualization capabilities make them invaluable for exploring data in diverse domains. By understanding the principles, benefits, and variations of treemaps, users can leverage their power to gain deeper insights and make informed decisions based on data-driven visualizations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Treemaps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data Hierarchies. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!