Unveiling the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographic Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographic Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographic Map

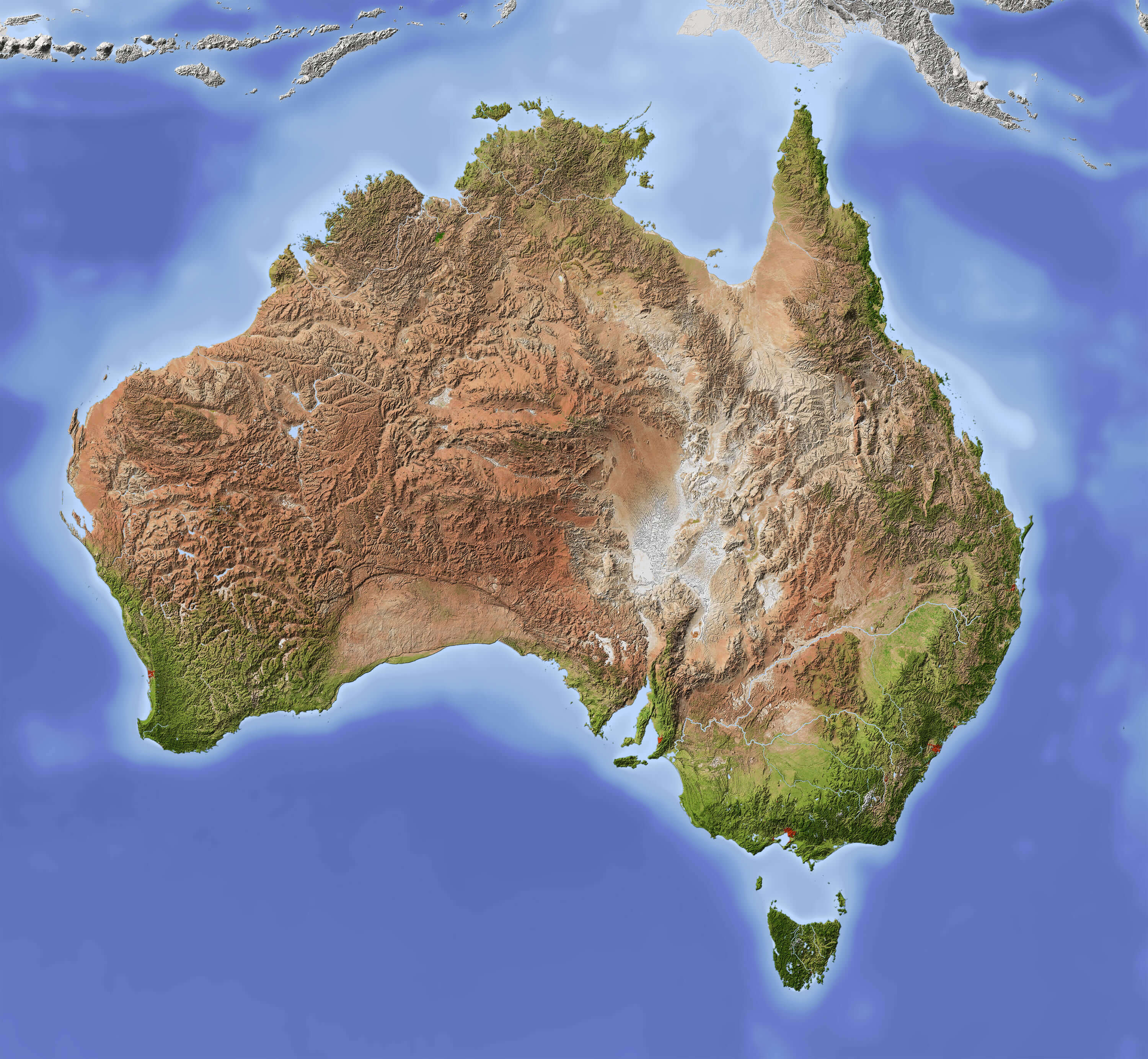
Australia, a landmass of immense size and diverse environments, is a fascinating subject for geographical exploration. Understanding the geographic map of Australia is crucial for comprehending its unique characteristics, intricate ecosystems, and diverse cultural landscapes. This article delves into the intricacies of the Australian map, providing a detailed analysis of its major features and the profound implications they have on the nation’s identity and development.
The Continent’s Shape and Dimensions:
Australia, the world’s sixth-largest country, occupies an entire continent. Its distinctive shape, resembling a large, flattened island, is defined by its vast coastline stretching over 36,000 kilometers. The mainland, encompassing the majority of the country, is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Tasman Sea to the east, and the Arafura Sea and Timor Sea to the north.
A Land of Extremes: Topography and Geology:
Australia’s topography is characterized by remarkable contrasts. The vast interior, known as the Outback, is dominated by arid plains and deserts, punctuated by rugged mountain ranges like the Great Dividing Range, which runs along the east coast. This range, culminating in the Snowy Mountains, is the highest point on the mainland.
The country’s geological history is equally diverse. Ancient Precambrian rocks form the base of the continent, while younger sedimentary formations, including the Great Artesian Basin, are found in the interior. The western half of Australia is dominated by the vast, flat, and arid Western Plateau, while the eastern portion exhibits a more varied landscape, including the fertile coastal plains and the lush rainforests of the northeast.
Climate and Bioregions:
Australia’s climate is as diverse as its topography. The interior experiences scorching summers and cold winters, with rainfall being scarce. The east coast, influenced by the Pacific Ocean, enjoys a more temperate climate, with rainfall varying from subtropical in the north to temperate in the south. The north experiences a tropical monsoon climate, characterized by wet summers and dry winters.
This diverse climate translates into a wide range of bioregions, each with unique flora and fauna. From the arid deserts of the interior to the rainforests of the east coast, the Australian landscape is a testament to the power of adaptation. The country is home to a remarkable array of endemic species, including the iconic kangaroo, koala, and platypus, highlighting the significance of its unique geographical features.
Major Cities and Urban Development:
Despite its vast size, Australia’s population is concentrated in a relatively small number of cities. Sydney, located on the east coast, is the largest city and a major economic and cultural hub. Other significant cities include Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Adelaide, and Canberra, the nation’s capital.
Urban development in Australia is characterized by a strong focus on sustainability and livability. Cities are designed with green spaces, efficient public transport systems, and a commitment to environmental conservation. This approach reflects the growing awareness of the importance of preserving the natural environment while fostering economic growth.
Natural Resources and Economic Significance:
Australia is rich in natural resources, including vast reserves of coal, iron ore, and natural gas. These resources have played a significant role in the country’s economic development. The mining sector is a major contributor to the Australian economy, providing jobs and generating revenue.
However, the exploitation of these resources also raises concerns about environmental sustainability. The government is actively working to balance economic growth with environmental protection, promoting sustainable practices and investing in renewable energy sources.
Geographic Map of Australia: A Vital Tool for Understanding the Nation
The geographic map of Australia is not merely a static representation of the landmass. It is a dynamic tool for understanding the nation’s complexities, from its diverse landscapes and ecosystems to its intricate social and economic structures.
By studying the map, we gain insights into:
- Spatial distribution of resources: Identifying the locations of key resources like minerals, water, and agricultural land helps in optimizing their management and utilization.
- Population distribution and urban planning: Understanding the spatial distribution of population allows for efficient planning of infrastructure, services, and urban development.
- Environmental issues and conservation: Analyzing the geographical distribution of environmental challenges, such as drought, bushfires, and coastal erosion, facilitates the development of targeted conservation strategies.
- Cultural and historical influences: The map reveals the impact of geography on the development of different cultures, indigenous communities, and historical events.
- Economic development and trade: Understanding the geographical location of key industries, ports, and transportation networks is crucial for facilitating trade and economic growth.
FAQs on the Geographic Map of Australia
1. What are the major geographic features of Australia?
Australia is characterized by its vast size, diverse topography, and unique climate. Key features include the Great Dividing Range, the Western Plateau, the Outback, and the numerous coastal plains.
2. What are the major bioregions of Australia?
Australia’s bioregions are diverse, ranging from the arid deserts of the interior to the lush rainforests of the east coast. Some notable bioregions include the Outback, the Great Barrier Reef, the Tasmanian Wilderness, and the tropical rainforests of Queensland.
3. How does the geographic map of Australia impact its economic development?
The geographic map plays a significant role in shaping Australia’s economy. The distribution of natural resources, particularly minerals and energy, has driven significant economic growth. The location of major cities and transportation networks also influences trade and economic activity.
4. What are the major environmental challenges facing Australia?
Australia faces a range of environmental challenges, including climate change, drought, bushfires, and land degradation. The geographic map helps in understanding the spatial distribution of these challenges and developing effective mitigation strategies.
5. How does the geographic map of Australia contribute to its cultural identity?
The geographic map plays a crucial role in shaping Australia’s cultural identity. The vast landscapes, unique wildlife, and diverse indigenous cultures are all influenced by geography. The map serves as a visual representation of the nation’s unique character and heritage.
Tips for Utilizing the Geographic Map of Australia
- Use a variety of map types: Explore different map types, such as physical maps, political maps, and thematic maps, to gain a comprehensive understanding of Australia’s geography.
- Focus on specific regions: Instead of attempting to study the entire country at once, focus on specific regions of interest, such as the Outback, the Great Barrier Reef, or the major cities.
- Relate the map to real-world events: Connect the geographic features on the map to current events, such as natural disasters, political developments, or economic trends.
- Use online resources: Explore online mapping tools and resources to access interactive maps, satellite imagery, and detailed information about specific locations.
- Engage in discussions: Discuss the geographic map with others, sharing insights and perspectives to deepen your understanding.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of the Geographic Map
The geographic map of Australia is a powerful tool for understanding the nation’s past, present, and future. By studying its features, we gain insights into the country’s natural resources, cultural heritage, environmental challenges, and economic development.
The map serves as a foundation for informed decision-making, facilitating sustainable development, environmental conservation, and responsible resource management. As we continue to explore the complexities of the Australian landscape, the geographic map will remain an indispensable guide, unveiling the secrets and wonders of this unique and fascinating continent.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Australian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographic Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!