Unraveling the Tapestry of Thrace: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Thrace: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Thrace: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Thrace: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Thrace, a region steeped in history and rich in geographical diversity, has played a pivotal role in shaping the cultural and political landscape of southeastern Europe. Its strategic location, spanning the crossroads of the Aegean Sea, the Black Sea, and the Balkan Peninsula, has attracted empires, civilizations, and migratory peoples for millennia. Understanding the map of Thrace is not merely a geographical exercise; it is a journey through time, tracing the footsteps of empires and witnessing the interplay of cultures that have left their indelible mark on the region.
A Geographical Overview:
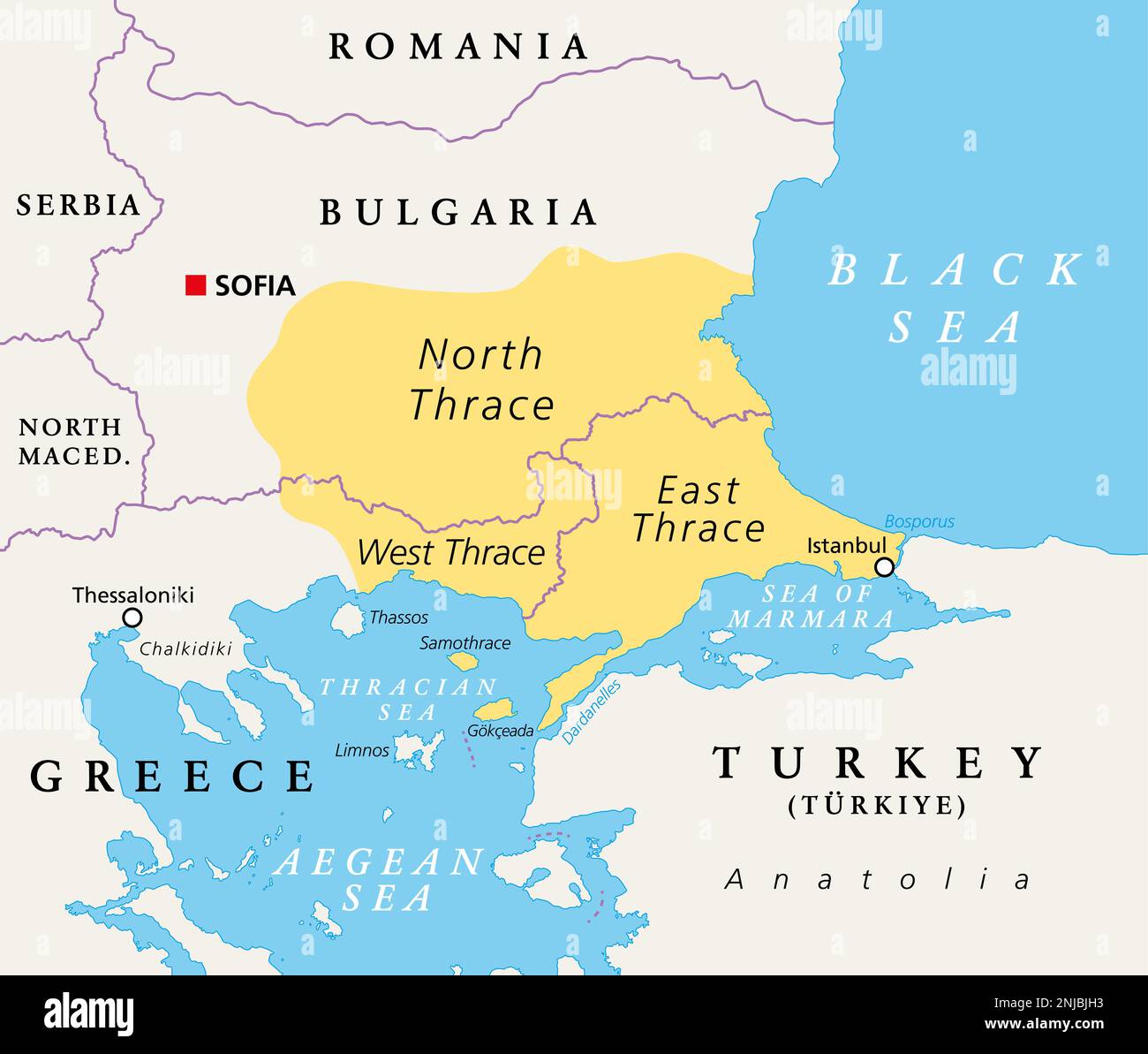
Thrace, in its broadest sense, encompasses a vast territory extending from the Balkan Mountains in the north to the Aegean Sea in the south, encompassing parts of modern-day Greece, Turkey, and Bulgaria. The region can be broadly divided into three distinct geographical zones:
- Eastern Thrace: Situated in modern-day Turkey, this region is primarily characterized by the fertile plains of the Maritsa River valley, extending to the shores of the Sea of Marmara. It is a vital agricultural hub, known for its production of wheat, cotton, and tobacco.
- Western Thrace: Located in modern-day Greece, this region is characterized by its diverse topography, ranging from the rolling hills of the Rhodope Mountains to the coastal plains of the Aegean Sea. It is home to a variety of agricultural products, including olives, grapes, and citrus fruits.
- Southern Thrace: Situated in the southernmost part of the region, this area encompasses the Thracian Sea, a portion of the Aegean Sea, and the Thracian coastline. It is a significant maritime hub, connecting the Aegean Sea to the Black Sea.
Historical Significance:
Thrace’s strategic location at the crossroads of civilizations has made it a battleground for empires and a melting pot of cultures. Its history is a tapestry woven with threads of ancient civilizations, Byzantine rule, Ottoman conquest, and modern nation-building.
- Ancient Thrace: In ancient times, Thrace was inhabited by various Thracian tribes, each with its own distinct language, culture, and traditions. The region was known for its skilled warriors, particularly its renowned horsemen, who were highly sought after by the armies of ancient Greece and Rome.
- Roman Empire: Thrace became part of the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD, playing a vital role in its expansion and defense. The region served as a strategic buffer zone against barbarian incursions and a major source of manpower for the Roman legions.
- Byzantine Empire: After the fall of the Roman Empire, Thrace became part of the Byzantine Empire, serving as a vital link between Constantinople and the eastern provinces. The region was heavily fortified, with numerous castles and fortresses built to defend against invasions.
- Ottoman Empire: In the 14th and 15th centuries, the Ottoman Empire conquered Thrace, marking the beginning of a long period of Ottoman rule. Thrace became a vital part of the Ottoman Empire, serving as a bridge between Europe and Asia.
- Modern Thrace: In the 20th century, Thrace was divided between Greece, Turkey, and Bulgaria, reflecting the complex geopolitical dynamics of the region.
Cultural Heritage:
Thrace’s rich history has left an enduring legacy on its cultural landscape. The region boasts a wealth of archaeological sites, ancient ruins, and historical monuments that offer a glimpse into its past.
- The Thracian Tombs: These elaborate burial structures, often adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures, offer a unique insight into the funerary practices and beliefs of the ancient Thracians.
- The Ancient City of Perinthus: Located in Eastern Thrace, this ancient city was a major port and commercial center during the classical period. Its ruins offer a glimpse into the urban life of ancient Thrace.
- The Monastery of Rila: Situated in the Rhodope Mountains, this medieval monastery is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, renowned for its stunning architecture and intricate frescoes.
- The Thracian Tomb of Kazanlak: Located in Bulgaria, this tomb is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, famous for its exquisite frescoes depicting scenes from Thracian mythology and daily life.
The Importance of Understanding the Map of Thrace:
Understanding the map of Thrace is crucial for comprehending the historical, cultural, and geopolitical significance of the region. It helps us:
- Trace the flow of history: The map provides a visual framework for understanding the ebb and flow of empires, the rise and fall of civilizations, and the movements of people across the region.
- Appreciate the cultural diversity: The map highlights the diverse cultural influences that have shaped the region, from the ancient Thracian tribes to the Byzantine Empire and the Ottoman Empire.
- Understand the geopolitical complexities: The map reveals the intricate geopolitical dynamics of the region, including the division of Thrace between Greece, Turkey, and Bulgaria, and the ongoing disputes over territory and resources.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the significance of the Thracian Sea?
The Thracian Sea, a portion of the Aegean Sea, is strategically located between the Aegean Sea and the Black Sea. Its importance lies in its role as a maritime hub, connecting the two seas and facilitating trade and transportation.
2. What are the major cities in Thrace?
Major cities in Thrace include:
- Istanbul (Turkey): Situated on the shores of the Sea of Marmara, Istanbul is a major metropolis and the largest city in Thrace.
- Edirne (Turkey): Located in Eastern Thrace, Edirne is a historic city, renowned for its Ottoman-era architecture and its annual wrestling festival.
- Komotini (Greece): Situated in Western Thrace, Komotini is a major commercial center and a hub for agricultural production.
- Alexandroupolis (Greece): Located on the Thracian Sea, Alexandroupolis is a significant port city and a hub for trade and transportation.
- Plovdiv (Bulgaria): Situated in the Rhodope Mountains, Plovdiv is a historic city, known for its ancient Roman ruins and its vibrant cultural scene.
3. What are the major rivers in Thrace?
Major rivers in Thrace include:
- Maritsa River: The longest river in Thrace, the Maritsa River flows through Eastern Thrace, providing vital irrigation for agriculture and serving as a major transportation route.
- Evros River: This river forms the border between Greece and Turkey, serving as a natural boundary and a source of water for both countries.
- Struma River: The Struma River flows through Bulgaria, providing vital irrigation for agriculture and serving as a major transportation route.
4. What are the major mountain ranges in Thrace?
Major mountain ranges in Thrace include:
- Rhodope Mountains: This mountain range spans across Greece and Bulgaria, offering stunning scenery and opportunities for hiking and skiing.
- Balkan Mountains: This mountain range forms the northern boundary of Thrace, separating it from the Balkan Peninsula.
Tips for Exploring Thrace:
- Visit historical sites: Immerse yourself in the region’s rich history by visiting the numerous archaeological sites, ancient ruins, and historical monuments.
- Explore the natural beauty: Hike through the Rhodope Mountains, enjoy the beaches of the Thracian Sea, and explore the diverse landscapes of the region.
- Experience the local culture: Sample the local cuisine, attend traditional festivals, and engage with the friendly locals to gain a deeper understanding of Thrace’s cultural heritage.
Conclusion:
The map of Thrace is not merely a geographical representation; it is a window into a complex and fascinating world. It reveals the region’s strategic importance, its rich history, its diverse cultures, and its enduring legacy. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the profound impact that Thrace has had on the world and its ongoing role in shaping the future of southeastern Europe.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Thrace: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!