Unraveling the Tapestry of Indigenous Mexico: A Map of Pre-Columbian Tribes
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Indigenous Mexico: A Map of Pre-Columbian Tribes
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Indigenous Mexico: A Map of Pre-Columbian Tribes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Indigenous Mexico: A Map of Pre-Columbian Tribes

The vibrant tapestry of Mexican culture is woven from the threads of its indigenous heritage. A map of pre-Columbian tribes reveals a mosaic of diverse cultures, languages, and traditions that flourished across the vast expanse of present-day Mexico before the arrival of the Spanish. This map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the rich history and cultural complexity of the region, highlighting the remarkable diversity of indigenous life that existed prior to European contact.
A Geographic and Cultural Panorama:
The map reveals a wide array of distinct tribes, each with its own unique language, customs, and societal structure. From the arid deserts of the north to the lush rainforests of the south, from the towering mountains to the fertile valleys, each region nurtured its own indigenous communities. These communities developed complex social, political, and economic systems, leaving behind a legacy of architectural marvels, intricate art forms, and sophisticated agricultural practices.
Key Tribes and Their Territories:
-
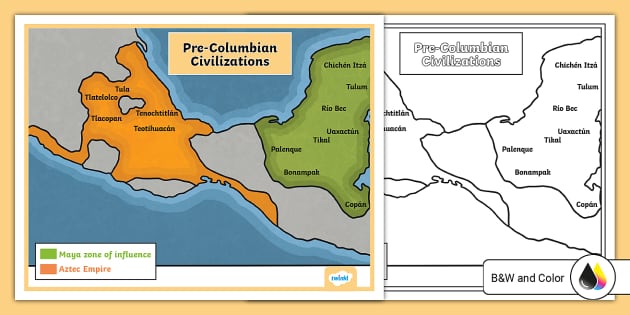
The Aztec (Mexica): Dominating central Mexico, the Aztec empire, with its capital at Tenochtitlán (present-day Mexico City), exerted significant political and cultural influence over a vast region. Known for their sophisticated social organization, advanced agriculture, and complex religious practices, the Aztec left a lasting mark on Mexican history and culture.
-
The Maya: Occupying the Yucatan Peninsula and parts of Guatemala and Belize, the Maya civilization is renowned for its advanced writing system, astronomical knowledge, and impressive architectural achievements. Their cities, such as Chichén Itzá and Tikal, stand as testaments to their ingenuity and cultural sophistication.
-
The Toltec: Preceding the Aztec, the Toltec civilization flourished in central Mexico, leaving behind a legacy of intricate sculptures, impressive pyramids, and a vibrant artistic tradition. Their influence extended across Mesoamerica, contributing to the development of later civilizations.
-
The Zapotec: Inhabiting the Oaxaca region, the Zapotec civilization is known for its impressive city of Monte Albán, with its intricate carvings, monumental architecture, and advanced agricultural practices. Their influence extended beyond their core territory, impacting the development of other indigenous cultures in the region.
-
The Mixtec: Sharing territory with the Zapotec, the Mixtec people were known for their exquisite goldwork, intricate codices (painted books), and their unique artistic style. Their contributions to Mesoamerican art and culture remain significant.
Beyond the Map: A Deeper Understanding of Indigenous Mexico:
While the map provides a visual representation of the geographic distribution of pre-Columbian tribes, it is crucial to recognize that it merely offers a glimpse into the complex tapestry of indigenous life. Each tribe possessed its own unique language, customs, beliefs, and social structures. Furthermore, the map does not capture the dynamic nature of these communities, their interactions with each other, and the constant evolution of their cultures over centuries.
The Importance of the Map:
The map of pre-Columbian tribes holds immense value for understanding the rich history and diverse cultural heritage of Mexico. It serves as a reminder of the remarkable achievements of indigenous civilizations, their contributions to human knowledge, and their enduring legacy. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of Mexican history, the resilience of indigenous communities, and the enduring influence of their traditions on modern Mexican culture.
FAQs:
Q: What is the significance of the map of pre-Columbian tribes?
A: The map provides a visual representation of the diverse indigenous communities that inhabited Mexico before the arrival of Europeans, highlighting their geographical distribution and cultural diversity. It serves as a valuable tool for understanding the rich history and cultural complexity of the region.
Q: What are some of the key tribes depicted on the map?
A: The map highlights prominent tribes such as the Aztec, Maya, Toltec, Zapotec, and Mixtec, each known for their unique cultural contributions and historical significance.
Q: How did the map come to be created?
A: The map is based on archaeological evidence, historical records, and linguistic studies, piecing together information from diverse sources to depict the distribution of pre-Columbian tribes.
Q: What can we learn from studying the map?
A: Studying the map helps us understand the geographic distribution of indigenous communities, their cultural diversity, and their interactions with each other. It provides valuable insights into the history, social structures, and cultural practices of pre-Columbian Mexico.
Q: How does the map contribute to our understanding of Mexican culture today?
A: The map underscores the enduring influence of indigenous cultures on modern Mexican society. It highlights the diverse traditions, languages, and artistic expressions that continue to enrich Mexican culture today.
Tips for Using the Map:
-
Focus on the Geographic Context: Pay attention to the location of each tribe and its relationship to the surrounding environment. Consider the impact of geography on their culture, economy, and social organization.
-
Explore Linguistic Diversity: Identify the different language families represented on the map and consider their connections to the broader Mesoamerican linguistic landscape.
-
Recognize Cultural Differences: Avoid generalizing about indigenous communities. Each tribe possessed its own unique beliefs, customs, and social structures.
-
Connect the Past to the Present: Explore the ways in which indigenous traditions continue to influence Mexican culture today. Consider the role of indigenous languages, art forms, and social practices in contemporary Mexican society.
Conclusion:
The map of pre-Columbian tribes serves as a powerful reminder of the rich cultural tapestry that existed in Mexico before European contact. It highlights the remarkable diversity of indigenous civilizations, their contributions to human knowledge, and their enduring legacy. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complexity of Mexican history, the resilience of indigenous communities, and the ongoing influence of their traditions on modern Mexican culture. The map invites us to appreciate the beauty and complexity of indigenous heritage, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation for the vibrant cultural landscape of Mexico.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Indigenous Mexico: A Map of Pre-Columbian Tribes. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!