Understanding the Power of Precinct Maps: A Guide to Political Geography
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Precinct Maps: A Guide to Political Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Precinct Maps: A Guide to Political Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Precinct Maps: A Guide to Political Geography

Precinct maps, often referred to as electoral maps, are fundamental tools in the realm of political geography and electoral processes. They represent the division of a geographic area into smaller, geographically defined units called precincts. These units serve as the building blocks for conducting elections, organizing political campaigns, and analyzing voting patterns. This article delves into the multifaceted world of precinct maps, exploring their creation, significance, and applications in various contexts.
Delving into the Structure of Precinct Maps:
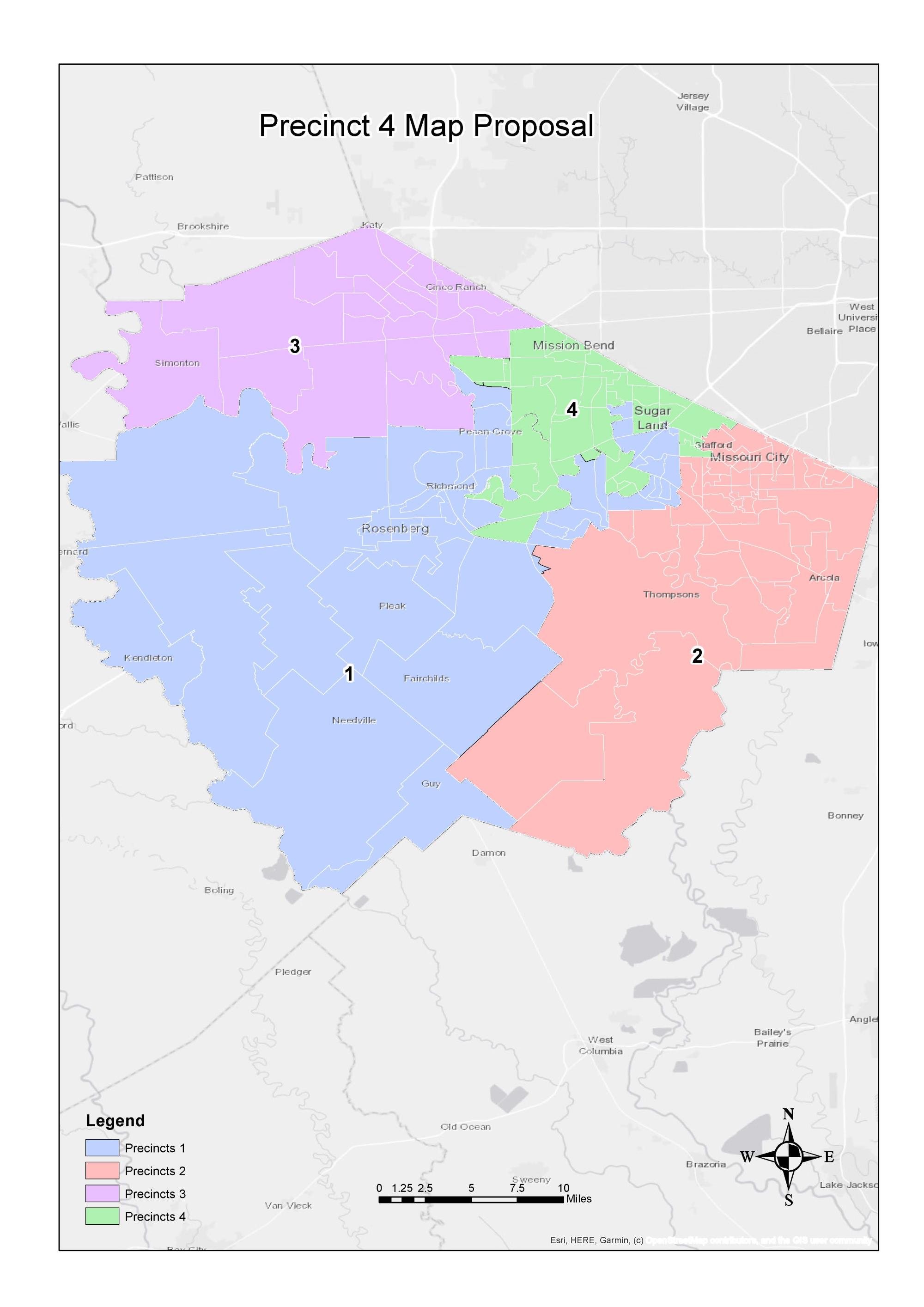
Precinct maps are typically created by government agencies responsible for elections, such as state or county election commissions. The process of drawing these maps involves carefully considering factors such as population density, geographic features, and community boundaries. The goal is to create precincts that are:
- Equally populated: This ensures fair representation and prevents one group from having undue influence due to a disproportionate number of voters in a single precinct.
- Compact and contiguous: Precincts should be geographically cohesive, minimizing the need for voters to travel long distances to reach their polling place.
- Reflecting community interests: Precinct boundaries should align with natural or historical divisions, respecting community identity and preserving the integrity of neighborhoods.
The Importance of Precinct Maps in Elections:
Precinct maps play a critical role in the electoral process, serving as the foundation for:
- Voter registration: Individuals register to vote based on their residential address, which falls within a specific precinct.
- Polling place allocation: Precinct maps dictate the location of polling places, ensuring accessibility for voters within their designated area.
- Election results tabulation: Votes are tallied and reported at the precinct level, providing a granular view of voting patterns and trends.
- Campaign strategy: Candidates and political parties utilize precinct maps to identify areas of support, target specific demographics, and allocate resources strategically.
- Redistricting: When population shifts occur, precinct maps are adjusted through a process called redistricting to maintain equal representation and ensure fair elections.
Beyond Elections: Applications of Precinct Maps:
Precinct maps transcend their electoral function, finding applications in various fields:
- Community planning: Local governments use precinct maps to assess demographic trends, allocate resources, and plan infrastructure development.
- Public health initiatives: Health officials leverage precinct maps to identify areas with higher disease rates, target public health campaigns, and track the spread of infectious diseases.
- Social research: Academics and researchers use precinct maps to analyze social and economic disparities, study voting behavior, and conduct demographic analysis.
- Marketing and advertising: Businesses and organizations use precinct maps to understand consumer demographics, target specific customer segments, and optimize advertising campaigns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Regarding Precinct Maps:
Q: Who is responsible for creating precinct maps?
A: Precinct maps are typically created by government agencies responsible for elections, such as state or county election commissions. However, in some cases, independent commissions or non-partisan bodies may be involved in the redistricting process.
Q: What are the criteria used to draw precinct boundaries?
A: Precinct boundaries are drawn based on factors such as population density, geographic features, community boundaries, and the need to ensure fair representation. The specific criteria may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the governing laws.
Q: Can precinct maps be manipulated for political gain?
A: Yes, there is a potential for manipulation of precinct maps, known as gerrymandering, which involves drawing boundaries to favor a particular political party or candidate. This practice is often controversial and subject to legal challenges.
Q: How often are precinct maps updated?
A: Precinct maps are typically updated after each decennial census, when population shifts and demographic changes are reflected in the data. However, some jurisdictions may update their maps more frequently, depending on local needs.
Tips for Understanding Precinct Maps:
- Consult official sources: Refer to the websites of your state or county election commission for accurate and up-to-date information on precinct maps.
- Utilize online mapping tools: Various online platforms offer interactive precinct maps, allowing you to explore boundaries, view demographic data, and analyze election results.
- Engage in community discussions: Participate in public forums and meetings related to redistricting to voice your concerns and advocate for fair representation.
- Stay informed about legal challenges: Follow legal developments related to gerrymandering and redistricting to understand how these issues impact your community.
Conclusion:
Precinct maps are indispensable tools for understanding and navigating the complexities of political geography and electoral processes. They serve as a foundation for fair elections, community planning, and a wide range of social and economic research. Understanding the creation, significance, and applications of precinct maps empowers individuals to participate actively in democratic processes, advocate for fair representation, and contribute to informed decision-making at all levels of government. By engaging with these maps, we can foster a more informed and equitable society.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Precinct Maps: A Guide to Political Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
