The Sea of Azov: A Shallow, Strategic, and Biologically Rich Body of Water
Related Articles: The Sea of Azov: A Shallow, Strategic, and Biologically Rich Body of Water
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Sea of Azov: A Shallow, Strategic, and Biologically Rich Body of Water. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Sea of Azov: A Shallow, Strategic, and Biologically Rich Body of Water

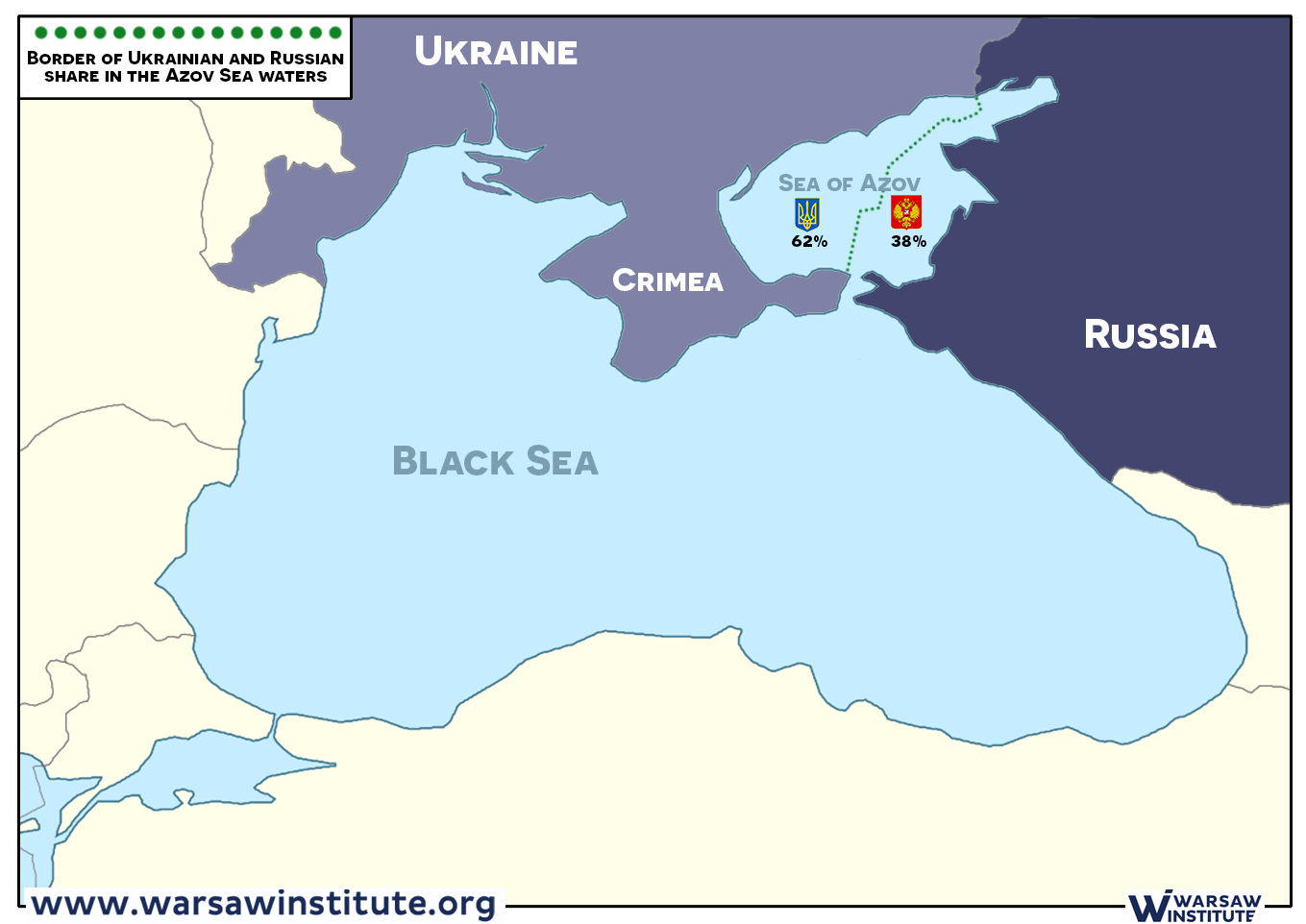
The Sea of Azov, a shallow, saline body of water located in the northwestern corner of the Black Sea, holds significant historical, economic, and ecological importance. It is connected to the Black Sea through the narrow Kerch Strait, and its unique features, such as its shallow depth, limited salinity, and abundant nutrient supply, create a rich and diverse ecosystem.
Geography and Physical Characteristics:
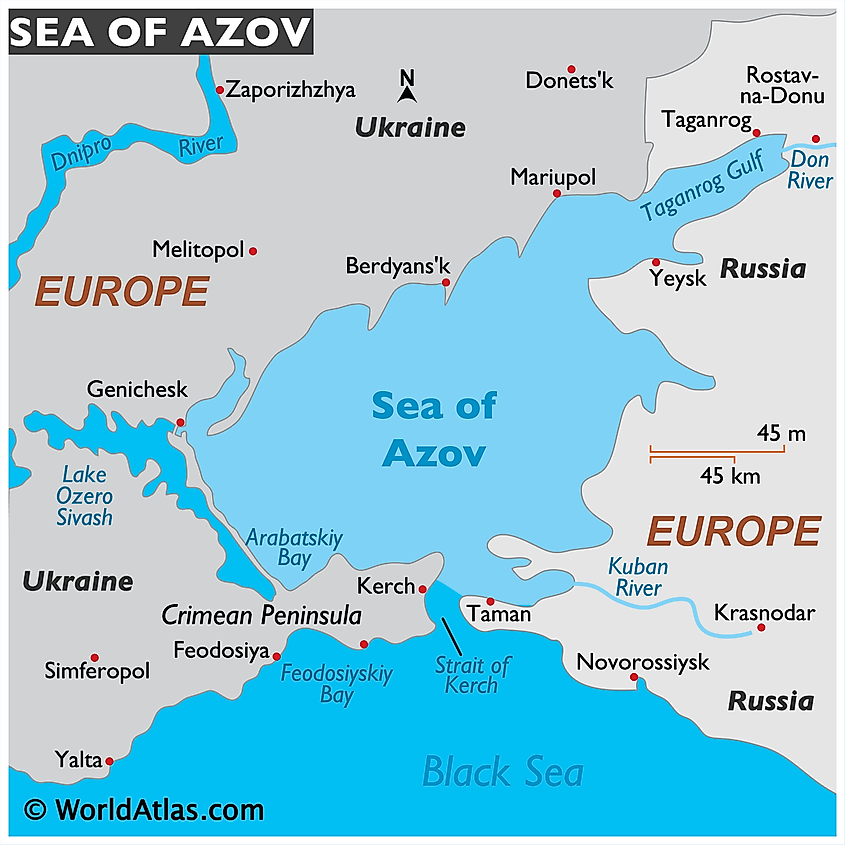
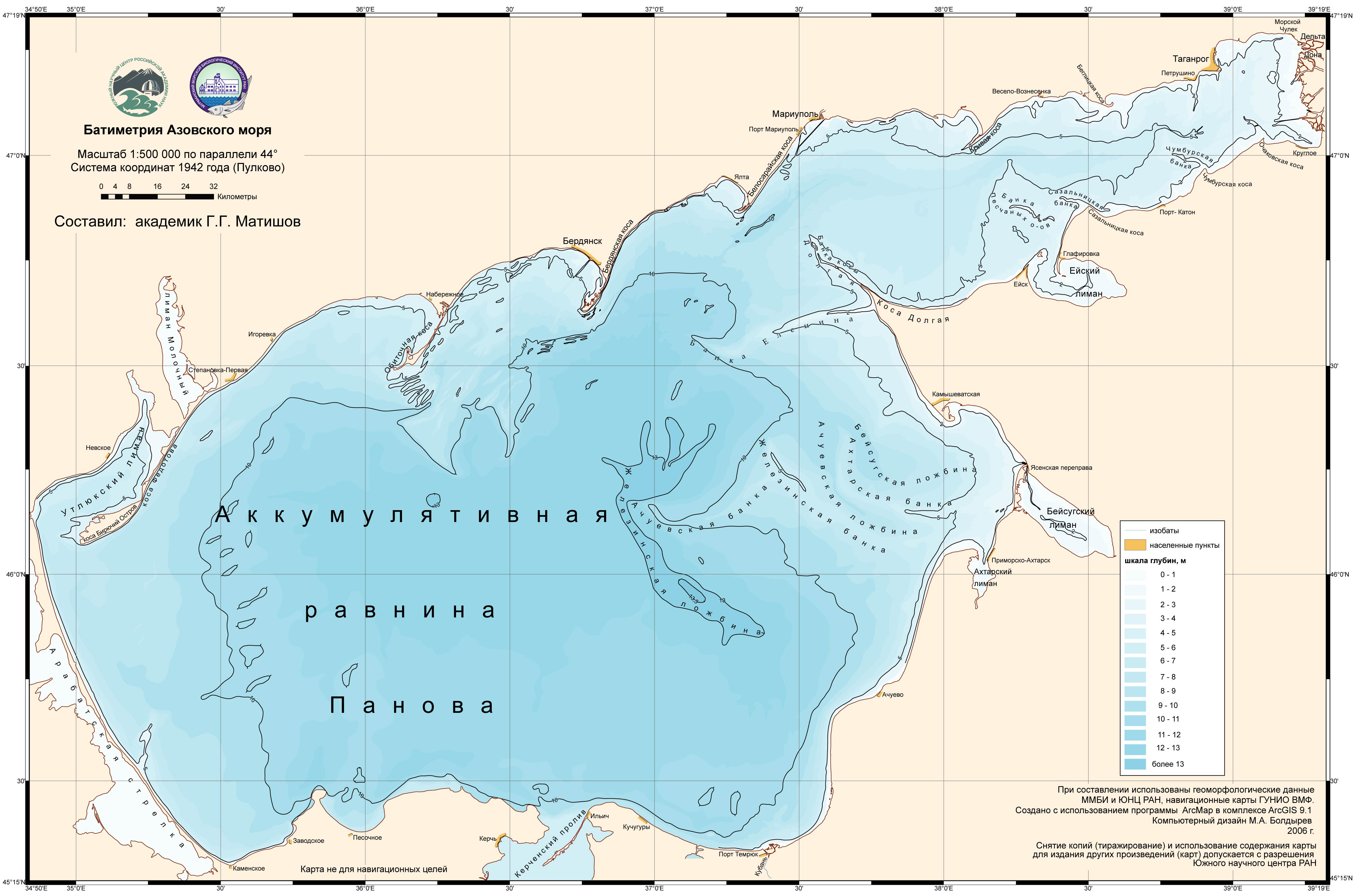
The Sea of Azov is the shallowest sea in the world, with an average depth of just 7 meters (23 feet) and a maximum depth of 14 meters (46 feet). Its relatively small size, covering an area of approximately 37,600 square kilometers (14,500 square miles), makes it highly susceptible to environmental influences. Its salinity levels are significantly lower than the Black Sea due to the influx of freshwater from the Don and Kuban rivers, which flow into the sea from the north and east, respectively.
Historical Significance:
The Sea of Azov has been a focal point of human activity for centuries. Its strategic location, connecting the Black Sea to the Don River and beyond, has made it a crucial trade route and a battleground for various empires throughout history. The ancient Greeks referred to the sea as the "Maeotis Lake," and it was later controlled by the Scythians, the Khazars, the Golden Horde, and the Ottoman Empire. In modern times, the Sea of Azov has been a major economic hub for Ukraine and Russia, serving as a vital source of fish, oil, and natural gas.
Economic Importance:
The Sea of Azov plays a vital role in the economies of Ukraine and Russia. Its rich fishing grounds have traditionally supported a thriving fishing industry, with sturgeon, herring, and anchovies being among the most valuable catches. The sea also holds significant oil and natural gas reserves, contributing to the energy sector of both countries. Additionally, the Sea of Azov is an important transportation route, connecting the Black Sea to the Don River and its vast agricultural and industrial regions.
Ecological Importance:
The Sea of Azov is a unique ecosystem characterized by its shallowness, low salinity, and abundant nutrient supply. These factors have fostered a rich biodiversity, with over 80 species of fish, numerous bird species, and diverse aquatic plant life thriving in its waters. The sea’s shallow depth allows for ample sunlight penetration, promoting the growth of phytoplankton, which forms the base of the food chain. The Don and Kuban rivers bring nutrients from the surrounding land, further enriching the ecosystem.
Environmental Challenges:
The Sea of Azov faces several environmental challenges, primarily due to human activities. Overfishing, pollution from industrial and agricultural sources, and the construction of dams on the Don and Kuban rivers have negatively impacted the sea’s ecosystem. Overfishing has depleted fish stocks, while pollution has contaminated the water and harmed marine life. The construction of dams has reduced the flow of freshwater and nutrients into the sea, altering its salinity and nutrient levels.
Current Status and Management:
Recognizing the importance of preserving the Sea of Azov’s unique ecosystem, both Ukraine and Russia have implemented measures to protect the sea. These include fishing quotas, pollution control regulations, and efforts to restore the flow of freshwater from the Don and Kuban rivers. However, the sea remains vulnerable to environmental pressures, and continued cooperation between Ukraine and Russia is crucial for its long-term sustainability.
FAQs about the Sea of Azov:
Q: What is the largest city on the Sea of Azov?
A: The largest city on the Sea of Azov is Mariupol, located in Ukraine.
Q: What are the main rivers that flow into the Sea of Azov?
A: The two main rivers that flow into the Sea of Azov are the Don River and the Kuban River.
Q: Why is the Sea of Azov so shallow?
A: The Sea of Azov is shallow due to the deposition of sediment from the Don and Kuban rivers, as well as the accumulation of sand and silt over time.
Q: What are the main economic activities on the Sea of Azov?
A: The main economic activities on the Sea of Azov include fishing, oil and gas extraction, and transportation.
Q: What are the major environmental challenges facing the Sea of Azov?
A: The major environmental challenges facing the Sea of Azov include overfishing, pollution, and the construction of dams on the Don and Kuban rivers.
Q: What are the key measures being taken to protect the Sea of Azov?
A: Key measures being taken to protect the Sea of Azov include fishing quotas, pollution control regulations, and efforts to restore the flow of freshwater from the Don and Kuban rivers.
Tips for Visiting the Sea of Azov:
- Explore the diverse coastline: The Sea of Azov offers a variety of landscapes, from sandy beaches to rocky cliffs, providing opportunities for swimming, sunbathing, and exploring.
- Visit historical sites: The region around the Sea of Azov is rich in history, with numerous ancient settlements, fortresses, and museums to explore.
- Enjoy the local culture: The region has a vibrant culture, with traditional music, dance, and cuisine to experience.
- Try the local seafood: The Sea of Azov is renowned for its fresh seafood, including sturgeon, herring, and anchovies.
Conclusion:
The Sea of Azov, despite its small size, plays a vital role in the history, economy, and ecology of the region. Its shallow depth, low salinity, and abundant nutrient supply create a unique ecosystem that supports a diverse range of flora and fauna. However, the sea faces significant environmental challenges due to human activities, requiring continued efforts to protect its rich biodiversity and ensure its long-term sustainability. Understanding and appreciating the importance of this vital body of water is crucial for the well-being of the surrounding communities and the preservation of its ecological treasures.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Sea of Azov: A Shallow, Strategic, and Biologically Rich Body of Water. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!