The Moses Journey Map: A Framework for Understanding Customer Experience
Related Articles: The Moses Journey Map: A Framework for Understanding Customer Experience
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Moses Journey Map: A Framework for Understanding Customer Experience. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Moses Journey Map: A Framework for Understanding Customer Experience
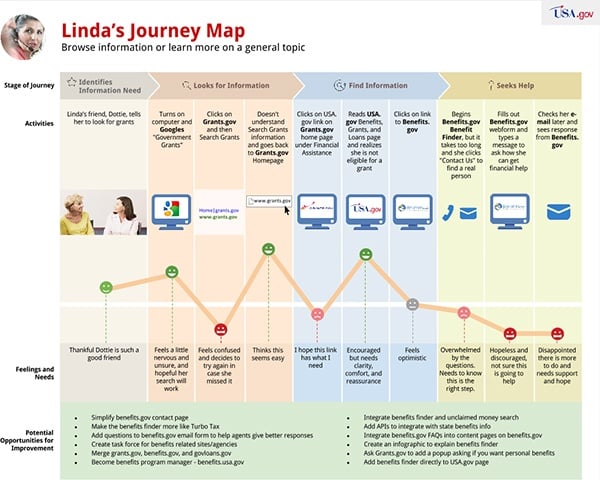
The Moses Journey Map, a powerful tool in the realm of user experience design, provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the intricate journey a customer takes when interacting with a product or service. This map, named after the biblical figure who led the Israelites through the wilderness, visually represents the customer’s experiences, emotions, and motivations throughout their interaction with a brand.
Understanding the Components of a Moses Journey Map
The Moses Journey Map comprises several key components:
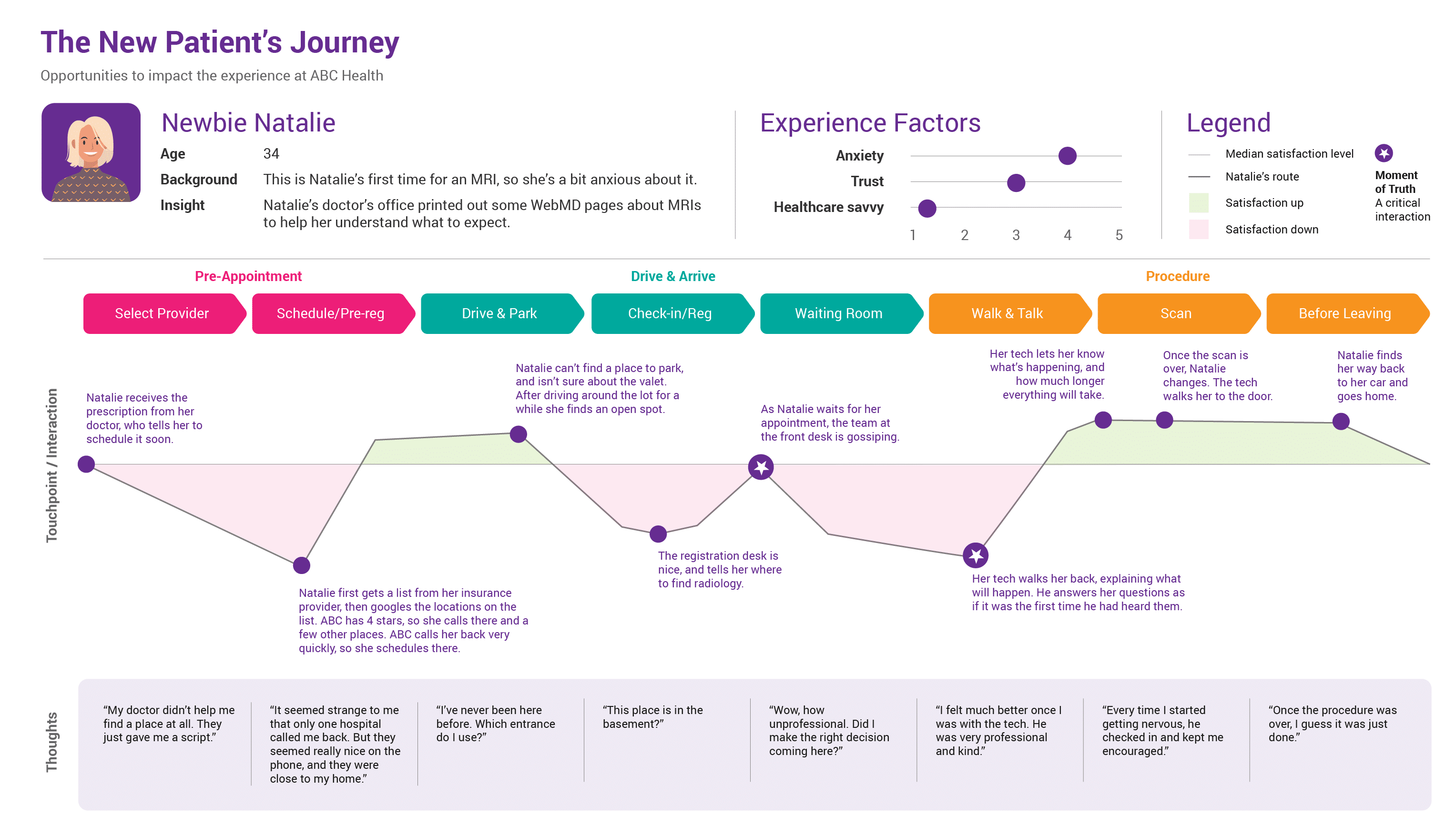
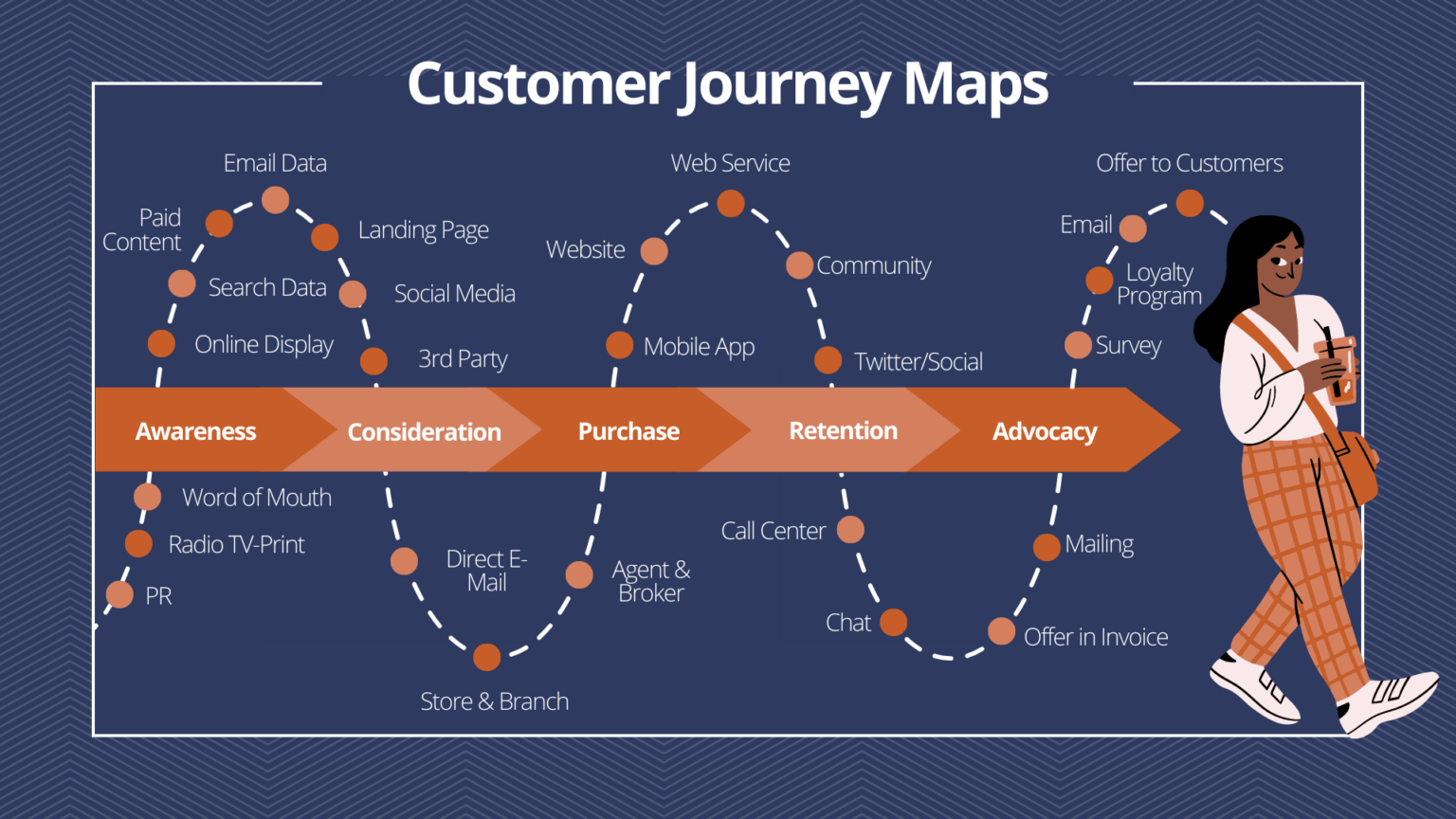
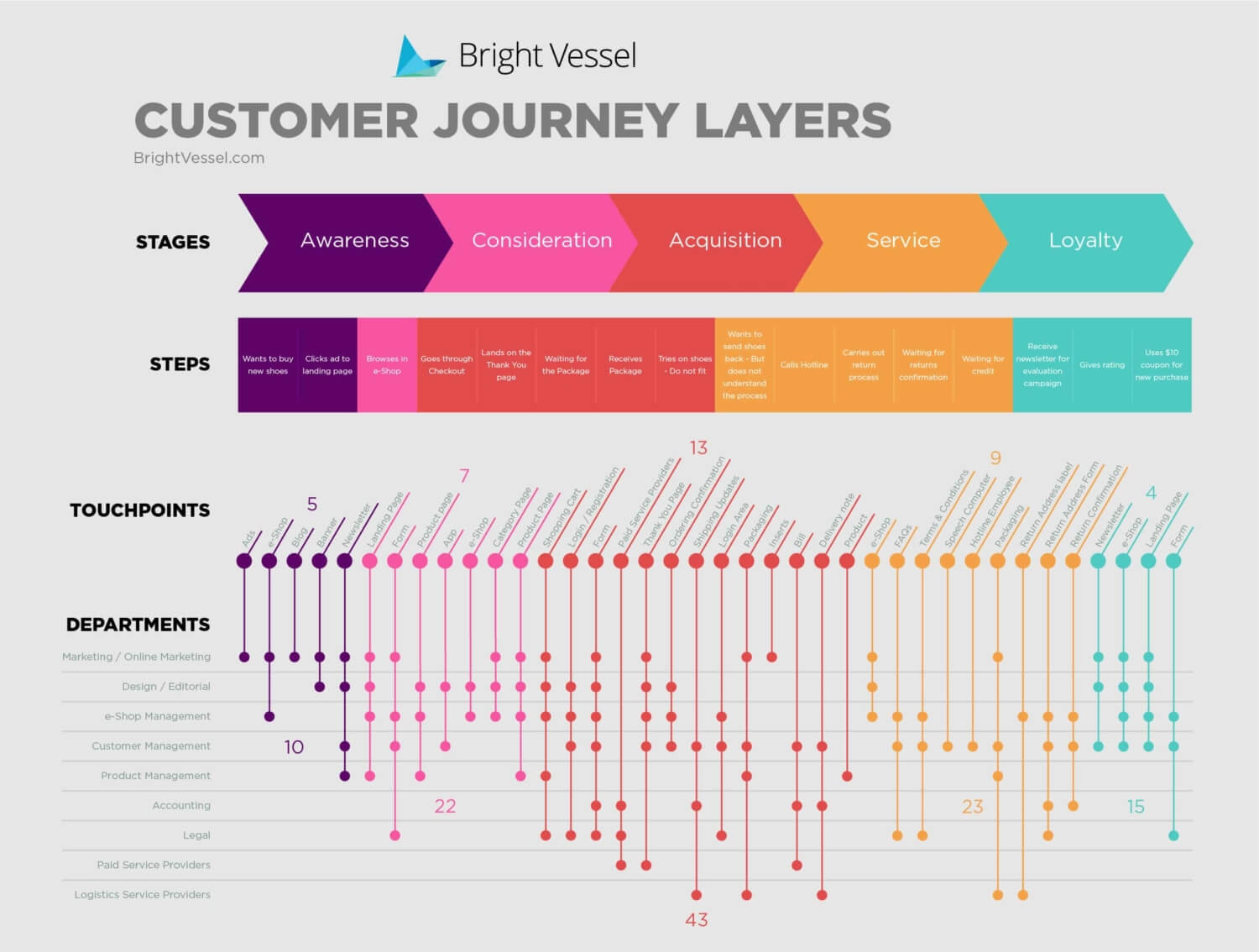
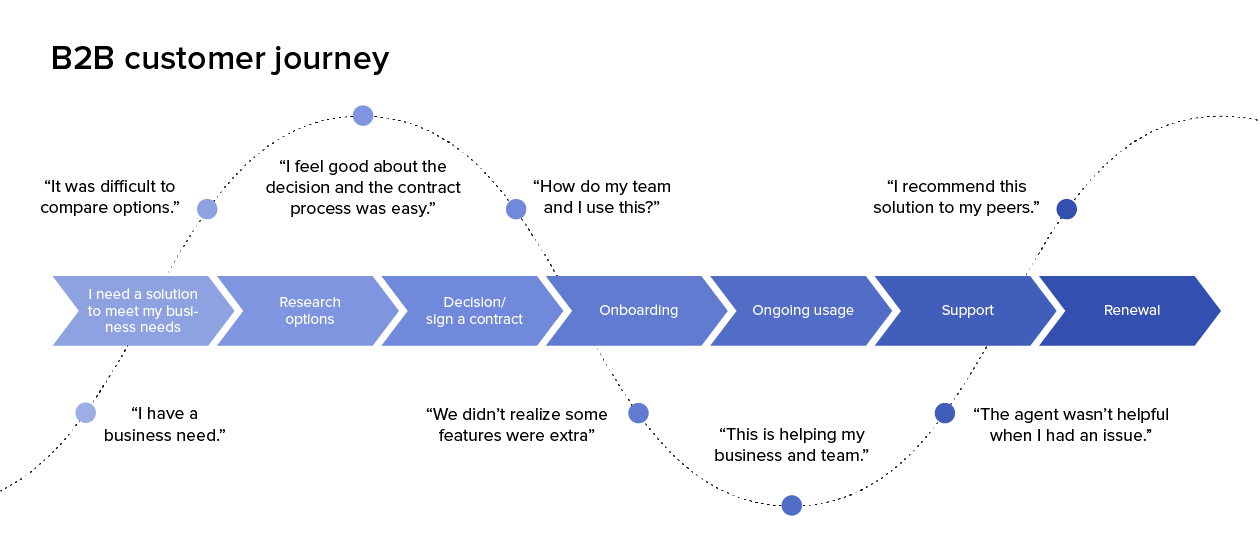
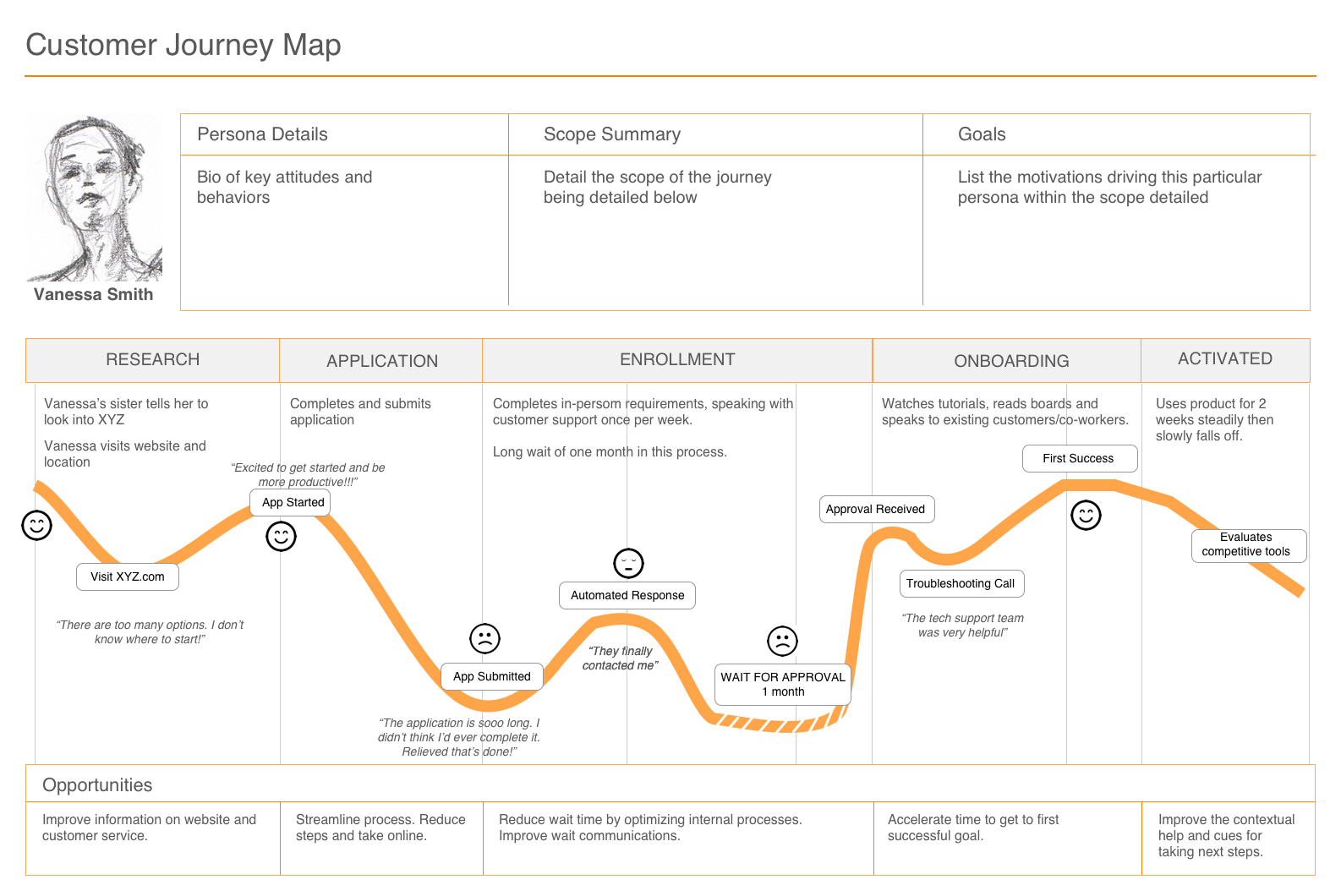
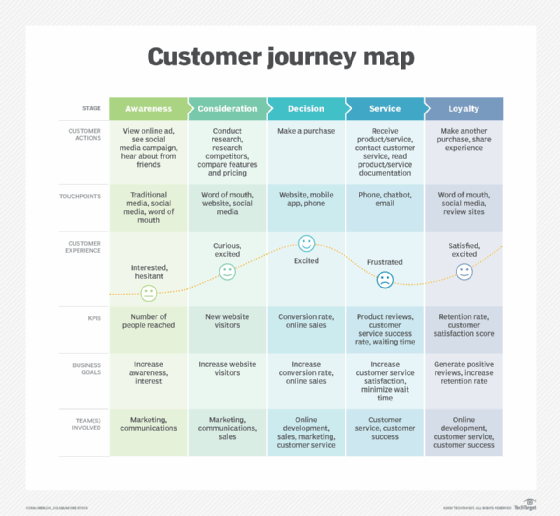
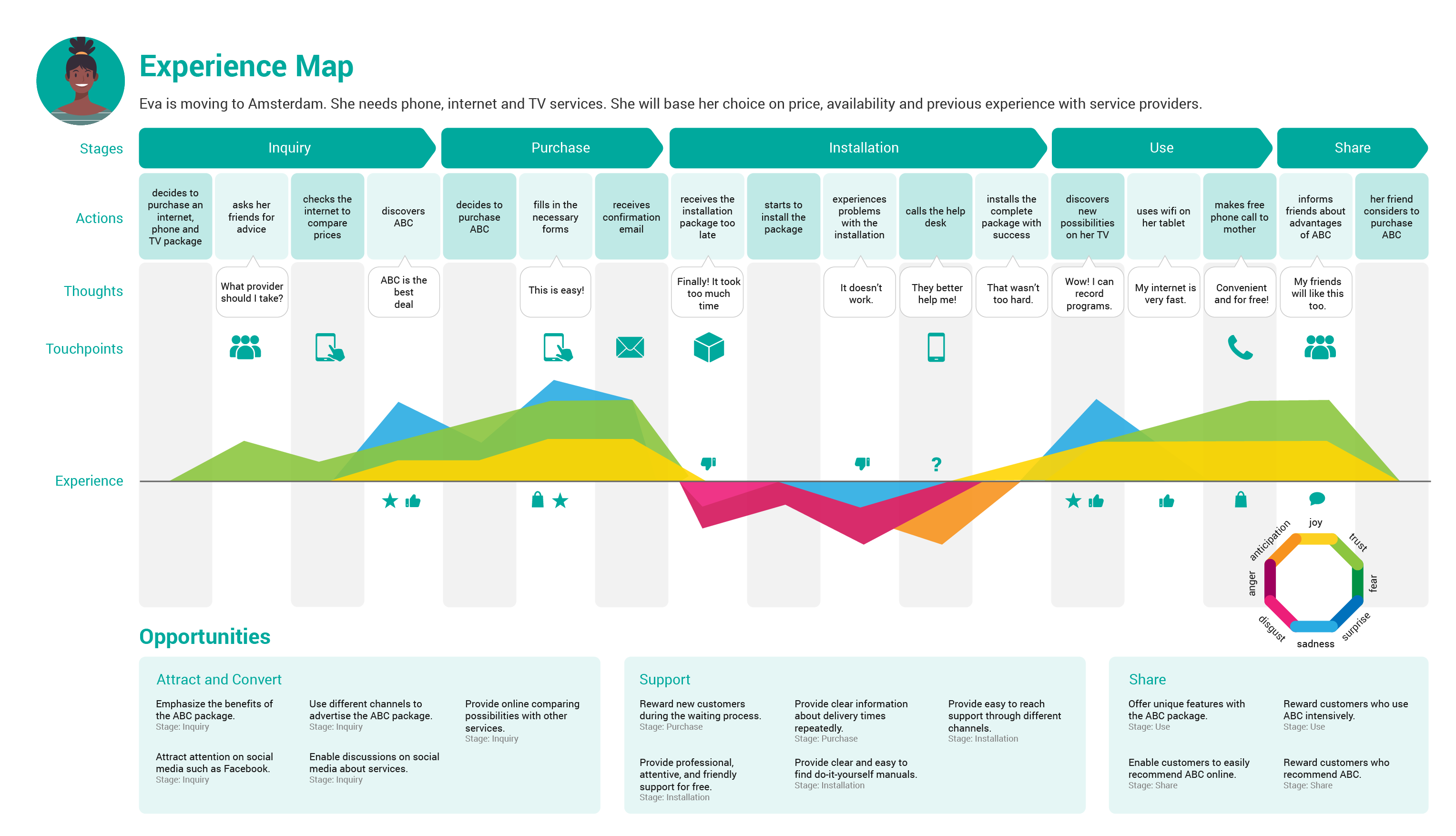
1. Stages of the Journey: This element outlines the distinct phases a customer goes through when interacting with a product or service. These stages typically include:
- Awareness: This stage represents the initial point where the customer becomes aware of the product or service. It encompasses how they discover it, what triggers their interest, and their initial perceptions.
- Consideration: Here, the customer actively evaluates the product or service. They research options, compare features, and weigh potential benefits. This stage is crucial for understanding customer decision-making processes.
- Decision: This stage marks the point where the customer chooses to purchase or utilize the product or service. Factors influencing this decision, such as price, convenience, and brand reputation, are crucial to understand.
- Action: This stage encompasses the actual use or engagement with the product or service. It includes the customer’s experience with the product, their interactions with support systems, and their overall satisfaction.
- Post-Purchase: This final stage focuses on the customer’s experience after the initial purchase or engagement. It includes factors like customer loyalty, repeat purchases, and brand advocacy.
2. Customer Touchpoints: These are specific moments of interaction between the customer and the brand. They can include:
- Website: The brand’s website is often the primary touchpoint, providing information, facilitating purchases, and offering customer support.
- Social Media: Social media platforms play an increasingly crucial role in customer engagement, offering communication channels, brand awareness, and customer feedback opportunities.
- Customer Service: Direct interactions with customer service representatives, whether through phone, email, or chat, are critical touchpoints for resolving issues and improving customer satisfaction.
- Physical Stores: For brick-and-mortar businesses, physical stores are essential touchpoints, offering product exploration, purchase opportunities, and in-person customer service.
- Marketing Materials: Advertisements, brochures, and other marketing materials influence customer perception and can be significant touchpoints.
3. Customer Needs and Expectations: This element focuses on understanding the underlying needs and expectations of customers at each stage of their journey. It explores:
- Functional Needs: These are the practical needs the customer seeks to fulfill by using the product or service.
- Emotional Needs: These are the emotional desires and aspirations the customer seeks to satisfy through their interaction with the brand.
- Social Needs: These are the needs related to belonging, recognition, and social status that the customer may be seeking to fulfill.
4. Customer Emotions and Thoughts: This component delves into the emotional and cognitive responses of the customer at each touchpoint. It explores:
- Frustrations: Understanding the frustrations customers experience can help identify areas for improvement.
- Delights: Identifying moments of delight can help understand what resonates with customers and create more positive experiences.
- Pain Points: Pinpointing pain points allows for addressing areas where the customer experience falters.
- Opportunities: Recognizing opportunities for enhancement helps identify areas where the customer experience can be further optimized.
5. Customer Actions: This element focuses on the behaviors and actions of the customer at each touchpoint. It explores:
- Purchases: Understanding purchasing patterns, including frequency, volume, and preferred channels, provides valuable insights.
- Engagement: Measuring engagement with the product or service, such as time spent on the website or interaction with social media content, is crucial.
- Feedback: Analyzing customer feedback, whether through reviews, surveys, or direct communication, provides valuable insights into customer satisfaction and areas for improvement.
Benefits of Utilizing a Moses Journey Map
Creating a Moses Journey Map offers significant benefits for businesses aiming to enhance customer experience:
- Improved Customer Understanding: By mapping the customer journey, businesses gain a deeper understanding of their customers’ needs, expectations, and behaviors.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Identifying pain points, frustrations, and opportunities allows businesses to refine their offerings and processes, resulting in a more positive and satisfying customer experience.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: By addressing customer needs and exceeding expectations, businesses can foster stronger customer relationships and encourage loyalty.
- Enhanced Product and Service Development: Understanding customer needs and behaviors can guide product development, ensuring that offerings are aligned with customer expectations.
- Improved Marketing Strategies: By understanding customer touchpoints and engagement patterns, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts for greater effectiveness.
- Streamlined Operations: Identifying inefficiencies in the customer journey allows businesses to optimize processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
FAQs About the Moses Journey Map
1. What is the difference between a Moses Journey Map and a Customer Journey Map?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, a Moses Journey Map focuses on a more detailed and nuanced understanding of the customer experience, emphasizing the emotional and cognitive aspects of the journey. A Customer Journey Map, on the other hand, typically focuses on the more functional aspects of the journey, outlining the steps and touchpoints without necessarily delving into the emotional and cognitive dimensions.
2. How do I create a Moses Journey Map?
Creating a Moses Journey Map involves several steps:
- Define your target audience: Clearly identify the customer segment you are focusing on.
- Identify the stages of the journey: Outline the distinct phases the customer goes through.
- Map the touchpoints: Identify all points of interaction between the customer and the brand.
- Gather data: Collect data on customer needs, expectations, emotions, and behaviors through research, surveys, and feedback analysis.
- Visualize the map: Create a visual representation of the journey, highlighting key elements and insights.
3. What tools can be used to create a Moses Journey Map?
Various tools can be utilized for creating a Moses Journey Map, including:
- Digital Whiteboard Tools: Tools like Miro or Mural allow for collaborative brainstorming and visual mapping.
- Spreadsheet Software: Excel or Google Sheets can be used to organize data and create basic maps.
- Specialized Journey Mapping Software: Dedicated software like Customer Journey Map or Smaply offer advanced features for creating and analyzing journey maps.
4. How often should a Moses Journey Map be updated?
The frequency of updating a Moses Journey Map depends on the industry, the rate of change in the market, and the business’s internal processes. However, it is generally recommended to update the map at least annually to ensure it reflects current customer behavior and market trends.
Tips for Effective Moses Journey Map Creation
- Focus on the customer: The map should be centered around the customer’s perspective and experiences.
- Use a collaborative approach: Involve stakeholders from various departments to gain diverse perspectives.
- Utilize data: Back up your insights with data from surveys, feedback analysis, and customer behavior tracking.
- Prioritize insights: Identify the most significant findings and focus on addressing key areas for improvement.
- Visualize effectively: Create a visually appealing and easy-to-understand map that effectively communicates insights.
Conclusion
The Moses Journey Map is a powerful tool that empowers businesses to understand their customers on a deeper level. By mapping the customer journey, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive business growth. Through a meticulous understanding of customer needs, emotions, and behaviors, businesses can create truly exceptional customer experiences that foster loyalty, advocacy, and lasting brand relationships.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Moses Journey Map: A Framework for Understanding Customer Experience. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!