The Greenbelt: A Map for Sustainable Growth
Related Articles: The Greenbelt: A Map for Sustainable Growth
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Greenbelt: A Map for Sustainable Growth. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Greenbelt: A Map for Sustainable Growth

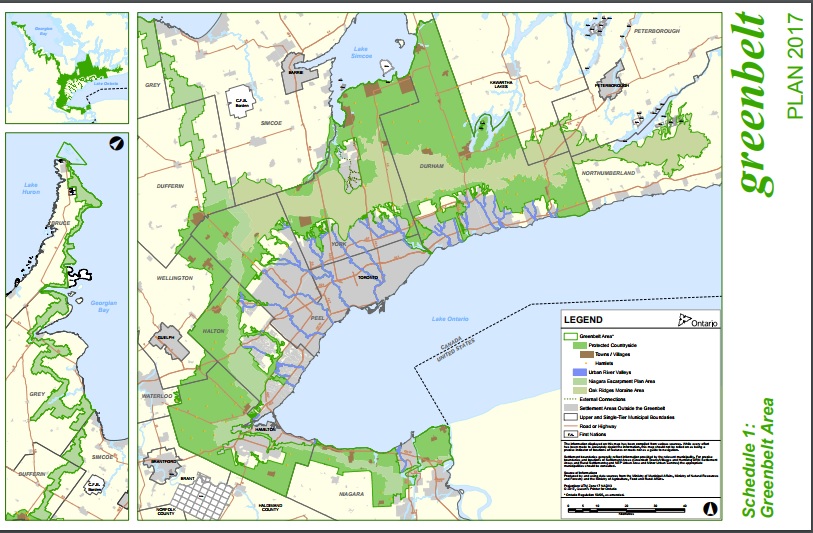
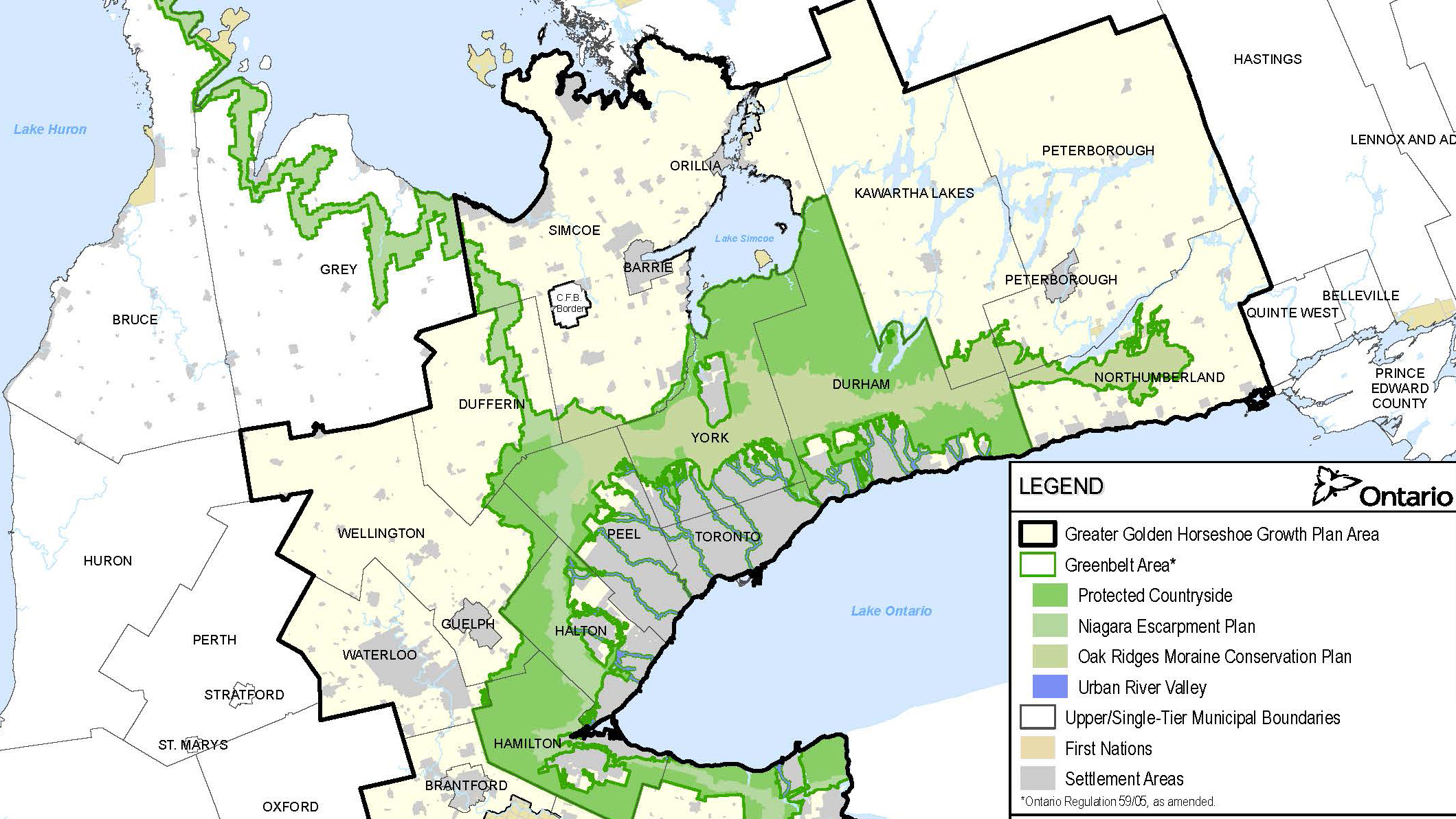
The concept of a greenbelt, a designated area of protected land surrounding urban areas, has gained significant traction in recent years as a critical tool for sustainable development. This approach, often visualized through a greenbelt map, aims to balance urban expansion with environmental preservation, fostering a harmonious relationship between human settlements and the natural world.
Understanding the Greenbelt Map
A greenbelt map is a visual representation of designated areas surrounding a city or urban region. These areas are typically characterized by natural landscapes, including forests, parks, agricultural lands, and waterways. The map delineates the boundaries of the greenbelt, highlighting the areas protected from development.
Benefits of Greenbelt Maps
Greenbelt maps offer a range of benefits, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient urban environment:
- Preservation of Biodiversity: By safeguarding natural habitats, greenbelts protect a wide range of plant and animal species, contributing to biodiversity conservation.
- Environmental Protection: Greenbelts act as natural filters, mitigating pollution and providing essential ecosystem services like clean air and water. They also help regulate climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and mitigating the urban heat island effect.
- Recreation and Leisure: Greenbelts offer valuable recreational opportunities for residents, providing access to nature for hiking, biking, and other outdoor activities. They promote physical and mental well-being, fostering a healthier lifestyle.
- Sustainable Urban Development: Greenbelts serve as a buffer between urban areas and surrounding landscapes, preventing uncontrolled sprawl and encouraging more compact, efficient development. They guide urban expansion in a planned manner, promoting sustainable growth.
- Economic Benefits: Greenbelts can boost local economies by attracting tourism, supporting agriculture, and creating job opportunities in conservation and recreation sectors.
Implementing Greenbelt Maps
The implementation of a greenbelt map requires a comprehensive approach, involving various stakeholders and processes:
- Planning and Design: The creation of a greenbelt map involves detailed planning, taking into account existing land use, environmental sensitivities, and future development needs. It requires collaboration between government agencies, urban planners, environmental experts, and community members.
- Land Acquisition: Securing land for the greenbelt may involve purchasing existing land, implementing conservation easements, or establishing partnerships with landowners. This process can be complex and require careful negotiation and funding strategies.
- Enforcement and Monitoring: Once established, the greenbelt map needs to be enforced to prevent unauthorized development. This involves regular monitoring, enforcement mechanisms, and public education to ensure the long-term preservation of the designated areas.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How does a greenbelt map differ from a zoning map?
A: While both zoning and greenbelt maps regulate land use, they differ in scope and purpose. Zoning maps focus on regulating the types of development allowed within specific areas, while greenbelt maps primarily aim to protect natural landscapes from development.
Q: How can I get involved in greenbelt planning in my community?
A: You can engage with local government agencies, attend public meetings, and participate in community groups focused on environmental issues. You can also advocate for the creation or expansion of greenbelts by contacting your elected officials and supporting relevant initiatives.
Q: What are the challenges associated with implementing greenbelt maps?
A: Challenges include securing funding for land acquisition, balancing competing land use interests, and ensuring effective enforcement mechanisms. Addressing these challenges requires strong political will, public support, and collaborative efforts from various stakeholders.
Tips for Creating and Maintaining Greenbelt Maps
- Engage with the Community: Involve residents in the planning process to ensure their needs and perspectives are considered.
- Prioritize Ecosystem Services: Focus on protecting areas that provide critical environmental benefits, such as water filtration, carbon sequestration, and wildlife habitat.
- Promote Economic Benefits: Highlight the economic opportunities associated with greenbelts, such as tourism, recreation, and agriculture, to gain broader support.
- Monitor and Adapt: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the greenbelt map and adapt it as needed based on changing environmental conditions and development pressures.
Conclusion
Greenbelt maps are essential tools for promoting sustainable urban development and preserving natural landscapes. They offer a range of benefits, from protecting biodiversity and promoting environmental health to fostering recreation and supporting economic growth. By embracing a comprehensive approach to planning, implementation, and ongoing management, communities can harness the power of greenbelts to create healthier, more resilient, and sustainable urban environments for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Greenbelt: A Map for Sustainable Growth. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!