The Equator: A Fundamental Line Dividing Our Planet
Related Articles: The Equator: A Fundamental Line Dividing Our Planet
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Fundamental Line Dividing Our Planet. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Fundamental Line Dividing Our Planet

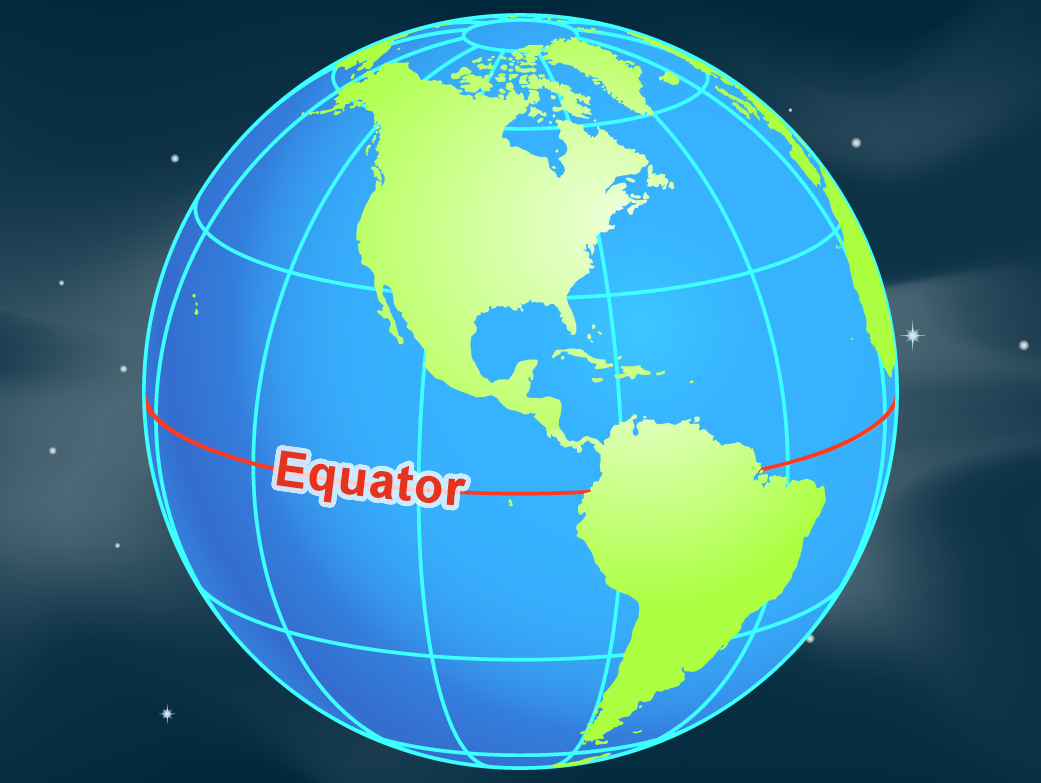
The Earth, our home, is a dynamic sphere constantly spinning in the vast expanse of space. While its surface appears as a continuous landmass, a crucial imaginary line, the equator, divides it into two distinct hemispheres: the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This line, an essential reference point in geography, plays a vital role in understanding our planet’s climate, weather patterns, and cultural diversity.
Defining the Equator: A Circle of Significance
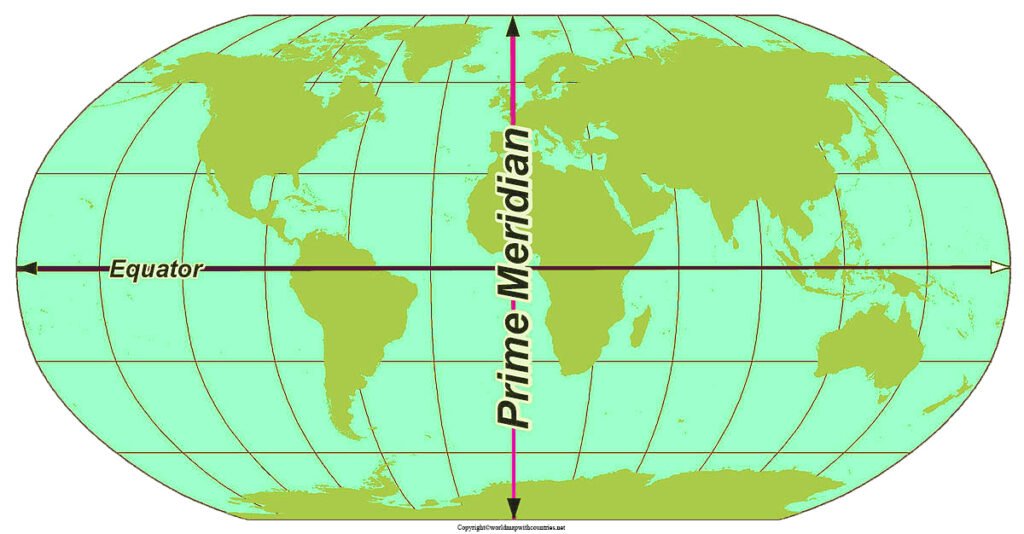
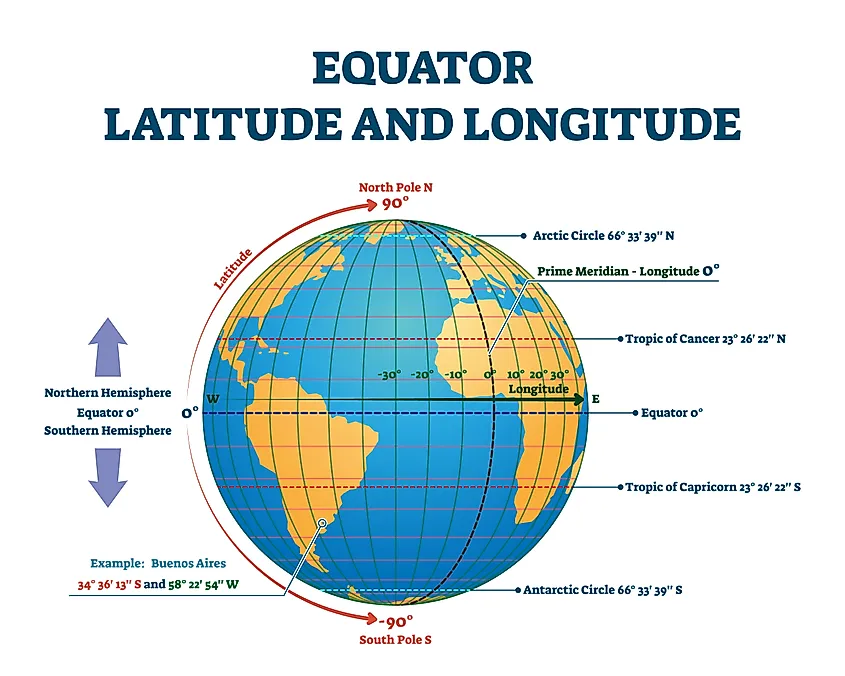
The equator is not a physical feature but an imaginary circle drawn around the Earth, equidistant from the North and South Poles. It runs horizontally, dividing the Earth into equal halves at 0 degrees latitude. This zero-degree line is the starting point for measuring latitude, a crucial geographical coordinate system that locates points on Earth’s surface.
Impact of the Equator: Shaping Climate and Culture
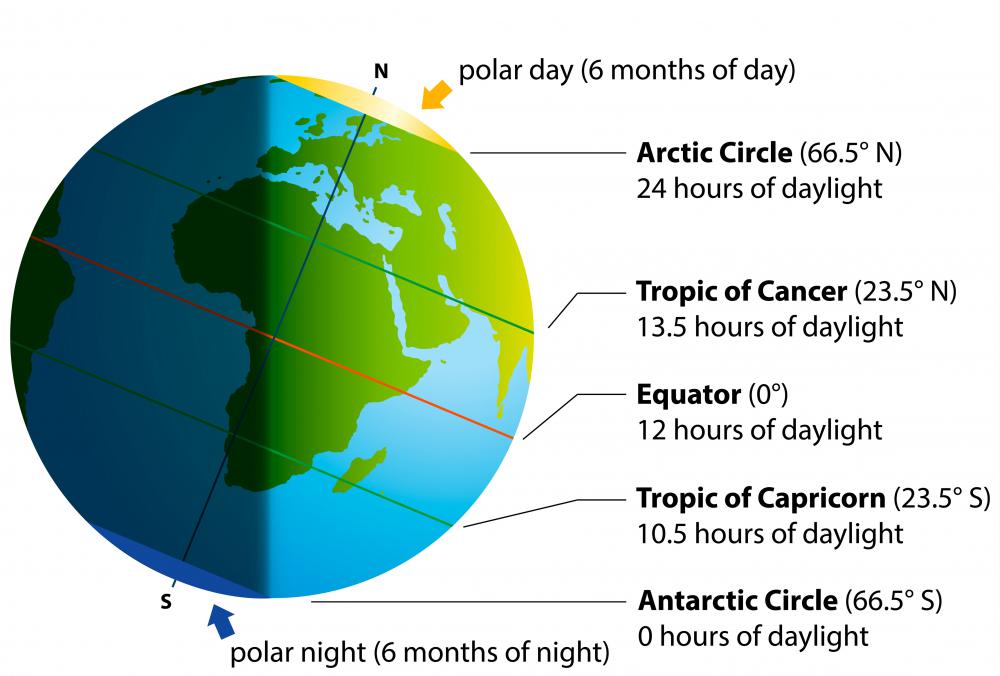
The equator’s influence on Earth’s climate is profound. The sun’s rays strike the equator at a nearly perpendicular angle, resulting in a consistent, high level of solar radiation throughout the year. This leads to a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and lush vegetation. The equatorial regions boast diverse ecosystems, including rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs, supporting a rich biodiversity.
The equator’s influence extends beyond climate, shaping the cultures and lifestyles of people living in equatorial regions. The abundance of natural resources, such as fertile land and plentiful rainfall, has historically supported agricultural societies. Equatorial cultures often exhibit a strong connection to nature, with traditions and customs deeply intertwined with their environment.
Navigating the Globe: The Equator as a Guiding Line
The equator serves as a fundamental reference point for navigation and cartography. Maps, globes, and other navigational tools utilize the equator to establish latitude, the angular distance north or south of the equator. This system, combined with longitude, provides precise coordinates for any location on Earth, facilitating navigation and understanding geographical relationships.
Understanding the Earth’s Rotation: The Equator’s Role
The equator plays a crucial role in understanding the Earth’s rotation. As the Earth spins on its axis, points on the equator experience the highest linear velocity, moving at approximately 1,000 miles per hour. This rotational speed influences the Earth’s gravitational pull, affecting weather patterns and ocean currents.
Equatorial Phenomena: A Unique Perspective
The equator is associated with several unique phenomena, including:
- The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ): A band of low pressure and high rainfall that shifts seasonally, bringing heavy precipitation to equatorial regions.
- The Coriolis Effect: A force caused by the Earth’s rotation that deflects moving objects, influencing wind and ocean currents.
- The Equatorial Countercurrent: A westward ocean current that flows against the prevailing eastward currents.
Exploring the Equator: A Journey Across the Globe
The equator passes through 14 countries, each offering a unique cultural and environmental experience. From the lush rainforests of the Amazon to the bustling cities of Singapore, the equator is a vibrant and diverse region.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Equator:
Q: Why is the equator important?
A: The equator is a crucial reference point for understanding Earth’s climate, weather patterns, and cultural diversity. It also plays a vital role in navigation and cartography.
Q: What are the effects of the equator on climate?
A: The equator receives high levels of solar radiation, resulting in a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and lush vegetation.
Q: What are some of the unique phenomena associated with the equator?
A: The equator is associated with phenomena such as the Intertropical Convergence Zone, the Coriolis Effect, and the Equatorial Countercurrent.
Q: What are some interesting facts about the equator?
A: The equator passes through 14 countries and is the only line of latitude that circles the entire Earth.
Tips for Understanding the Equator:
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the equator on a globe or map helps understand its location and significance.
- Research equatorial countries: Explore the diverse cultures and environments of countries that lie on the equator.
- Learn about equatorial phenomena: Understand how the equator influences weather patterns, ocean currents, and other natural processes.
Conclusion: The Equator – A Line of Significance
The equator, though an imaginary line, serves as a fundamental reference point for understanding our planet. It shapes climate, influences cultures, and plays a vital role in navigation and cartography. As we continue to explore and learn about our Earth, the equator remains a crucial element in comprehending its complexities and appreciating its unique beauty.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Fundamental Line Dividing Our Planet. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!