The Baltic Sea: A Vital Link in Europe’s History and Ecology
Related Articles: The Baltic Sea: A Vital Link in Europe’s History and Ecology
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Baltic Sea: A Vital Link in Europe’s History and Ecology. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Baltic Sea: A Vital Link in Europe’s History and Ecology

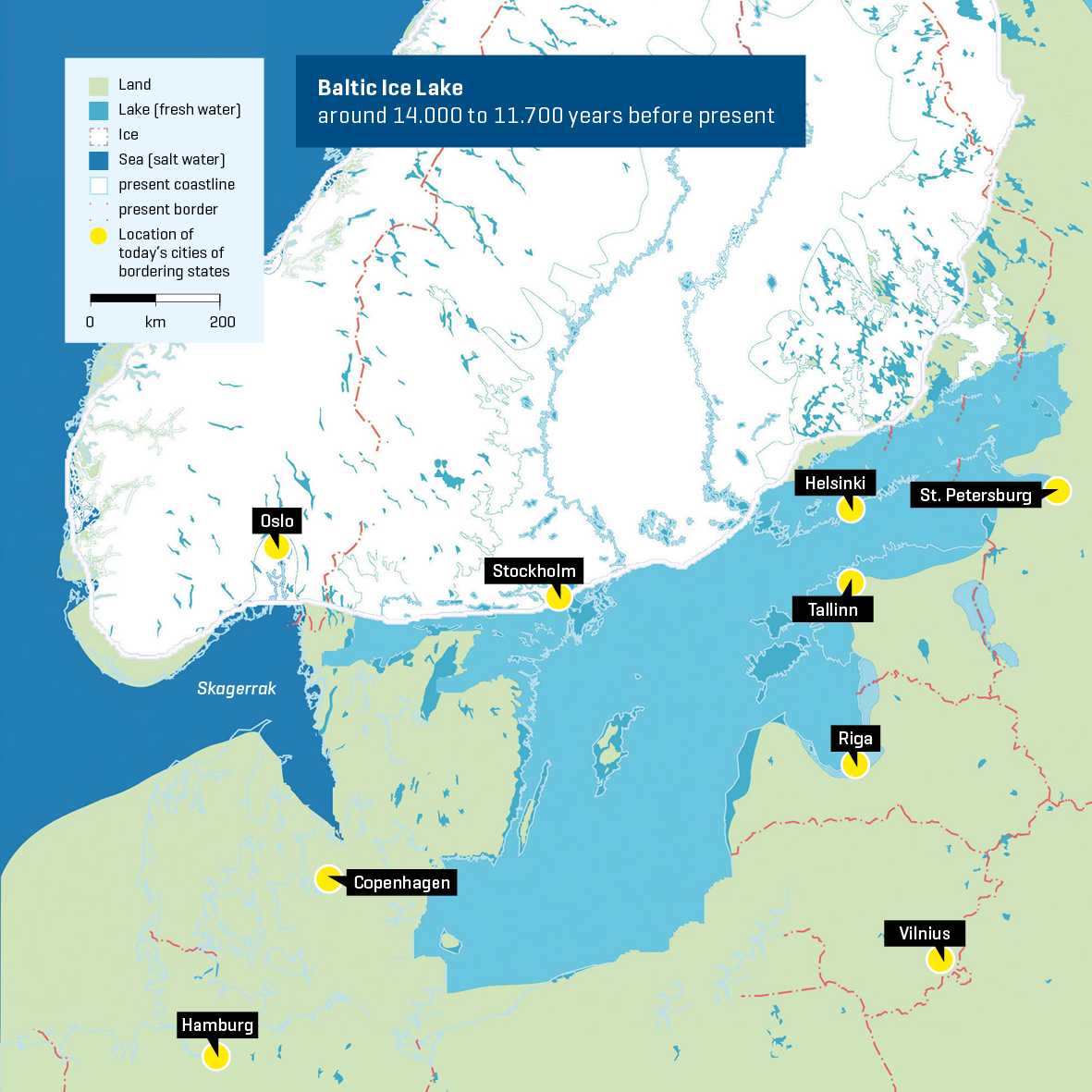
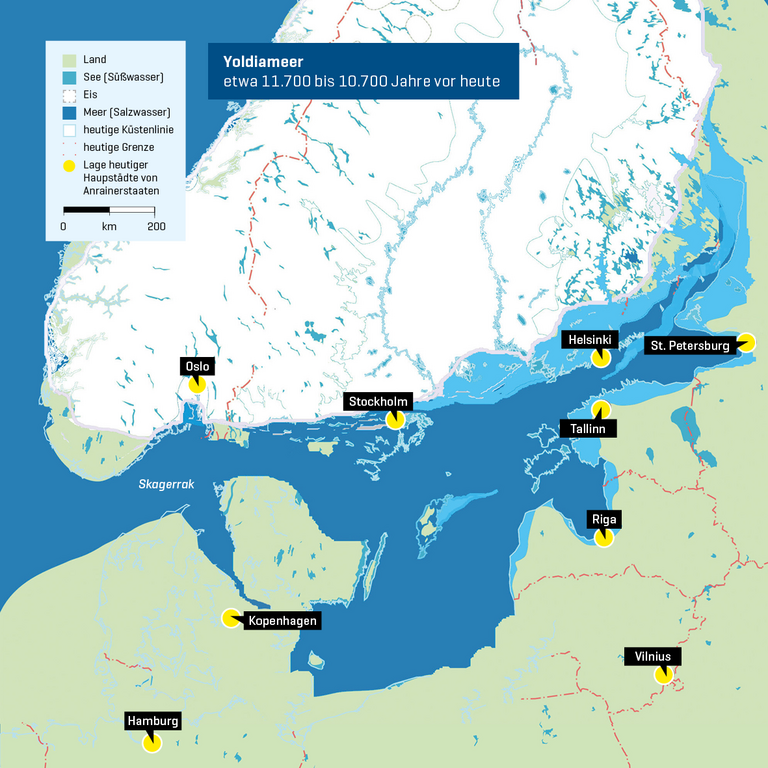
The Baltic Sea, a semi-enclosed inland sea located in Northern Europe, holds a significant place in the world’s geography and history. It is a vital link between numerous countries, connecting them through trade, cultural exchange, and shared resources. Understanding the Baltic Sea’s location on the world map reveals its intricate connections to the surrounding landmasses and its unique environmental characteristics.
Location and Geography
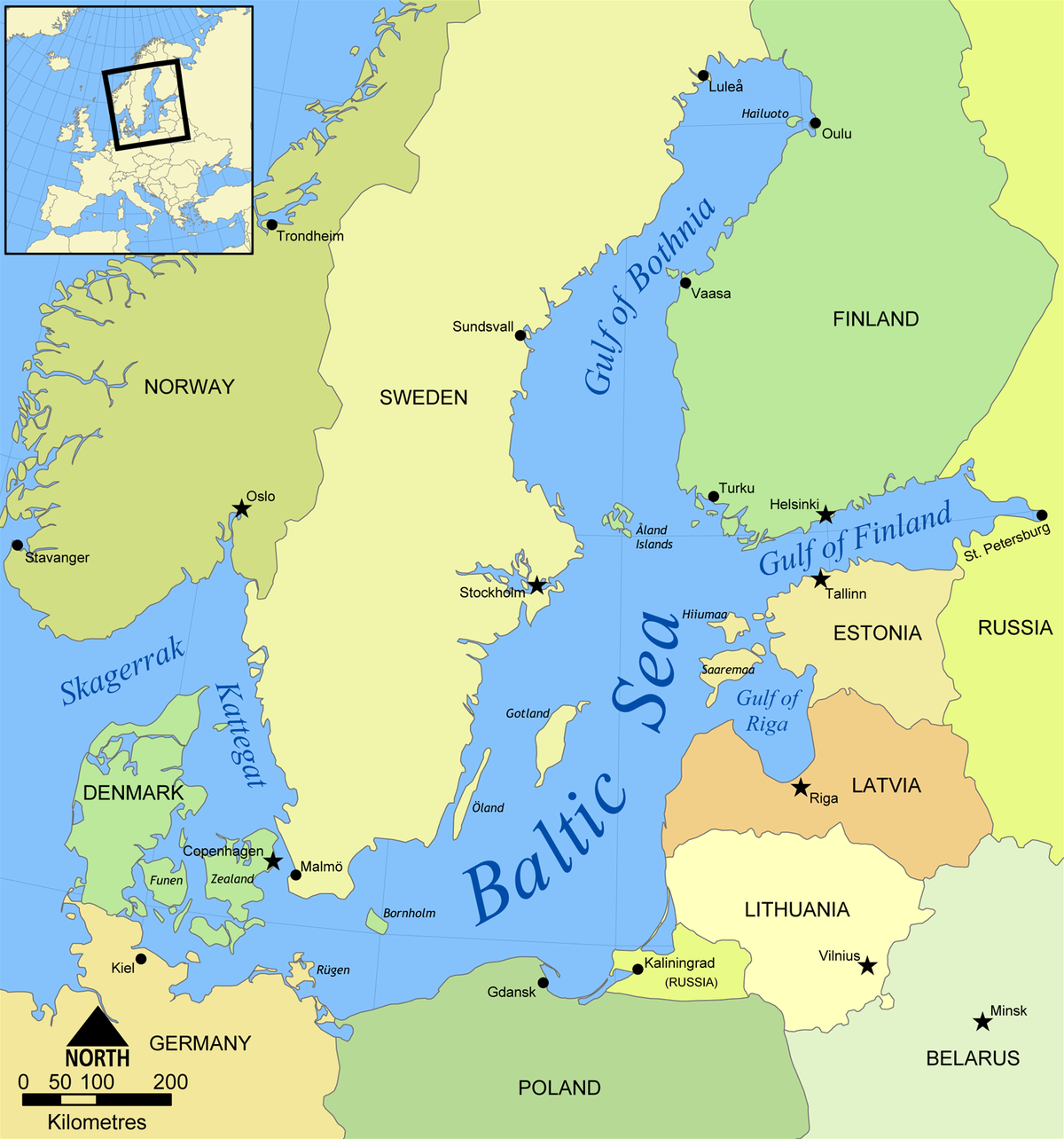
The Baltic Sea stretches for approximately 1,600 kilometers from the Skagerrak Strait in the southwest to the Gulf of Finland in the northeast. It is bordered by nine countries: Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Germany. This unique geographical positioning makes the Baltic Sea a crossroads of cultures and a vital waterway for regional transportation.
The sea’s semi-enclosed nature, with its narrow connection to the North Sea, influences its salinity levels and water circulation. The Baltic Sea is considered brackish, a unique mix of freshwater from numerous rivers flowing into it and saltwater from the North Sea. This brackish environment supports a distinct ecosystem, harboring both marine and freshwater species.
Historical Significance
The Baltic Sea has played a crucial role in shaping European history. Its strategic location, connecting Scandinavia, the Baltic states, and mainland Europe, made it a significant trade route for centuries. Viking expeditions traversed its waters, establishing trade networks and leaving their mark on the region’s history. The Baltic Sea also witnessed numerous conflicts and power struggles throughout history, influencing the political landscape of Europe.
The Hanseatic League, a powerful medieval trading association, flourished in the Baltic region, establishing commercial dominance and promoting economic prosperity. The Baltic Sea’s importance as a trade route continued into the modern era, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas between nations.
Ecological Importance
The Baltic Sea’s unique ecosystem is a crucial component of the global environment. Its brackish waters host a diverse range of flora and fauna, including seals, porpoises, salmon, cod, and numerous bird species. The sea’s shallow depths, averaging around 55 meters, contribute to its vulnerability to pollution and climate change.
The Baltic Sea faces several environmental challenges, including eutrophication caused by agricultural runoff and industrial pollution. These factors threaten the delicate balance of the ecosystem, impacting biodiversity and harming marine life. Additionally, climate change is causing rising sea levels and altering the sea’s temperature and salinity, further impacting its environment.
Economic Importance
The Baltic Sea is a vital economic resource for the surrounding nations. It supports significant fishing industries, providing livelihoods for many communities. The sea also facilitates maritime trade, transporting goods and materials between countries. Tourism plays a major role in the region’s economy, attracting visitors to its picturesque coastlines and historical cities.
The Baltic Sea is also a source of energy resources, with offshore wind farms being developed to harness the power of the wind. The region’s abundant natural resources, combined with its strategic location, make the Baltic Sea a crucial economic asset for the surrounding countries.
Challenges and Future Prospects
The Baltic Sea faces a range of challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. Addressing these issues requires international cooperation and sustainable management practices.
Efforts are underway to reduce pollution, protect marine life, and mitigate the impacts of climate change. The Baltic Sea Action Plan, a joint effort by the Baltic Sea countries, aims to achieve a healthy Baltic Sea by 2030. This plan focuses on reducing nutrient loads, controlling hazardous substances, and promoting sustainable fishing practices.
FAQs
- What is the largest city on the Baltic Sea? Stockholm, Sweden, is the largest city located on the Baltic Sea.
- What is the deepest point of the Baltic Sea? The deepest point of the Baltic Sea is the Landsort Deep, located in the southern Baltic Sea, reaching a depth of 459 meters.
- What is the largest island in the Baltic Sea? Gotland, located in Sweden, is the largest island in the Baltic Sea.
- What is the dominant current in the Baltic Sea? The Baltic Current, a clockwise current, is the dominant current in the Baltic Sea.
- What are the main environmental concerns facing the Baltic Sea? The main environmental concerns include eutrophication, pollution from industrial and agricultural activities, overfishing, and climate change.
Tips
- Visit the Baltic Sea region: Experience the diverse cultures, historical sites, and beautiful landscapes of the Baltic Sea region.
- Support sustainable tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and tours that minimize their environmental impact.
- Reduce your consumption of seafood from the Baltic Sea: Support sustainable fishing practices and consume seafood from sustainable sources.
- Advocate for environmental protection: Support organizations working to protect the Baltic Sea and its ecosystem.
- Educate yourself about the Baltic Sea: Learn more about its unique environment, history, and challenges.
Conclusion
The Baltic Sea holds a vital place in European history and ecology. Its strategic location, diverse ecosystem, and economic importance make it a crucial part of the region’s identity. Recognizing the challenges facing the Baltic Sea, such as pollution and climate change, requires collective efforts to ensure its long-term sustainability. Through international cooperation, sustainable management practices, and individual actions, we can preserve this valuable resource for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Baltic Sea: A Vital Link in Europe’s History and Ecology. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!