Proportional Maps: A Visual Tool for Understanding Distribution and Scale
Related Articles: Proportional Maps: A Visual Tool for Understanding Distribution and Scale
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Proportional Maps: A Visual Tool for Understanding Distribution and Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Proportional Maps: A Visual Tool for Understanding Distribution and Scale

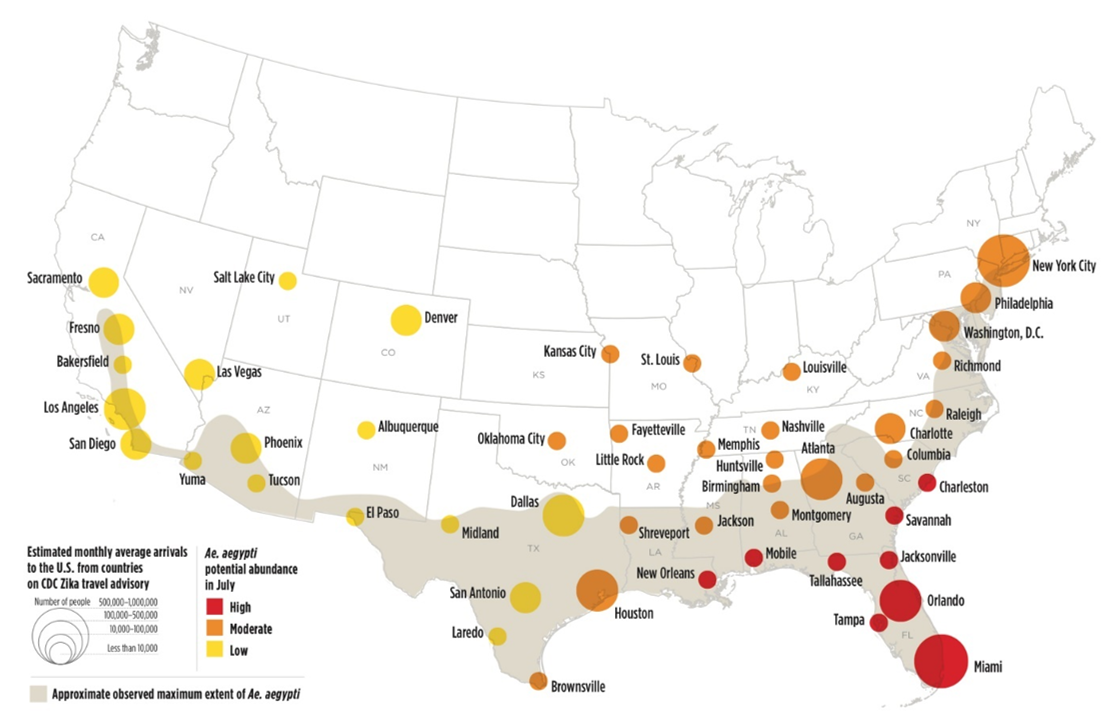
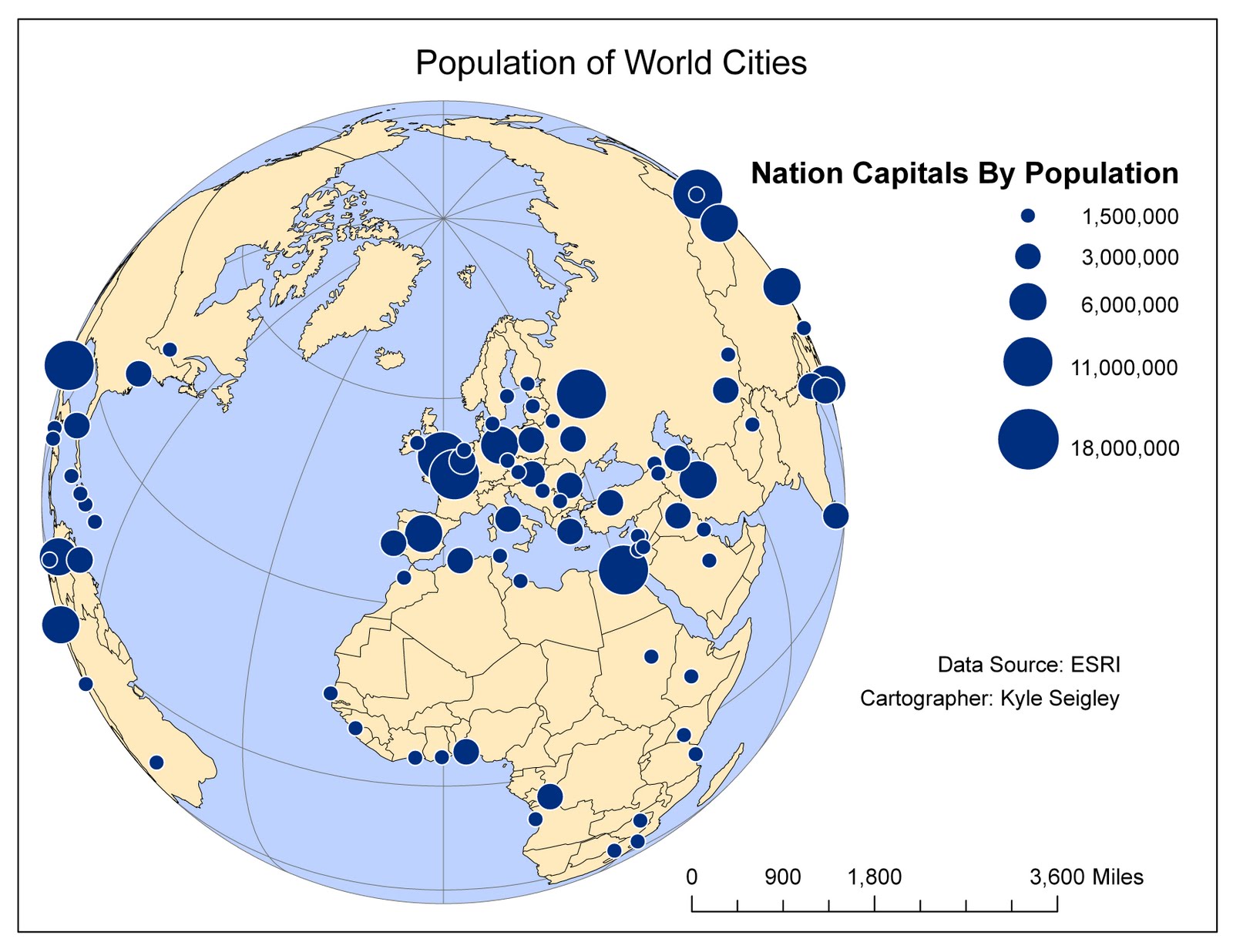
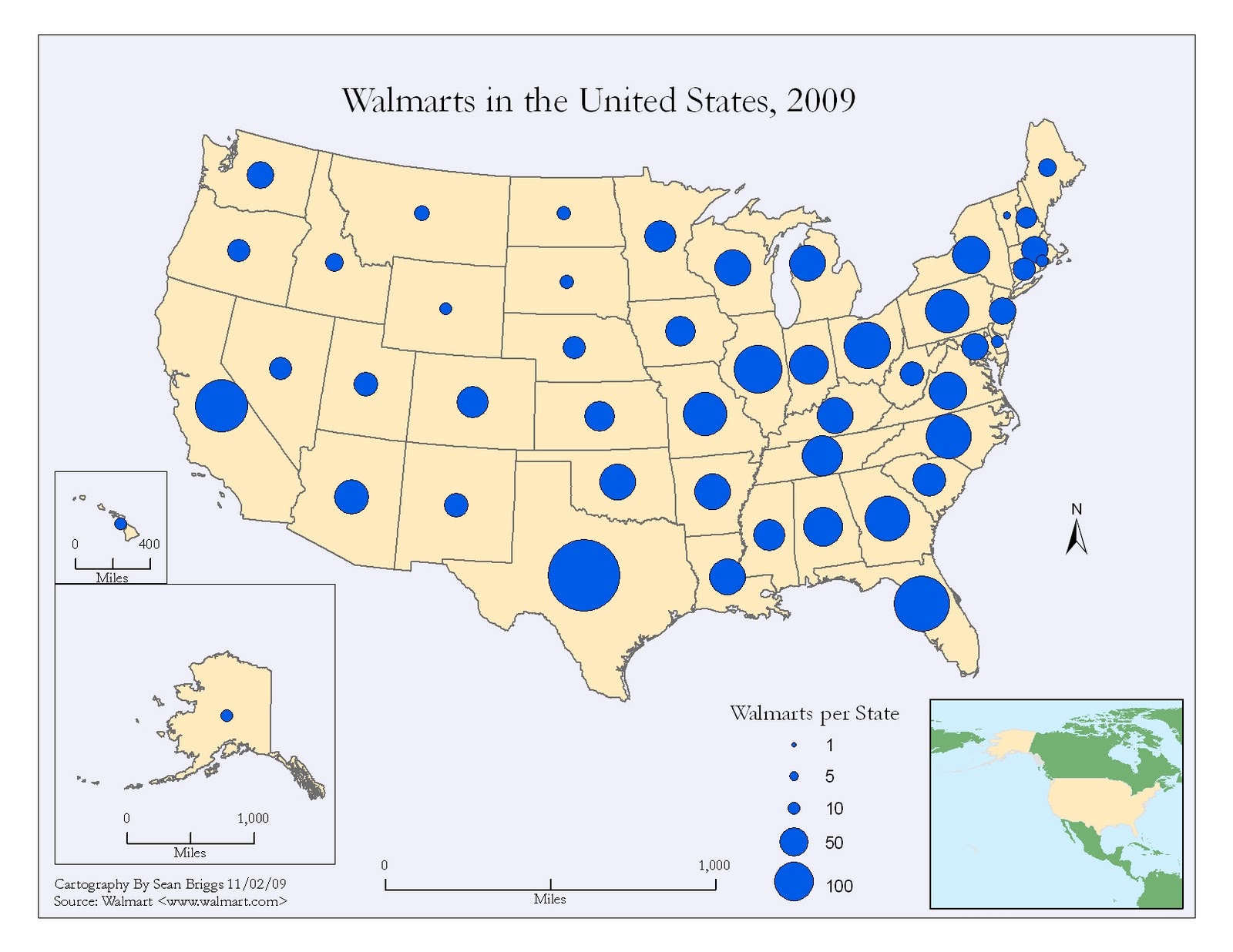
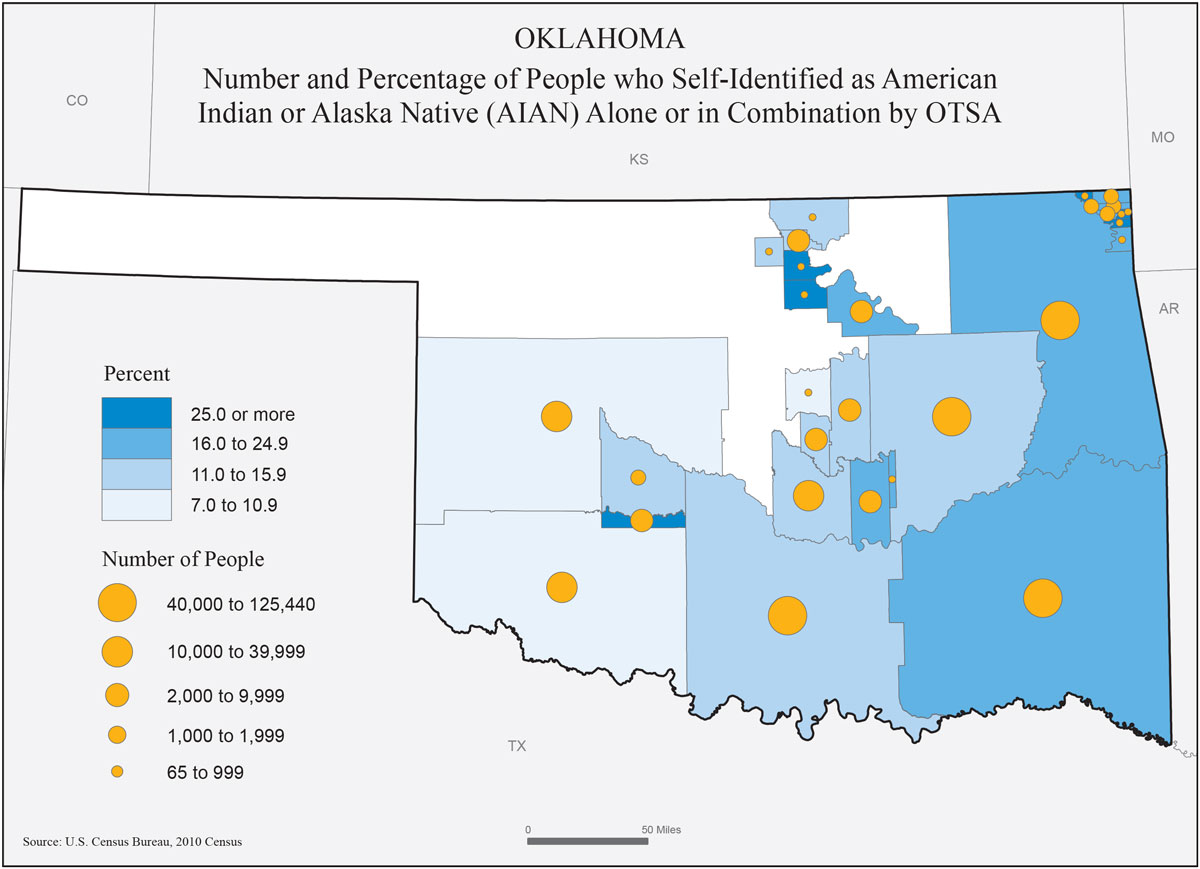
Proportional maps, also known as graduated symbol maps, are powerful visual tools that utilize the size of symbols to represent the magnitude of a particular phenomenon across a geographic area. This technique allows for a clear and intuitive understanding of spatial distribution, making it a valuable tool for various fields, including geography, demographics, economics, and environmental science.
Understanding the Concept
The core principle behind proportional maps is simple yet effective: the larger the symbol, the greater the value it represents. This can be applied to a wide range of data, from population density to economic output, disease prevalence, or even the intensity of natural disasters. By varying the size of symbols, proportional maps effectively convey the relative importance or magnitude of a specific variable across different locations.
Construction and Interpretation
Creating a proportional map involves several steps:
-
Data Collection: Gathering accurate and relevant data is crucial. This data must be spatially referenced, meaning each data point is associated with a specific location on the map.
-
Symbol Selection: Choosing the appropriate symbol is important for clarity and aesthetic appeal. Common choices include circles, squares, or even icons relevant to the data being represented.
-
Symbol Scaling: Determining the relationship between symbol size and data value is essential. This is typically done through a legend, which clearly outlines the scale of the map. A consistent scale ensures accurate interpretation.
-
Map Layout: The map should be designed for optimal clarity. This includes choosing appropriate colours, fonts, and background information to ensure the symbols stand out and the map remains easy to understand.
Benefits and Applications
Proportional maps offer numerous benefits over other map types, making them a versatile tool for visual communication:
- Intuitive Representation: The use of varying symbol sizes makes the data immediately accessible and understandable, even for individuals without specialized knowledge.
- Effective Comparison: Proportional maps allow for easy comparison of data across different locations, highlighting areas of high and low values.
- Spatial Patterns: They effectively reveal spatial patterns and trends, aiding in the identification of clusters, outliers, and areas of concentration.
- Data Exploration: Proportional maps can be used to explore data in different ways, allowing for the identification of relationships and insights that might be missed through other methods.
Applications of Proportional Maps:
- Demographics: Visualizing population density, age distribution, or ethnic composition across a region.
- Economics: Mapping economic activity, income levels, or unemployment rates across different areas.
- Environmental Science: Representing pollution levels, deforestation rates, or the distribution of natural resources.
- Public Health: Mapping disease prevalence, access to healthcare facilities, or the spread of epidemics.
- Disaster Management: Visualizing the intensity of natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, or wildfires.
Limitations and Considerations
While proportional maps are powerful tools, it’s important to consider their limitations:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the map relies heavily on the accuracy of the underlying data. Inaccurate data can lead to misleading interpretations.
- Symbol Overlap: In areas with high data density, symbols can overlap, obscuring information and hindering clarity.
- Scale Effects: The effectiveness of the map can be affected by the scale of the data. Large-scale maps may be less effective in highlighting small-scale variations.
- Perceptual Distortion: The human eye can be influenced by the size and shape of symbols, leading to potential misinterpretations.
FAQs about Proportional Maps:
Q: What is the difference between a proportional map and a choropleth map?
A: While both map types use colour to represent data, proportional maps use the size of symbols, while choropleth maps use different shades of colour to represent data values across different areas.
Q: How do I choose the appropriate symbol size for my proportional map?
A: The symbol size should be proportional to the data value, with a clear and consistent scale. The legend should provide a clear visual representation of this relationship.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a proportional map?
A: Avoid using too many symbols, as this can lead to clutter and confusion. Ensure the symbols are clearly visible against the background. Avoid using too many colours or shades, as this can make the map difficult to interpret.
Tips for Creating Effective Proportional Maps:
- Use a clear and concise legend: Ensure the legend is easy to understand and provides a clear visual representation of the data-symbol relationship.
- Choose appropriate symbols: Select symbols that are visually appealing and relevant to the data being represented.
- Avoid overcrowding: Ensure the symbols are spaced appropriately to avoid overlapping and visual clutter.
- Use colour effectively: Choose colours that enhance the visual clarity and contrast of the map.
- Consider the target audience: Tailor the map to the specific needs and understanding of the intended audience.
Conclusion
Proportional maps are valuable tools for visualizing and understanding spatial patterns and trends. By effectively conveying the relative magnitude of data across different locations, they provide insights that can inform decision-making in various fields. However, it’s important to be mindful of their limitations and to use them responsibly, ensuring data accuracy and clear communication. By applying best practices and considering the key elements of design and interpretation, proportional maps can serve as powerful visual aids for presenting data and fostering a deeper understanding of the world around us.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Proportional Maps: A Visual Tool for Understanding Distribution and Scale. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!