Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Labeled Map Unravels the Continent
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Labeled Map Unravels the Continent
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Labeled Map Unravels the Continent. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Labeled Map Unravels the Continent
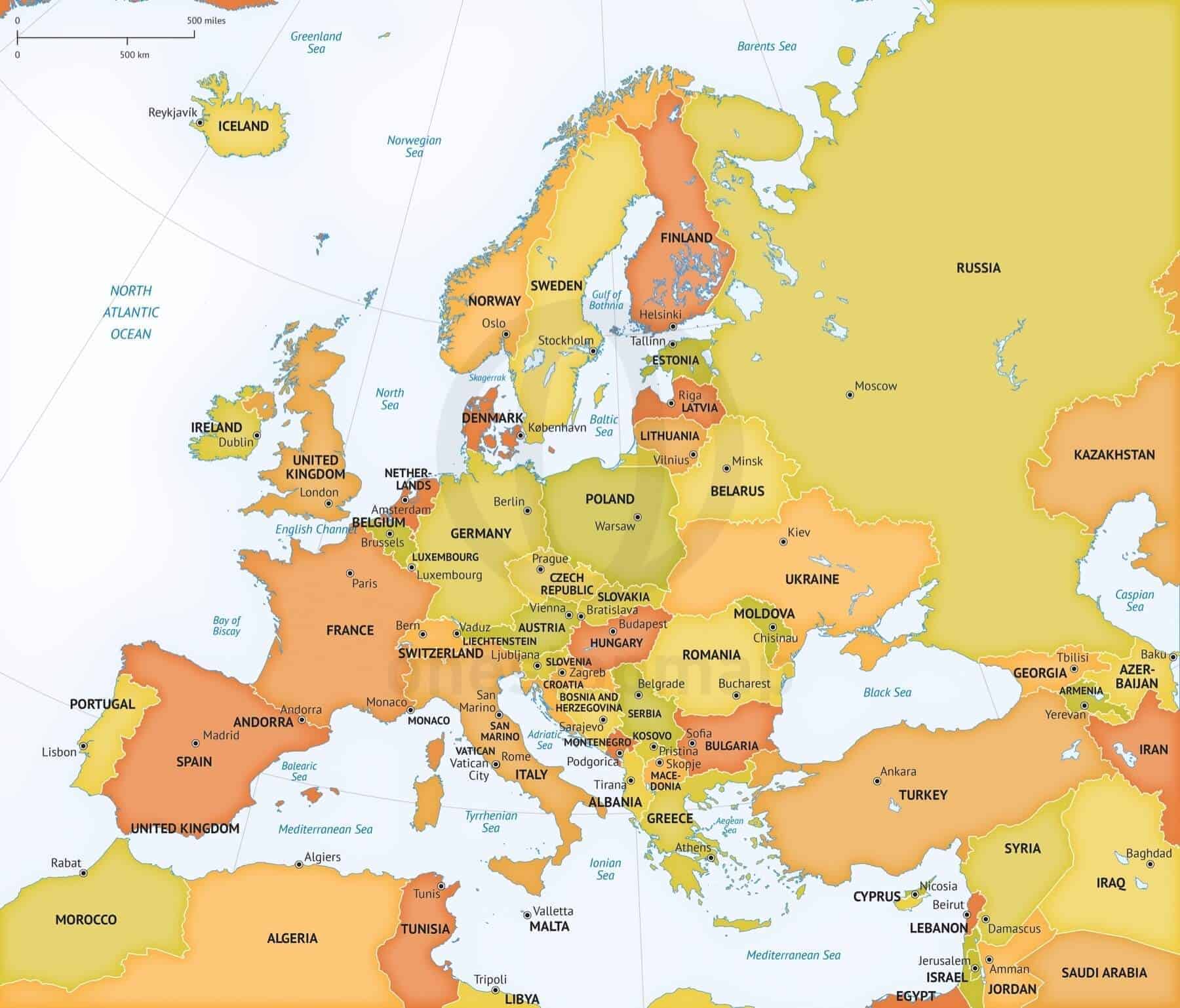
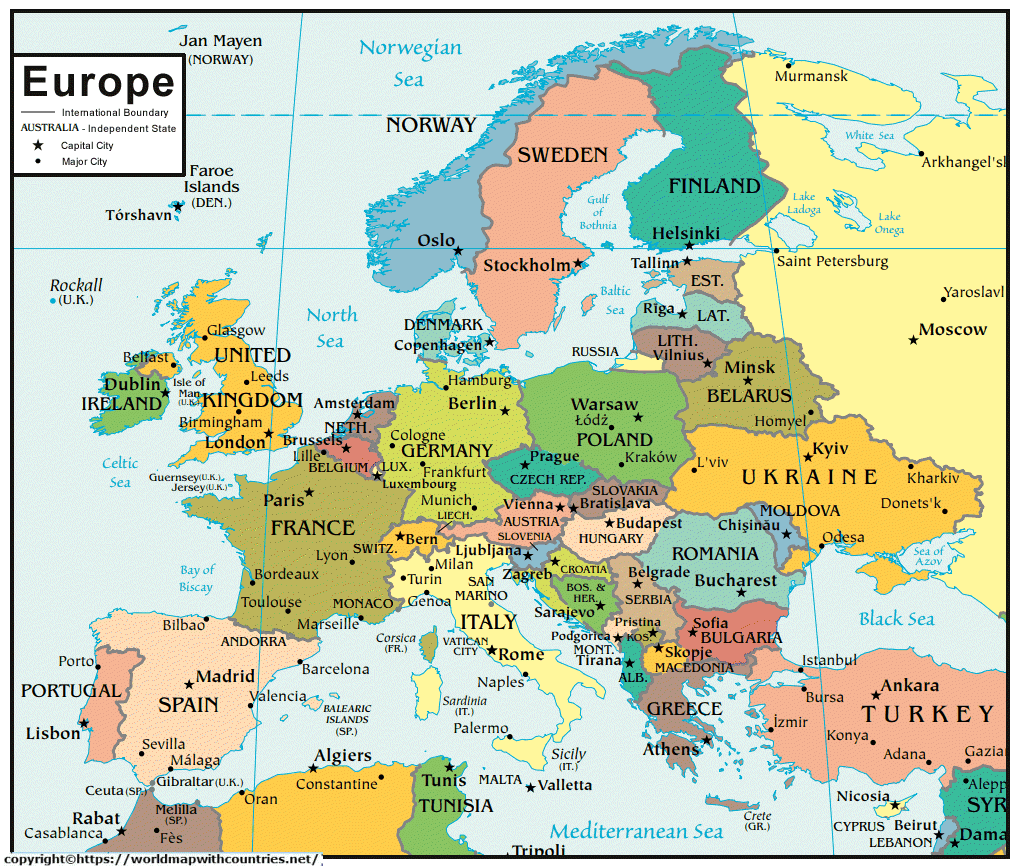
Western Europe, a vibrant tapestry of diverse cultures, languages, and histories, stretches across a landscape of rolling hills, snow-capped mountains, and sprawling coastlines. Understanding its intricate geography is crucial for comprehending the region’s political, economic, and cultural dynamics. A labeled map of Western Europe serves as a powerful tool for navigating this complex and fascinating region.
A Visual Guide to Western Europe’s Geography
A labeled map of Western Europe provides a comprehensive overview of the continent’s physical and political features, facilitating a deeper understanding of its complexities. Key features include:
1. Countries and Capitals: The map clearly delineates the boundaries of each nation, highlighting their respective capitals. From the bustling metropolis of London to the charming city of Lisbon, the map unveils the political landscape of Western Europe, showcasing the diverse range of cultures and identities that shape the region.
2. Major Cities: Prominent cities, centers of economic activity, and cultural hubs, are clearly marked on the map. This allows for a quick grasp of the distribution of urban centers and their relative importance within the larger context of the region.
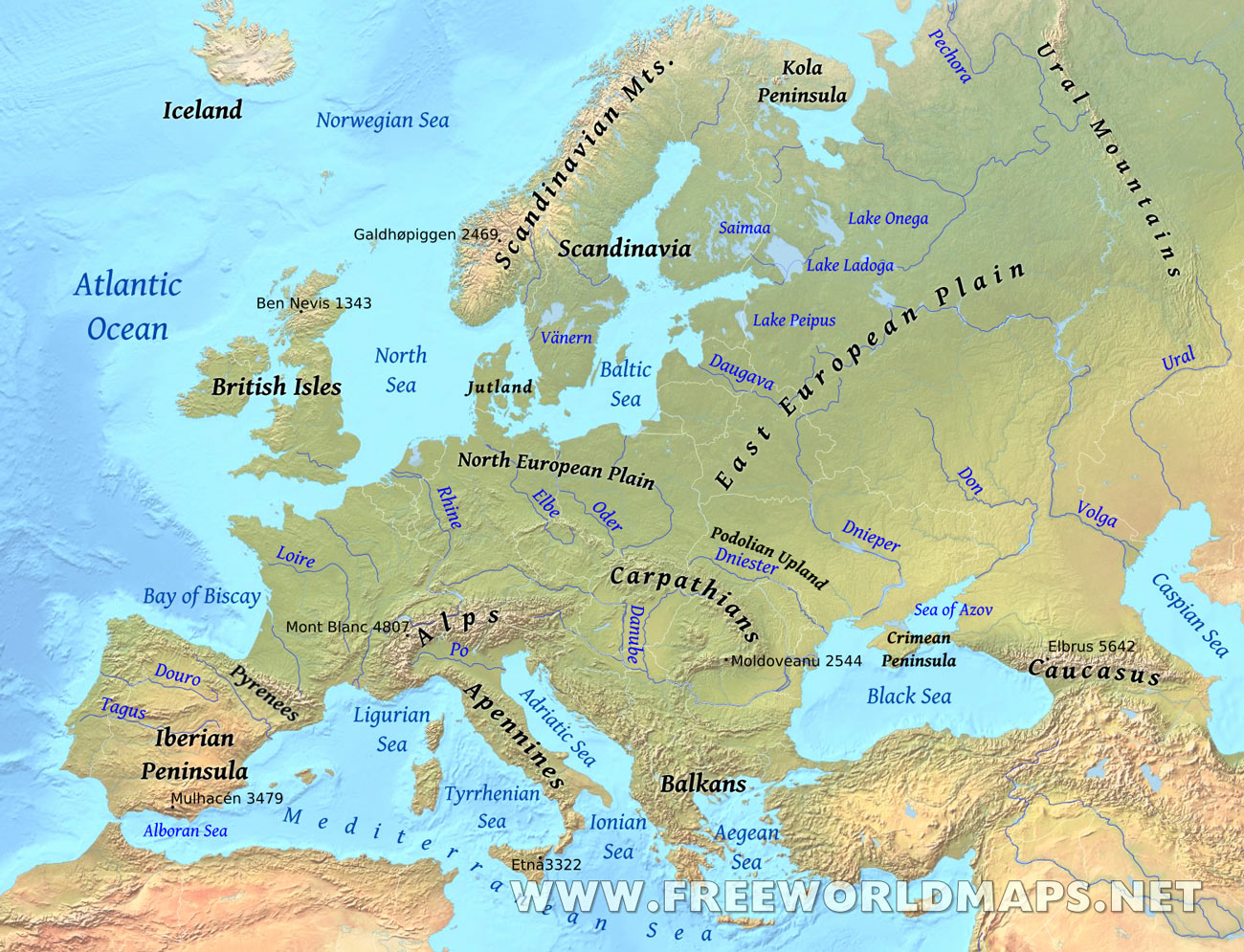
3. Physical Features: Mountains, rivers, and coastlines are accurately depicted, providing a visual representation of the landforms that define Western Europe’s geography. The towering Alps, the winding Rhine River, and the rugged coastline of the Iberian Peninsula are all vividly portrayed, highlighting the natural beauty and diverse landscapes that characterize the region.
4. Geographic Zones: The map may also include distinct geographical zones, such as the Mediterranean Basin, the Atlantic Coast, and the North European Plain. These zones often share similar climatic conditions, agricultural practices, and cultural influences, contributing to the regional diversity of Western Europe.
5. Key Transportation Networks: Major roads, railways, and waterways are typically indicated, providing insight into the infrastructure that connects the region and facilitates economic exchange. This visual representation underscores the significance of transportation in shaping the economic and social landscape of Western Europe.
Beyond the Surface: Unlocking Insights
A labeled map of Western Europe goes beyond simply marking locations. It serves as a springboard for deeper exploration, enabling us to:
-
Trace historical connections: By examining the geographical proximity of nations and the routes of ancient trade, the map reveals the historical influences that have shaped the region’s cultural landscape. The influence of the Roman Empire, the spread of Christianity, and the development of trade routes can be visualized and understood through the lens of geography.
-
Analyze economic and political relationships: The map can be used to analyze trade patterns, identify key economic hubs, and understand the geopolitical significance of certain locations. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the economic and political forces that drive the region’s development.
-
Explore cultural diversity: By examining the distribution of languages, religions, and cultural practices, the map reveals the richness and complexity of Western Europe’s cultural tapestry. The map serves as a visual guide to the diverse ethnicities, traditions, and artistic expressions that contribute to the region’s vibrant identity.
-
Identify environmental challenges: The map can be used to highlight areas vulnerable to climate change, pollution, or other environmental threats. This allows for a better understanding of the challenges facing Western Europe and the need for sustainable development practices.
FAQs: Unraveling the Map’s Mysteries
1. What are the most populated countries in Western Europe?
Western Europe is home to some of the most densely populated countries in the world. Germany, France, and the United Kingdom are among the most populous nations, with significant urban centers and high population densities.
2. What are the most important economic hubs in Western Europe?
Major economic hubs in Western Europe include London, Paris, Frankfurt, and Milan. These cities are centers of finance, trade, and innovation, driving the region’s economic growth and global influence.
3. What are the major mountain ranges in Western Europe?
The Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathian Mountains are prominent mountain ranges in Western Europe, shaping the region’s landscape and influencing its climate and cultural development.
4. How does the geography of Western Europe impact its climate?
Western Europe’s diverse geography influences its climate, resulting in a range of weather patterns from the temperate climates of the Atlantic Coast to the warmer Mediterranean regions.
5. What are the key transportation routes in Western Europe?
Major transportation routes in Western Europe include the Rhine River, the English Channel, and the Eurostar rail line. These routes facilitate the movement of people, goods, and ideas, connecting the region and fostering economic development.
Tips for Effective Map Interpretation
-
Pay attention to scale: The map’s scale determines the level of detail displayed. A larger scale map provides more specific information, while a smaller scale map offers a broader overview.
-
Look for symbols and legends: The map’s legend explains the meaning of different symbols and colors used to represent various features.
-
Consider the context: The map should be interpreted in the context of historical events, political developments, and cultural influences.
-
Use additional resources: Combining the map with other sources of information, such as historical accounts, economic data, and cultural studies, can provide a richer understanding of the region.
Conclusion: A Window into Western Europe’s Complexity
A labeled map of Western Europe serves as a powerful tool for understanding the region’s diverse geography, political landscape, and cultural heritage. By carefully examining its features and interpreting its symbols, we can gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of this dynamic and fascinating region. The map not only provides a visual representation of Western Europe’s physical and political features, but also serves as a gateway to understanding the historical forces, economic trends, and cultural expressions that have shaped its unique identity.
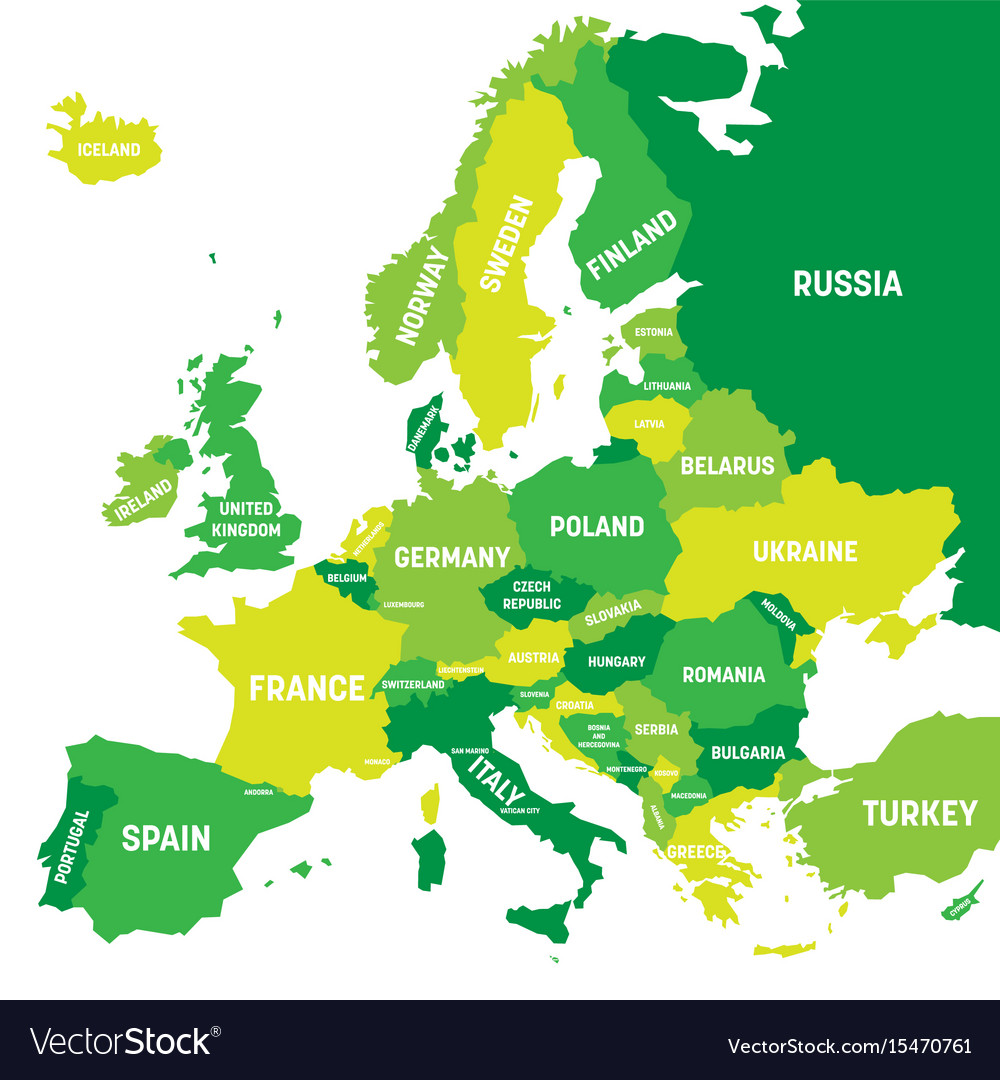


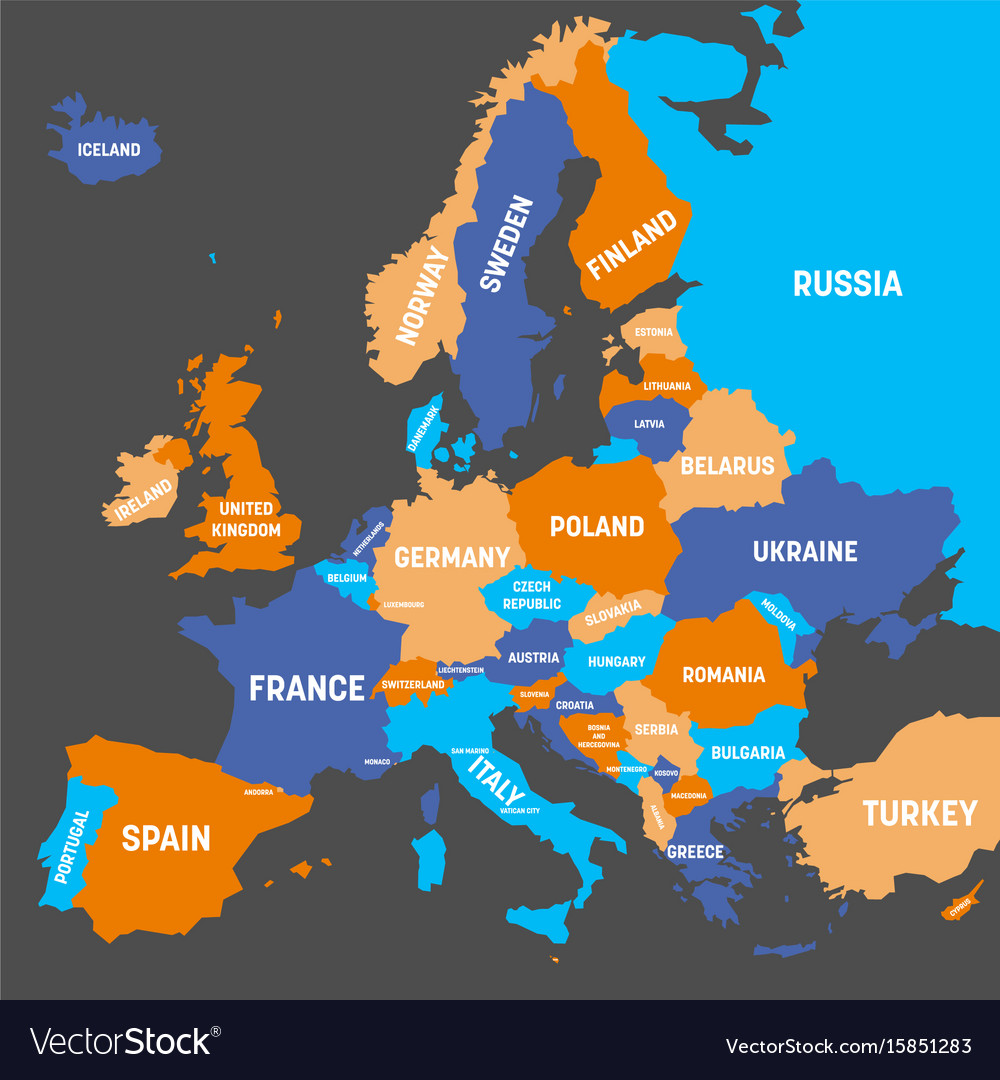

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Labeled Map Unravels the Continent. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!