Navigating the Tapestry of East Africa: A Geographical Overview
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of East Africa: A Geographical Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of East Africa: A Geographical Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of East Africa: A Geographical Overview
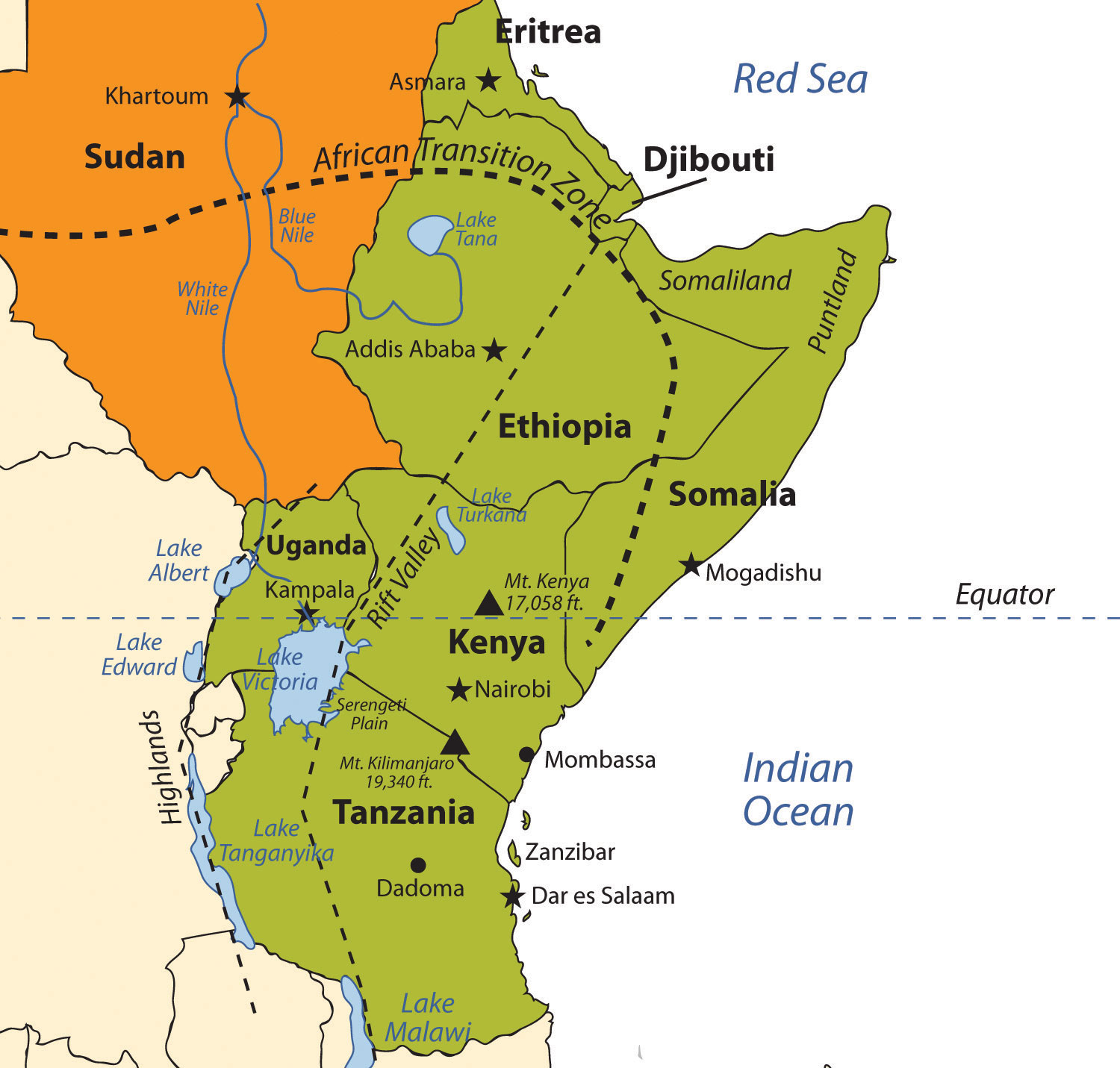
East Africa, a vibrant and diverse region spanning the eastern portion of the African continent, is a captivating tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and histories. Understanding the geography of this region is crucial for appreciating its rich cultural heritage, its unique environmental challenges, and its immense potential for economic growth and development. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the East African map, examining its key features and exploring the significance of its geographical configuration.
The Land and Its Boundaries:
East Africa is geographically defined by a series of natural and political boundaries. To the north, it borders the Red Sea and the Horn of Africa, a region encompassing countries like Eritrea, Djibouti, and Somalia. The eastern edge of East Africa is marked by the Indian Ocean, a vast expanse of water that has played a pivotal role in the region’s history and trade. To the south, East Africa blends into Southern Africa, with countries like Tanzania and Mozambique serving as transitional points. The western boundary is less clearly defined, encompassing the Great Rift Valley, a geological feature that stretches across the continent and serves as a natural dividing line between East and Central Africa.
The Diverse Landscape:
East Africa is a land of remarkable contrasts, boasting a diverse array of landscapes that range from towering mountains to vast savannas. The region is home to some of the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania, the tallest mountain in Africa, and Mount Kenya, a majestic peak with glaciers and snowfields. The East African Rift Valley, a geological marvel that runs through the heart of the region, is characterized by a series of volcanic craters, deep canyons, and freshwater lakes, including Lake Victoria, the largest lake in Africa. The region also encompasses vast savannas, like the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania, home to an incredible diversity of wildlife.
The Countries of East Africa:
The map of East Africa is populated by a collection of diverse countries, each with its unique history, culture, and economic landscape. These countries include:
- Burundi: A small, densely populated country located in the heart of East Africa, Burundi is known for its rolling hills and coffee production.
- Djibouti: Situated on the Horn of Africa, Djibouti is a strategically important country with a diverse landscape, including the Danakil Depression, one of the hottest and driest places on Earth.
- Eritrea: A nation with a rich history and a diverse landscape, Eritrea boasts mountains, deserts, and coastal plains.
- Ethiopia: The oldest independent country in Africa, Ethiopia is a landlocked nation with a rich cultural heritage and a diverse landscape, including the Ethiopian Highlands.
- Kenya: A country known for its stunning wildlife, diverse landscapes, and vibrant culture, Kenya is a popular tourist destination.
- Madagascar: A large island nation located off the coast of East Africa, Madagascar is renowned for its unique biodiversity and its diverse cultural heritage.
- Malawi: A landlocked country in southeast Africa, Malawi is known for its beautiful lakes, including Lake Malawi, one of the largest and most biodiverse lakes in the world.
- Mozambique: A coastal country with a diverse landscape, Mozambique is known for its beaches, its rich history, and its burgeoning tourism industry.
- Rwanda: A country known for its stunning landscapes, including the Virunga Mountains, and its ongoing efforts to rebuild after the Rwandan genocide.
- Somalia: Located on the Horn of Africa, Somalia is a country with a long history of conflict and instability, but also a rich cultural heritage.
- South Sudan: A newly independent country formed in 2011, South Sudan is a landlocked nation with a diverse landscape and a rich cultural heritage.
- Tanzania: A country known for its stunning wildlife, including the Serengeti National Park and the Ngorongoro Crater, Tanzania is a popular tourist destination.
- Uganda: A country with a diverse landscape, including the Rwenzori Mountains and Lake Victoria, Uganda is known for its wildlife, its beautiful scenery, and its rich cultural heritage.
- Zambia: A landlocked country in southern Africa, Zambia is known for its stunning waterfalls, including Victoria Falls, and its diverse wildlife.
- Zimbabwe: A country known for its stunning landscapes, including the Victoria Falls and the Matobo National Park, Zimbabwe is a popular tourist destination.
The Importance of the East African Map:
The map of East Africa is not merely a collection of lines and borders, but a reflection of the region’s complex history, its diverse cultures, and its immense potential for economic growth and development. Understanding the geographical configuration of East Africa is crucial for:
- Understanding the region’s history: The map reveals the intricate relationships between different countries, the impact of colonial boundaries, and the ongoing challenges of conflict and instability in some areas.
- Appreciating the region’s cultural diversity: The map highlights the rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions that make up East Africa.
- Identifying opportunities for economic development: The map reveals the region’s natural resources, its infrastructure, and its potential for trade and investment.
- Addressing environmental challenges: The map highlights the region’s vulnerability to climate change, its dependence on natural resources, and its need for sustainable development.
- Promoting regional integration: The map underscores the importance of cooperation between East African countries to address common challenges and capitalize on shared opportunities.
FAQs about the Map of East African Countries:
1. What are the major geographic features of East Africa?
East Africa is characterized by the East African Rift Valley, a geological feature that runs through the heart of the region and is responsible for its diverse landscapes, including volcanic mountains, deep canyons, and freshwater lakes. The region also encompasses vast savannas, towering mountains, and coastal plains.
2. What are the major economic activities in East Africa?
East Africa is a region with a diverse economy, with major economic activities including agriculture, tourism, mining, and manufacturing. The region is also home to a growing number of businesses and industries, particularly in the technology sector.
3. What are the major challenges facing East Africa?
East Africa faces a number of challenges, including poverty, inequality, conflict, and environmental degradation. The region is also vulnerable to climate change, which is threatening its natural resources and its agricultural sector.
4. What are the major opportunities for East Africa?
East Africa has a number of opportunities for growth and development, including its vast natural resources, its growing population, and its potential for trade and investment. The region is also home to a young and dynamic population, which is driving innovation and entrepreneurship.
5. What are the major political issues in East Africa?
East Africa is a region with a complex political landscape, with a history of conflict, instability, and political transitions. The region is also grappling with issues of governance, democracy, and human rights.
Tips for Understanding the Map of East African Countries:
- Study the map carefully: Pay attention to the location of countries, major cities, and geographic features.
- Learn about the history of the region: Understanding the historical context of East Africa is essential for understanding its current situation.
- Research the cultures and languages of the region: Explore the rich diversity of cultures and languages that make up East Africa.
- Follow the news and current events: Stay informed about the latest developments in East Africa.
- Travel to the region: Experiencing East Africa firsthand is the best way to understand its complexities and appreciate its beauty.
Conclusion:
The map of East Africa is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s unique geography, its diverse cultures, and its immense potential. By studying the map and learning about its history, its people, and its challenges, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of this fascinating region and its place in the world. The map serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of East Africa’s countries, highlighting the importance of cooperation, understanding, and sustainable development for a brighter future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of East Africa: A Geographical Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
