Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Middle Eastern Capitals
Related Articles: Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Middle Eastern Capitals
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Middle Eastern Capitals. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Middle Eastern Capitals
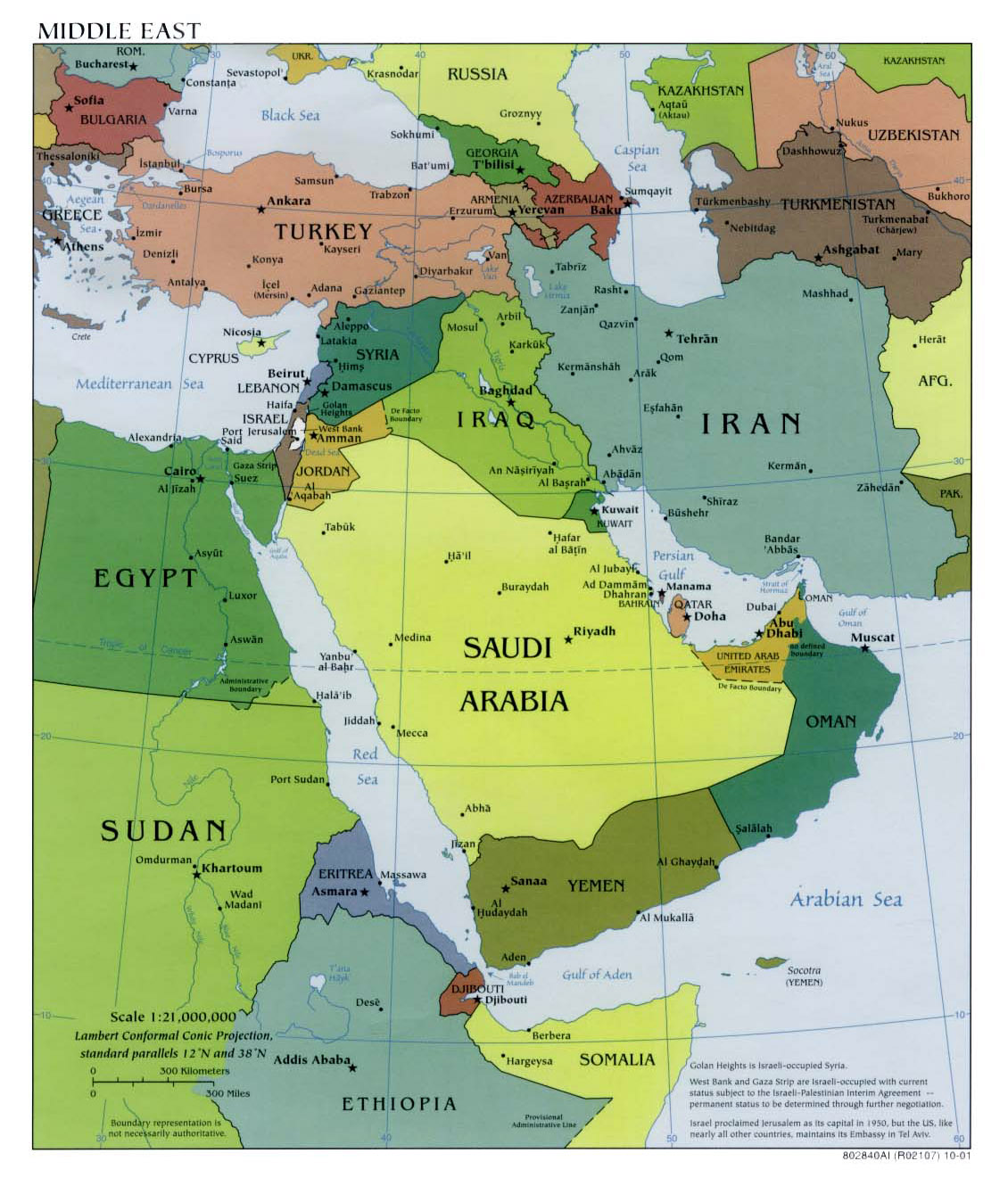
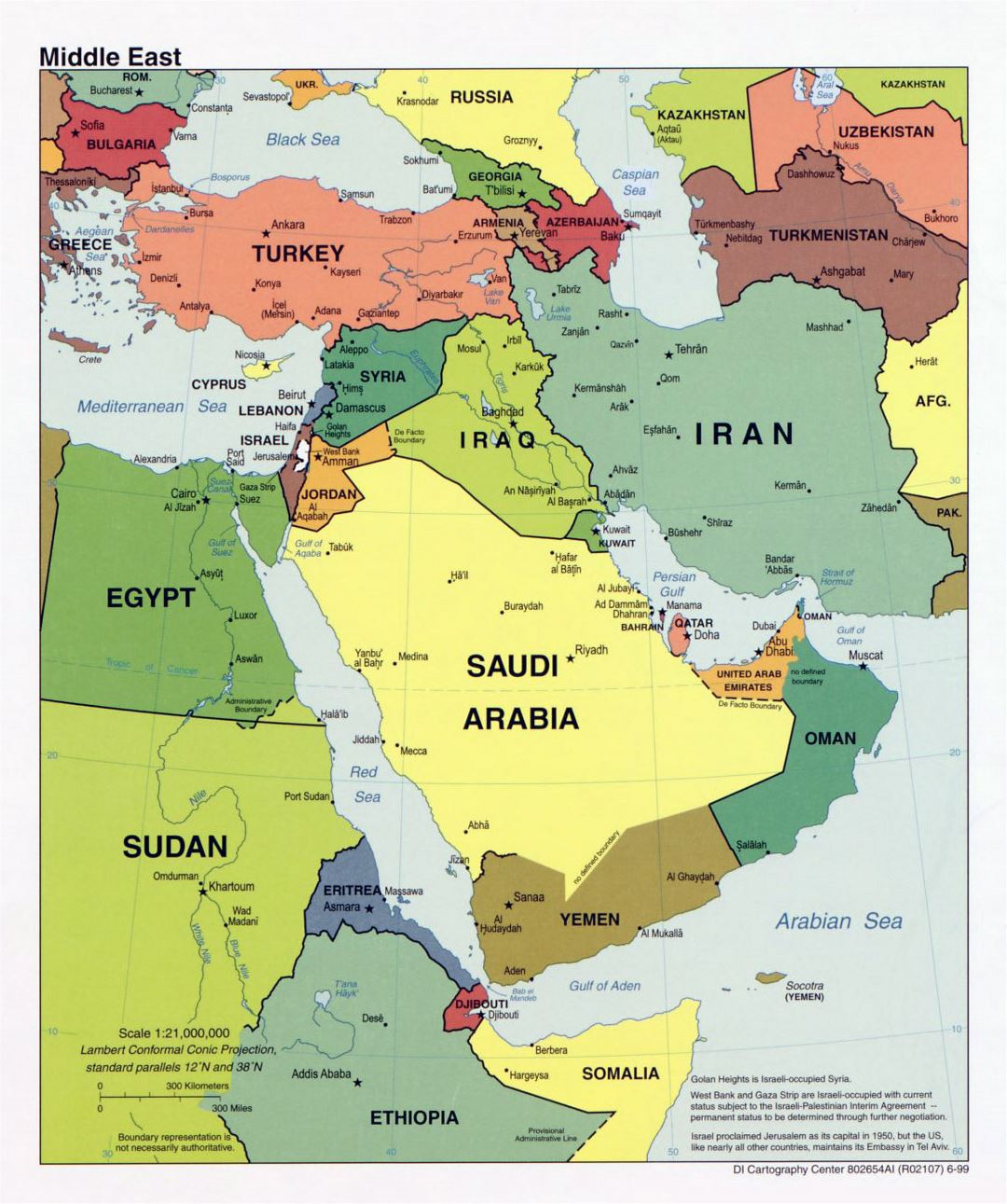
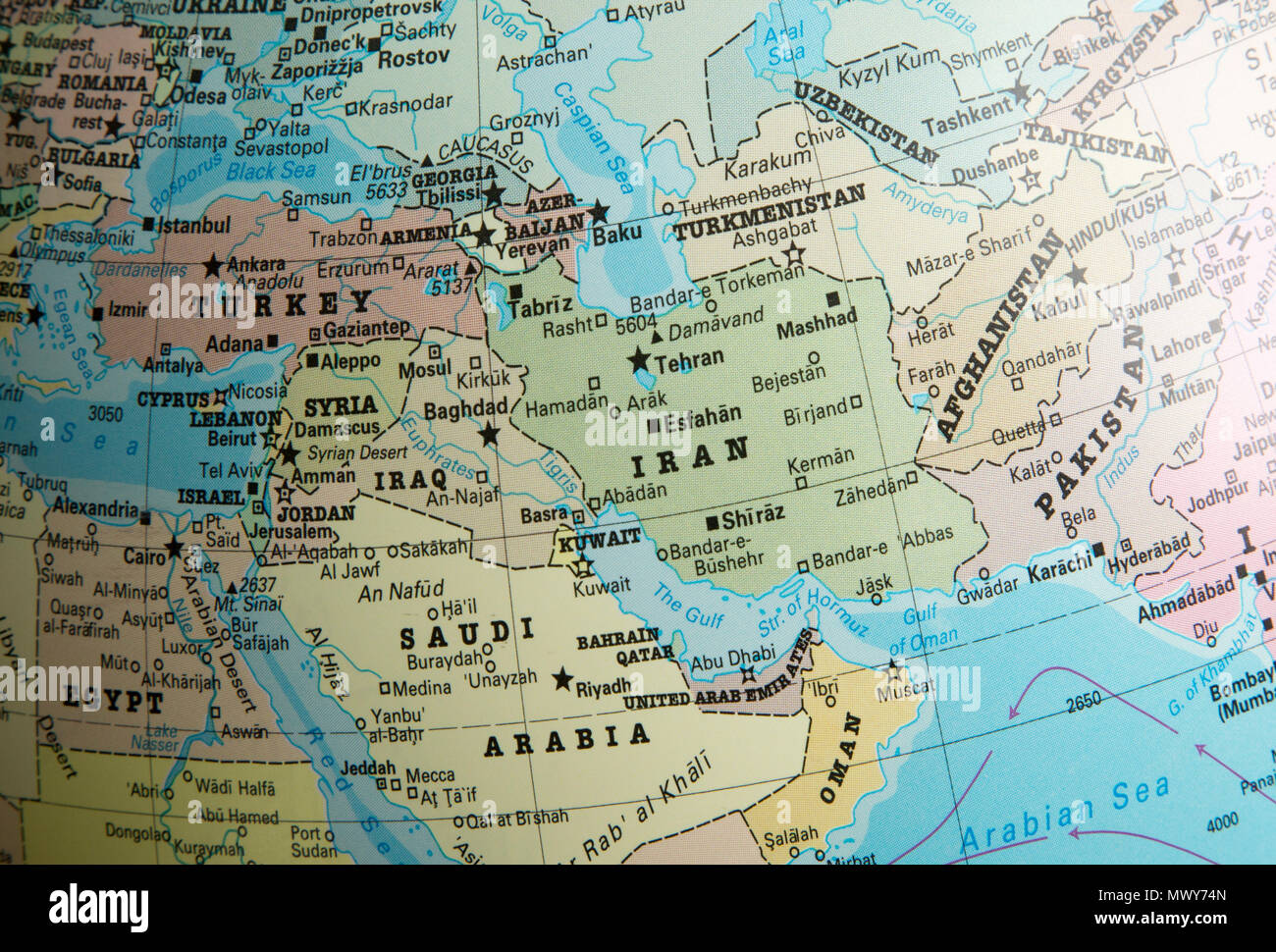
The Middle East, a region steeped in history, culture, and geopolitical complexity, is home to a diverse array of nations, each with its own unique capital city. Understanding the geographical distribution of these capitals is essential for comprehending the region’s political landscape, economic dynamics, and cultural nuances. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the Middle East capitals map, exploring its significance and offering insights into the individual cities and their roles within the region.
A Tapestry of Capitals:
The Middle East capitals map showcases a fascinating mix of ancient and modern cities, each reflecting the historical evolution and contemporary challenges of its respective nation. From the bustling metropolis of Cairo, Egypt’s ancient capital, to the futuristic skyline of Abu Dhabi, the United Arab Emirates’ modern hub, the map reveals a diverse array of urban landscapes.
The Importance of Geographic Context:
The location of a capital city often reflects its historical significance and strategic importance. For instance, Amman, Jordan’s capital, sits strategically at the crossroads of major trade routes, underscoring its role as a regional hub. Similarly, Damascus, Syria’s ancient capital, holds a significant place in history, having served as a vital center of trade and culture for centuries.
Understanding the Political Dynamics:
The Middle East capitals map provides a visual representation of the region’s political landscape, highlighting the distribution of power and influence. The location of capitals can indicate alliances, rivalries, and historical tensions. For example, the proximity of Baghdad, Iraq’s capital, to Tehran, Iran’s capital, reflects the complex relationship between these two nations.
Exploring the Cultural Mosaic:
Each capital city embodies the cultural heritage and identity of its nation. From the vibrant souks of Marrakech, Morocco’s capital, to the architectural wonders of Istanbul, Turkey’s historic capital, the map showcases the rich cultural tapestry of the region. These cities serve as centers of art, literature, music, and cuisine, reflecting the unique character of their respective nations.
Economic Hubs and Global Connections:
Many Middle Eastern capitals serve as economic powerhouses, driving regional and global trade. Dubai, the United Arab Emirates’ commercial hub, has emerged as a global center for finance, tourism, and trade. Similarly, Doha, Qatar’s capital, has become a major player in the energy sector, hosting international events and attracting foreign investment.
A Closer Look at Individual Capitals:
1. Cairo, Egypt:
- Historical Significance: Ancient capital of the Egyptian Empire, dating back to the Pharaonic era.
- Modern Role: Major center for culture, education, and commerce in the Arab world.
- Key Landmarks: Pyramids of Giza, Egyptian Museum, Khan el-Khalili Bazaar.
2. Amman, Jordan:
- Strategic Location: Situated at the crossroads of major trade routes.
- Modern Role: Regional hub for trade and investment, with a growing tourism sector.
- Key Landmarks: Citadel Hill, Roman Amphitheater, Petra (nearby).
3. Jerusalem, Israel:
- Religious Significance: Holy city for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
- Political Complexity: Subject to ongoing territorial disputes.
- Key Landmarks: Western Wall, Temple Mount, Dome of the Rock.
4. Damascus, Syria:
- Ancient Capital: One of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world.
- Cultural Heritage: Rich history and tradition, with a vibrant souk and ancient architecture.
- Key Landmarks: Umayyad Mosque, Straight Street, Old City.
5. Beirut, Lebanon:
- Mediterranean Hub: Major port city and commercial center.
- Cultural Vitality: Known for its vibrant nightlife, diverse cuisine, and artistic scene.
- Key Landmarks: Corniche, National Museum of Beirut, Roman Baths.
6. Baghdad, Iraq:
- Historical Capital: Center of the Abbasid Caliphate, a golden age of Islamic culture.
- Modern Challenges: Facing political instability and economic difficulties.
- Key Landmarks: Al-Mustansiriya University, Baghdad Zoo, National Museum of Iraq.
7. Doha, Qatar:
- Energy Hub: Major producer of natural gas and oil.
- Modern Development: Booming economy with investments in infrastructure and tourism.
- Key Landmarks: Museum of Islamic Art, Souq Waqif, Doha Corniche.
8. Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates:
- Modern Metropolis: Thriving financial center with a focus on sustainability.
- Cultural Initiatives: Investing in museums, art galleries, and cultural events.
- Key Landmarks: Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque, Louvre Abu Dhabi, Yas Island.
9. Muscat, Oman:
- Historical Port: Important trading center with a rich maritime history.
- Modern Development: Focus on tourism, with stunning natural landscapes.
- Key Landmarks: Sultan Qaboos Grand Mosque, Muttrah Souq, Royal Opera House Muscat.
10. Riyadh, Saudi Arabia:
- Economic Powerhouse: Center of Saudi Arabia’s oil industry and regional trade.
- Modern Architecture: Striking skyscrapers and modern infrastructure.
- Key Landmarks: King Fahd National Library, Masmak Fortress, Kingdom Centre Tower.
11. Kuwait City, Kuwait:
- Financial Center: Major oil producer and regional financial hub.
- Modern Architecture: Blending traditional Islamic architecture with modern skyscrapers.
- Key Landmarks: Kuwait Towers, Grand Mosque, National Museum of Kuwait.
12. Manama, Bahrain:
- Financial Hub: Major banking center with a growing tourism sector.
- Cultural Heritage: Blend of Islamic and Persian influences.
- Key Landmarks: Bahrain National Museum, Bab Al-Bahrain, Al Fateh Grand Mosque.
13. Sana’a, Yemen:
- Ancient Capital: Historic city with a unique architectural style.
- Cultural Heritage: Rich tradition of Islamic art and architecture.
- Key Landmarks: Old City of Sana’a, Great Mosque of Sana’a, National Museum of Yemen.
14. Ankara, Turkey:
- Modern Capital: Established in 1923 after the fall of the Ottoman Empire.
- Political Center: Home to the Turkish Parliament and government offices.
- Key Landmarks: Anıtkabir (Atatürk’s Mausoleum), Museum of Anatolian Civilizations, Ankara Castle.
15. Tehran, Iran:
- Historical Capital: Center of Persian culture and history.
- Political Influence: Home to the Iranian government and influential institutions.
- Key Landmarks: Golestan Palace, Azadi Tower, Grand Bazaar.
16. Beirut, Lebanon:
- Mediterranean Hub: Major port city and commercial center.
- Cultural Vitality: Known for its vibrant nightlife, diverse cuisine, and artistic scene.
- Key Landmarks: Corniche, National Museum of Beirut, Roman Baths.
17. Jerusalem, Israel:
- Religious Significance: Holy city for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
- Political Complexity: Subject to ongoing territorial disputes.
- Key Landmarks: Western Wall, Temple Mount, Dome of the Rock.
18. Amman, Jordan:
- Strategic Location: Situated at the crossroads of major trade routes.
- Modern Role: Regional hub for trade and investment, with a growing tourism sector.
- Key Landmarks: Citadel Hill, Roman Amphitheater, Petra (nearby).
19. Cairo, Egypt:
- Historical Significance: Ancient capital of the Egyptian Empire, dating back to the Pharaonic era.
- Modern Role: Major center for culture, education, and commerce in the Arab world.
- Key Landmarks: Pyramids of Giza, Egyptian Museum, Khan el-Khalili Bazaar.
20. Tunis, Tunisia:
- Mediterranean City: Historic capital with a blend of Arab and European influences.
- Cultural Heritage: Rich tradition of Islamic art and architecture.
- Key Landmarks: Medina of Tunis, Bardo Museum, Carthage (nearby).
FAQs on the Middle East Capitals Map:
Q: What is the significance of the Middle East capitals map?
A: The map provides a visual representation of the region’s political landscape, economic dynamics, and cultural diversity. It highlights the historical significance, strategic location, and modern role of each capital city.
Q: How does the location of a capital city affect its role in the region?
A: The location of a capital city often reflects its historical significance, strategic importance, and proximity to trade routes. It can influence its economic development, political alliances, and cultural interactions with neighboring countries.
Q: What are some of the common features of Middle Eastern capitals?
A: Many Middle Eastern capitals share common features, such as a rich history, vibrant cultural traditions, and a blend of modern and traditional architecture. They often serve as centers of commerce, education, and government, playing a vital role in the region’s economic and political landscape.
Tips for Using the Middle East Capitals Map:
- Focus on Geographic Context: Pay attention to the location of each capital city in relation to neighboring countries and major trade routes.
- Explore Historical Significance: Research the historical background of each capital, understanding its role in the region’s past.
- Identify Economic Hubs: Recognize the capitals that serve as major centers of trade, finance, and industry.
- Appreciate Cultural Diversity: Explore the unique cultural heritage of each capital city, from its architecture and art to its cuisine and traditions.
Conclusion:
The Middle East capitals map offers a compelling glimpse into the region’s intricate political, economic, and cultural landscape. Each capital city represents a unique blend of history, tradition, and modernity, reflecting the diverse tapestry of nations that make up the Middle East. By understanding the map’s significance and exploring the individual cities, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the region’s complexities and the fascinating stories woven into its urban fabric.
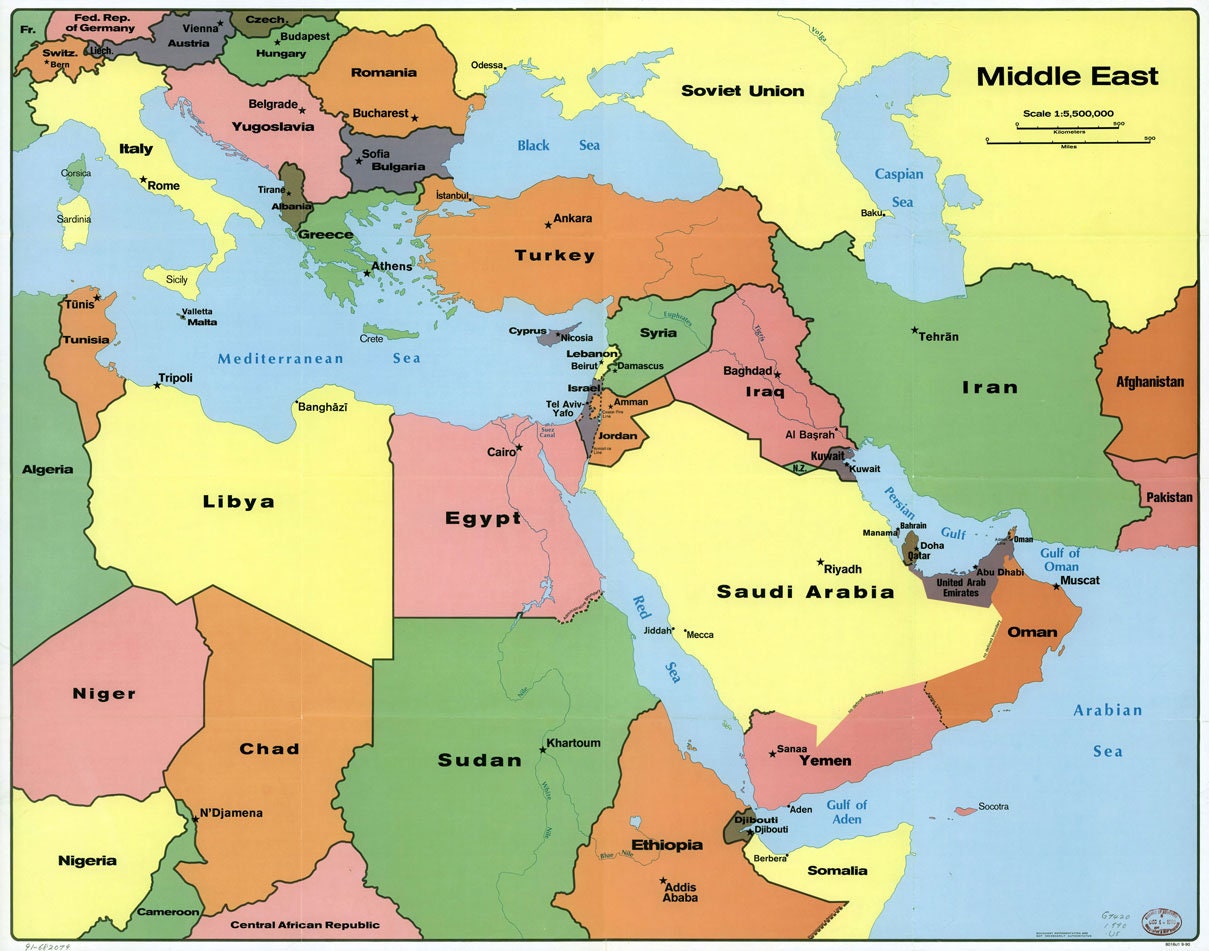



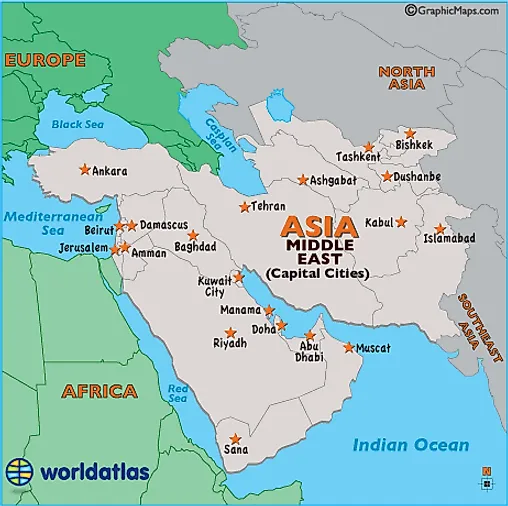
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Middle Eastern Capitals. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!