Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Indiana’s District Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Indiana’s District Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Indiana’s District Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Indiana’s District Maps
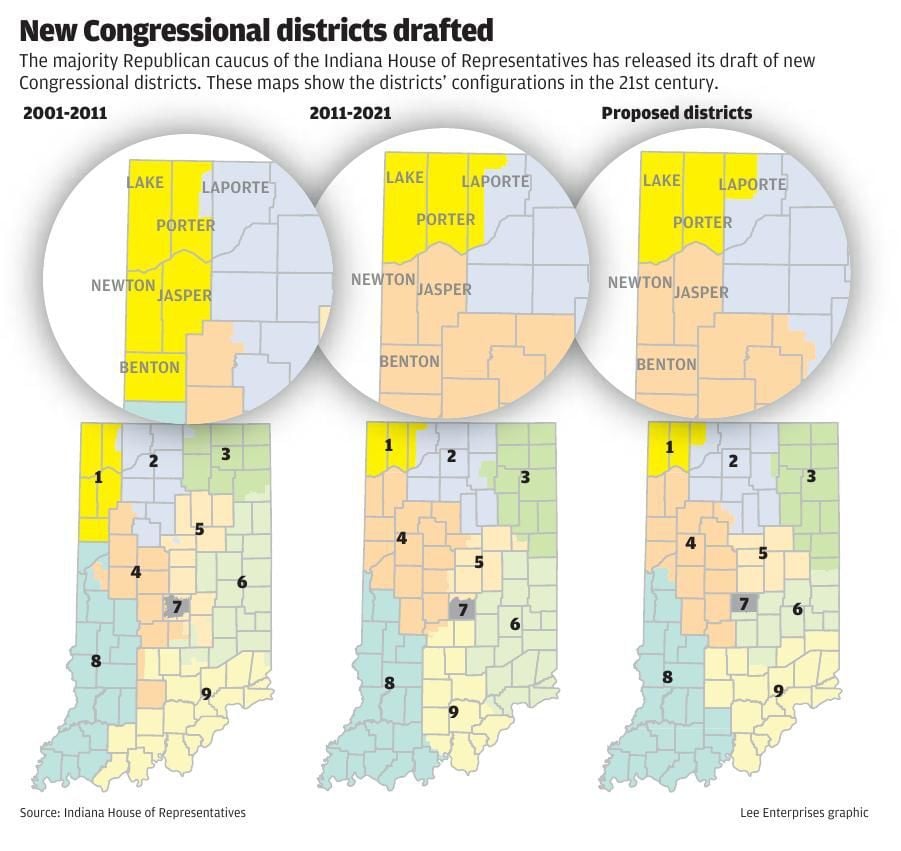
Indiana, like many states, utilizes district maps to divide its population into distinct geographic areas for various purposes, primarily political representation and administrative organization. These maps, often referred to as electoral maps or redistricting maps, are crucial for ensuring fair and equitable representation in government, allocating resources effectively, and fostering a sense of community within specific regions.
The Importance of District Maps
District maps serve as the foundation for democratic processes, ensuring that each citizen’s voice is heard and reflected in the legislative and administrative bodies that govern their lives. The maps define the boundaries of congressional, state legislative, and local electoral districts, determining which residents vote for which representatives.
Types of Districts in Indiana
Indiana’s district maps encompass several levels of governance, each with its unique purpose:
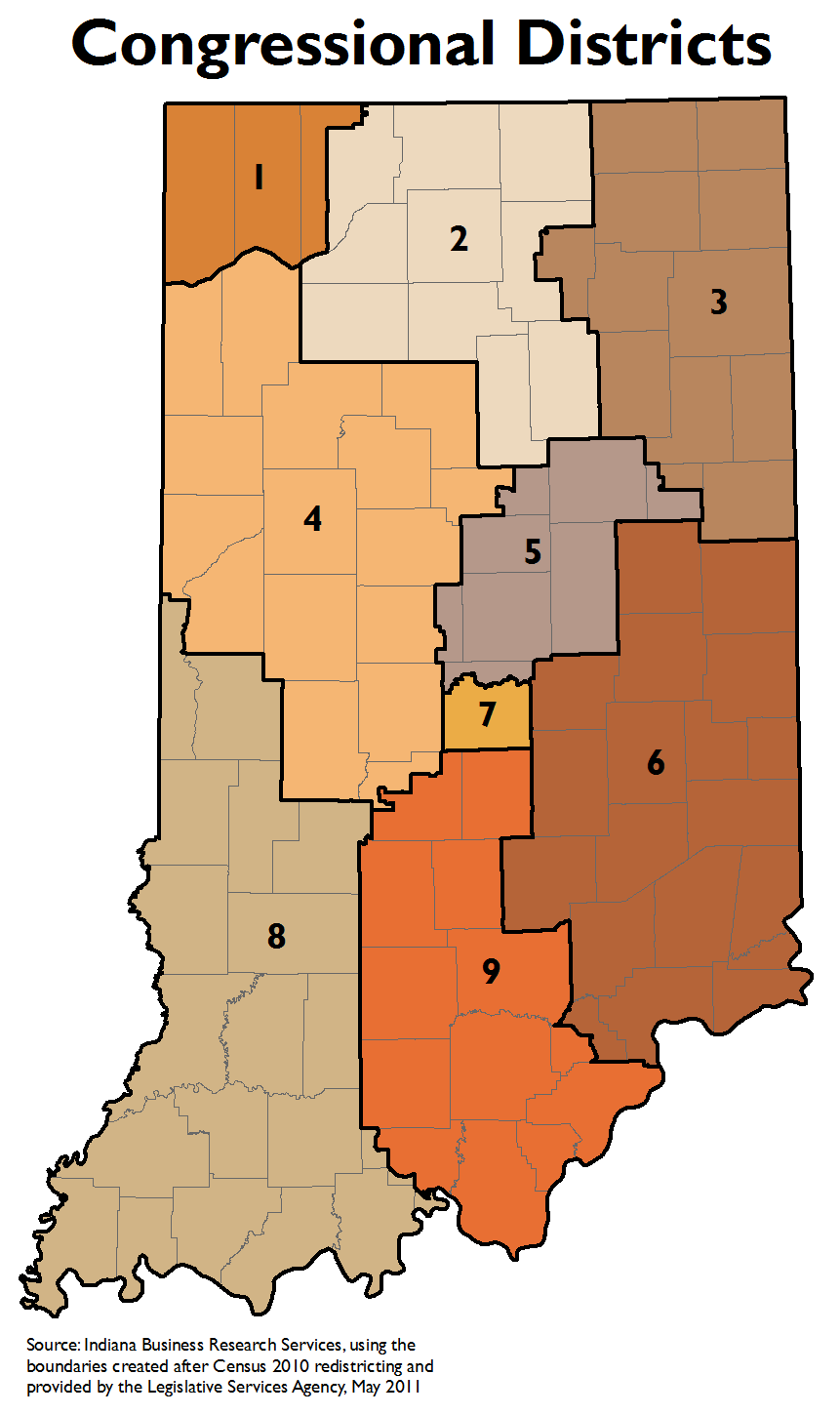
- Congressional Districts: These maps define the boundaries of nine congressional districts, each represented by a member of the U.S. House of Representatives.
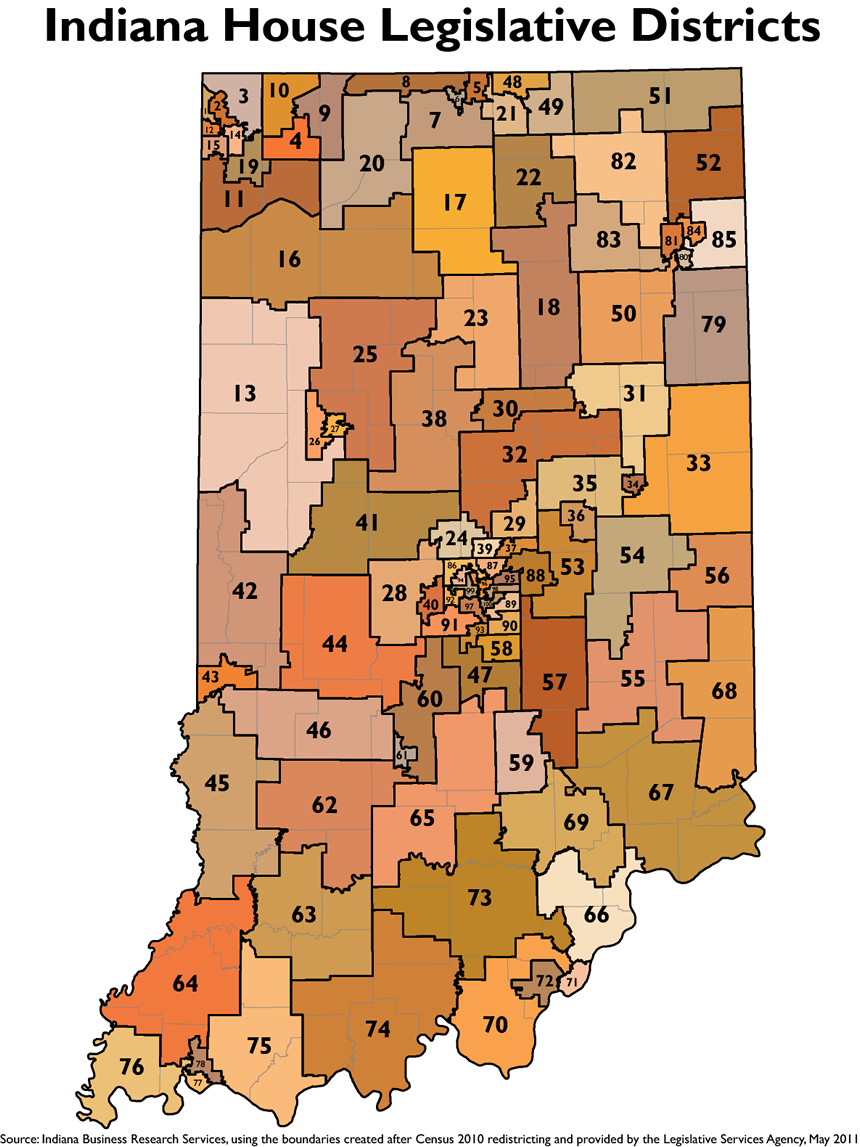
- State Legislative Districts: The state is divided into 50 state senate districts and 100 state house districts, each electing representatives to the Indiana General Assembly.
- County Districts: Counties are often subdivided into districts for various administrative purposes, such as school boards, county council, and other local bodies.
- Municipal Districts: Cities and towns may also be divided into districts for purposes like city council representation or service provision.
The Redistricting Process in Indiana
The process of drawing and redrawing district maps, known as redistricting, occurs every ten years following the decennial census. This process ensures that districts reflect population changes and maintain roughly equal populations, adhering to the principle of "one person, one vote."
The Role of the Indiana Districting Commission
In 2008, Indiana established the Indiana Districting Commission, a bipartisan body tasked with drawing the state’s congressional and state legislative districts. The commission consists of five members: three appointed by the majority party in the state legislature and two appointed by the minority party.
Challenges and Controversies
While the redistricting process aims for fairness and representation, it often faces challenges and controversies:
- Gerrymandering: The manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular political party or group is a significant concern. Gerrymandering can result in districts that are highly skewed in favor of one party, leading to uncompetitive elections and reduced voter choice.
- Minority Representation: Ensuring that minority communities have fair representation in government is a critical aspect of redistricting. However, drawing districts that effectively represent minority groups can be challenging and often involves balancing competing interests.
- Community of Interest: The redistricting process should consider the interests and needs of communities within each district. Dividing communities with shared interests or common concerns can undermine local representation and effective governance.
FAQs about Indiana District Maps
Q: How often are Indiana’s district maps redrawn?
A: District maps are redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census.
Q: Who is responsible for drawing Indiana’s district maps?
A: The Indiana Districting Commission, a bipartisan body, is responsible for drawing the state’s congressional and state legislative districts.
Q: What are the key principles guiding the redistricting process in Indiana?
A: The redistricting process in Indiana is guided by principles such as equal population, contiguity, compactness, and respect for communities of interest.
Q: What are the potential consequences of gerrymandering?
A: Gerrymandering can lead to uncompetitive elections, reduced voter choice, and diminished representation for certain groups.
Q: How can citizens participate in the redistricting process in Indiana?
A: Citizens can participate in the redistricting process by attending public hearings, submitting comments to the Indiana Districting Commission, and advocating for their preferred map proposals.
Tips for Understanding and Engaging with Indiana District Maps
- Familiarize yourself with the redistricting process: Understanding the process and its underlying principles is crucial for informed participation.
- Explore the maps and their impact: Examine the district maps and analyze their potential effects on representation, voter choice, and community interests.
- Engage with your elected officials: Communicate your concerns and preferences regarding redistricting to your local, state, and federal representatives.
- Support organizations advocating for fair redistricting: Numerous organizations work to ensure fair and equitable redistricting practices.
Conclusion
Indiana’s district maps play a vital role in shaping the state’s political landscape and influencing the lives of its residents. Understanding the complexities of district maps, the redistricting process, and the associated challenges is crucial for ensuring fair representation, fostering a sense of community, and upholding the principles of democracy. By actively engaging with the redistricting process, citizens can contribute to shaping the maps that define their communities and influence their future.
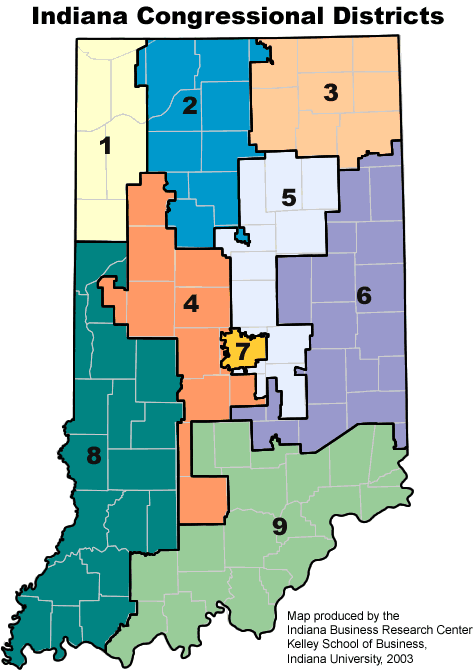
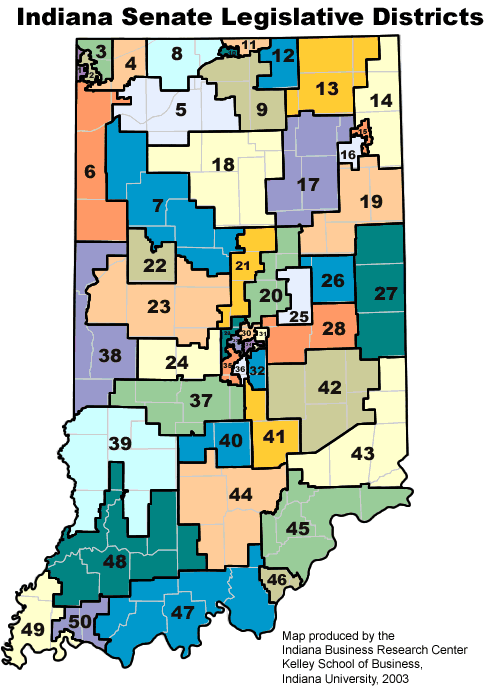


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Indiana’s District Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!