Navigating the Landscape of Customer Journeys: A Comprehensive Guide to Rider Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Customer Journeys: A Comprehensive Guide to Rider Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Customer Journeys: A Comprehensive Guide to Rider Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Customer Journeys: A Comprehensive Guide to Rider Maps
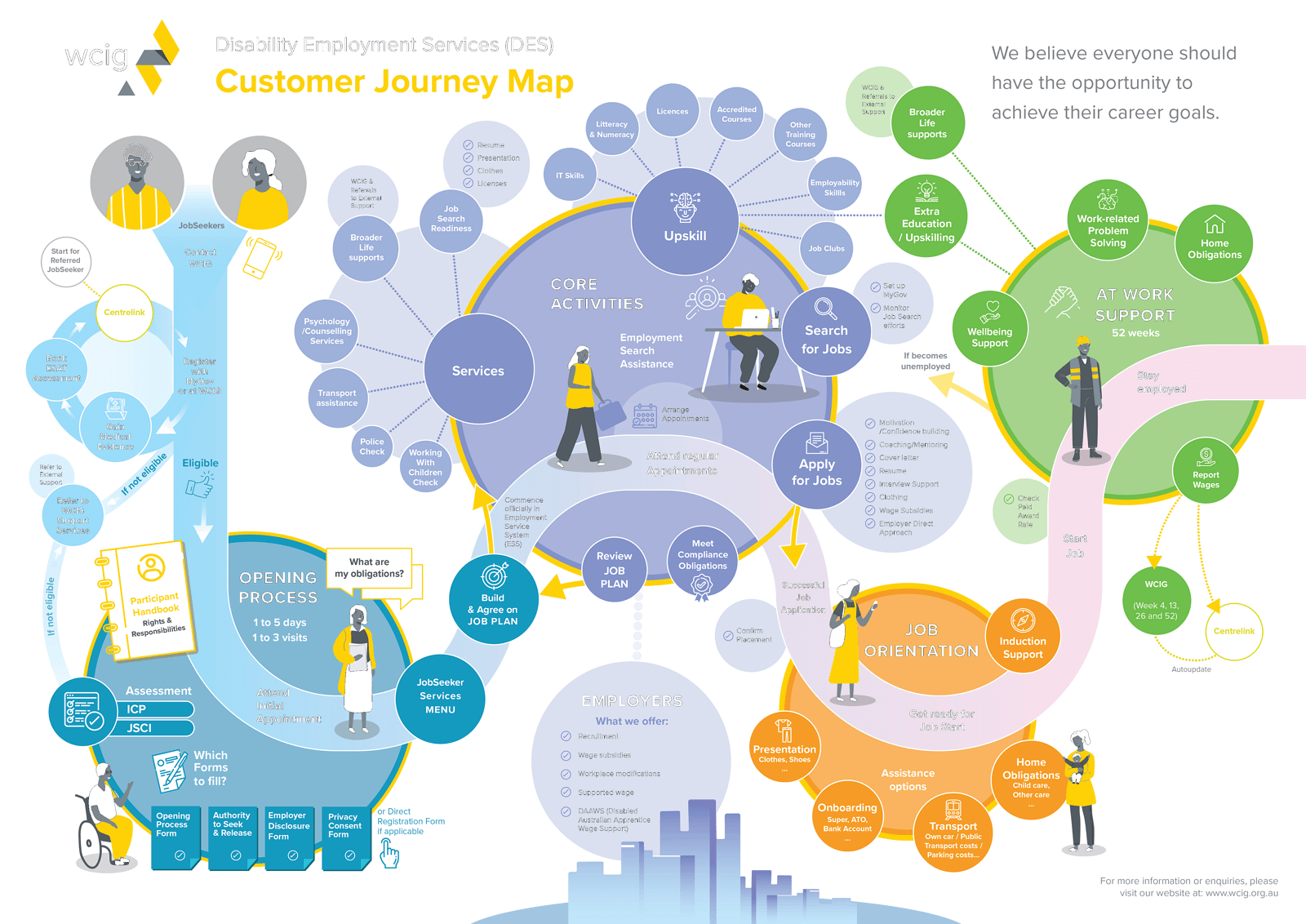
In the ever-evolving realm of customer experience, understanding the intricate pathways individuals traverse through their interactions with a brand is paramount. This intricate network of touchpoints, known as the customer journey, forms the bedrock upon which successful businesses are built. To effectively navigate this complex terrain and optimize the customer experience, a powerful tool emerges: the rider map.
Unveiling the Rider Map: A Visual Representation of Customer Engagement
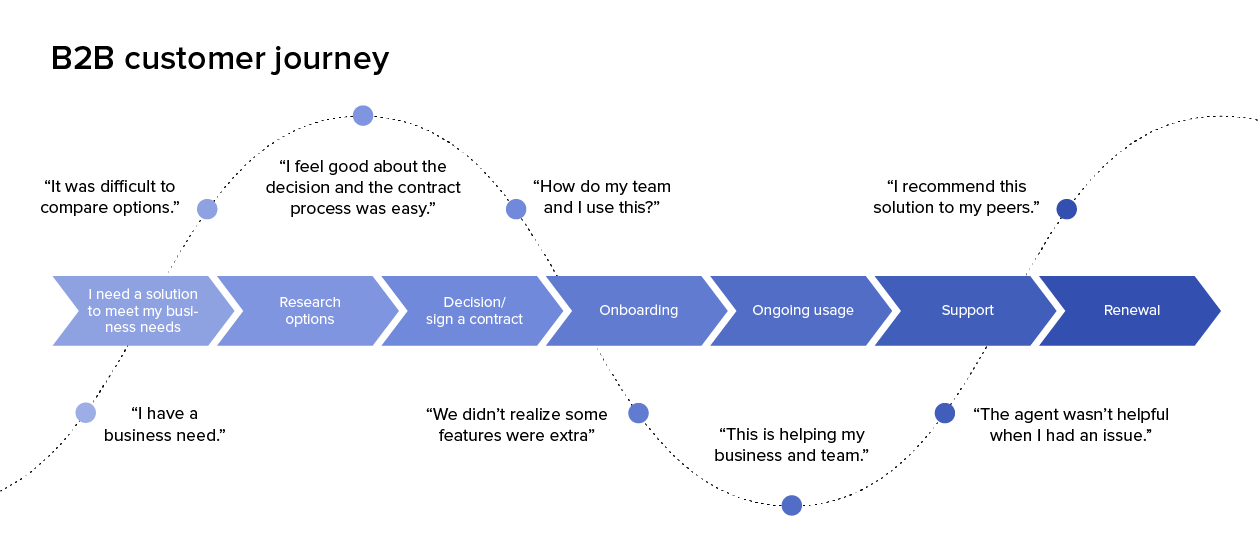
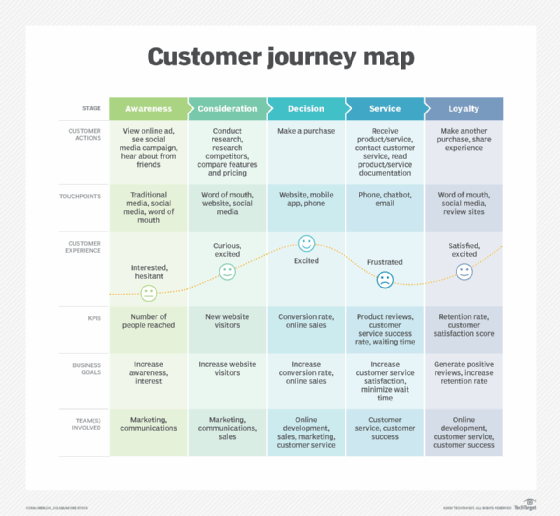
A rider map, often referred to as a journey map, is a visual representation of a customer’s interaction with a brand or service. It meticulously charts the steps a customer takes, from initial awareness to the ultimate resolution of their needs. This comprehensive visualization encompasses a wide range of aspects, including:
- Customer Personas: The map identifies and defines specific customer archetypes, capturing their unique motivations, goals, and pain points.
- Touchpoints: Each interaction a customer has with the brand, from website visits to phone calls to social media engagement, is meticulously documented.
- Emotions and Feelings: The map delves into the emotional landscape of the customer journey, tracing the shifts in sentiment, frustration, or satisfaction at each stage.
- Channels: The various communication channels employed by the customer and the brand are highlighted, providing a holistic view of the interaction flow.
- Obstacles and Opportunities: Potential roadblocks and areas for improvement are identified, offering valuable insights for enhancing the customer experience.
The Power of Visualization: A Framework for Strategic Decision-Making
The rider map’s strength lies in its ability to translate complex customer interactions into a clear and concise visual narrative. This visual framework offers numerous benefits, empowering organizations to:
- Gain a Deeper Understanding of Customer Needs: By mapping the customer journey, businesses can gain a nuanced understanding of customer motivations, pain points, and expectations. This invaluable insight enables organizations to tailor their offerings and communication strategies to meet specific customer needs.
- Identify Critical Touchpoints: The map highlights key interaction points where customers are most engaged, frustrated, or delighted. This granular level of understanding allows businesses to prioritize resources and optimize these critical touchpoints for maximum impact.
- Optimize Customer Experience: By pinpointing areas for improvement, the rider map provides a roadmap for enhancing the overall customer experience. This could involve streamlining processes, improving communication, or addressing specific pain points identified in the map.
- Align Teams and Foster Collaboration: The visual nature of the rider map facilitates a shared understanding of the customer journey across different departments. This fosters collaboration and alignment, ensuring a consistent and positive customer experience across all touchpoints.
- Drive Innovation and Growth: The map serves as a springboard for innovation, identifying opportunities to enhance customer interactions, develop new products and services, and ultimately drive business growth.
Crafting a Comprehensive Rider Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Developing an effective rider map requires a systematic approach, encompassing the following key steps:
- Define the Customer Journey: Clearly define the specific customer journey to be mapped, focusing on a specific product, service, or experience.
- Identify Customer Personas: Create detailed profiles of your target customers, encompassing their demographics, motivations, goals, and pain points.
- Map Touchpoints and Channels: Document every interaction a customer has with the brand, including website visits, phone calls, emails, social media engagement, and in-store experiences.
- Capture Customer Emotions and Feelings: Analyze the emotional landscape of the customer journey, noting the emotions evoked at each touchpoint, such as joy, frustration, confusion, or satisfaction.
- Identify Obstacles and Opportunities: Analyze the map to pinpoint potential roadblocks and areas for improvement, highlighting opportunities to enhance the customer experience.
- Iterate and Refine: Continuously refine the rider map based on feedback, data analysis, and evolving customer behavior.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What is the difference between a rider map and a customer journey map?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, a rider map typically focuses on a specific customer journey, such as the process of purchasing a product or resolving a customer service issue. A customer journey map, on the other hand, can encompass a broader range of customer interactions across different products or services.
2. How often should a rider map be updated?
Rider maps should be reviewed and updated regularly, ideally at least once a year, to reflect changes in customer behavior, market trends, and business strategies.
3. Can a rider map be used for internal processes?
Yes, rider maps can be used to map internal processes, such as employee onboarding or product development, to identify bottlenecks and optimize workflow.
4. What tools can be used to create rider maps?
There are numerous software tools available for creating rider maps, including Lucidchart, Miro, Mural, and Adobe XD.
5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating rider maps?
Common mistakes include failing to define the customer journey clearly, neglecting to capture customer emotions, focusing solely on positive experiences, and neglecting to iterate and refine the map based on feedback.
Tips for Effective Rider Map Development:
- Involve stakeholders from different departments: Ensure representation from sales, marketing, customer service, and product development to gain a holistic perspective.
- Use real customer data: Incorporate data from customer surveys, website analytics, and social media monitoring to ground the map in real-world insights.
- Keep it simple and visual: Use clear and concise language and compelling visuals to effectively communicate the customer journey.
- Focus on key touchpoints: Prioritize the most important interactions and areas for improvement, avoiding unnecessary detail.
- Regularly review and update: Continuously refine the map based on feedback, data analysis, and evolving customer behavior.
Conclusion: Embracing the Rider Map for Customer-Centric Success
The rider map is a powerful tool for navigating the complex landscape of customer journeys. By visualizing the customer experience, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of customer needs, identify critical touchpoints, optimize the customer experience, align teams, and drive innovation. By embracing this powerful tool, businesses can embark on a journey towards customer-centric success, building lasting relationships and driving sustainable growth.
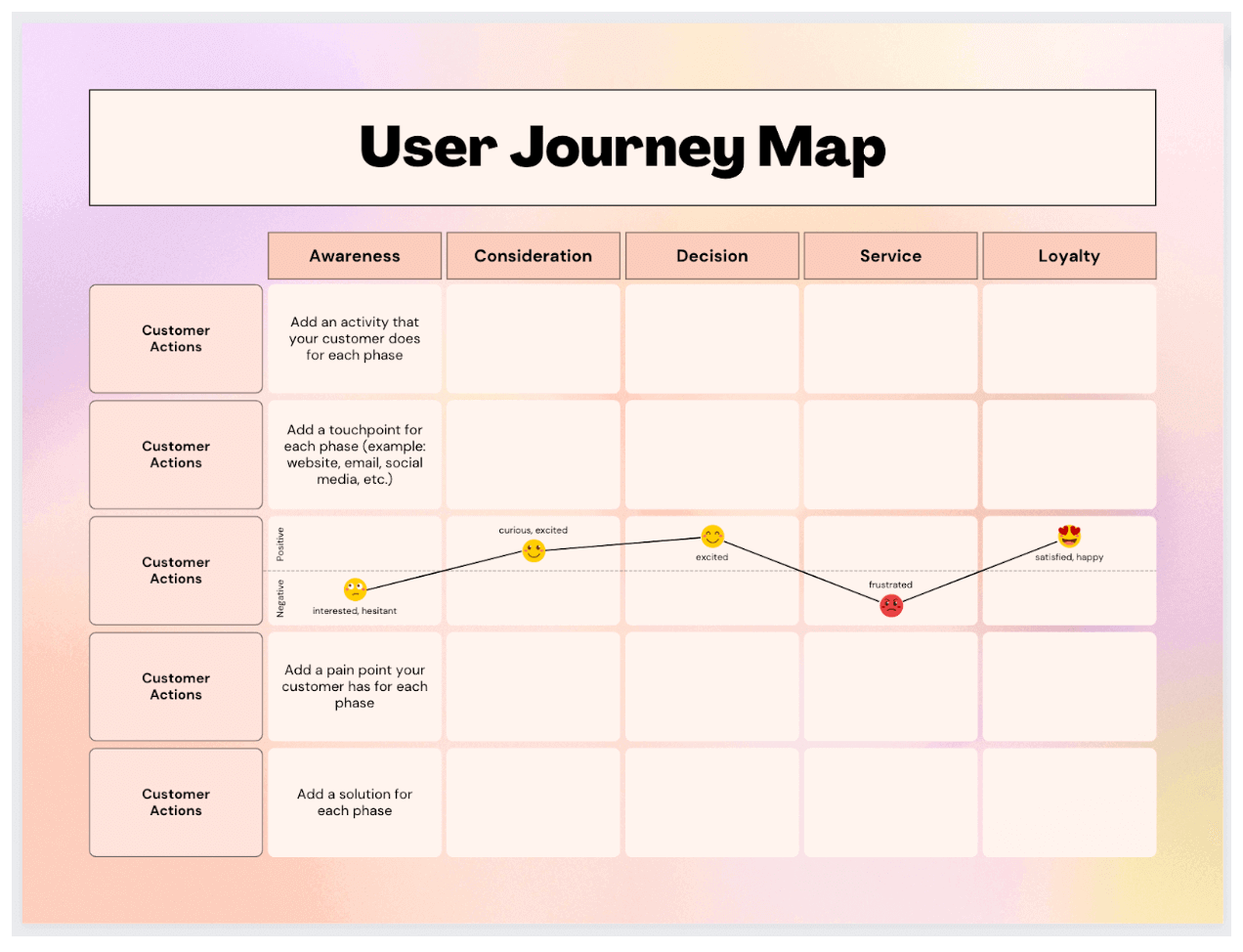
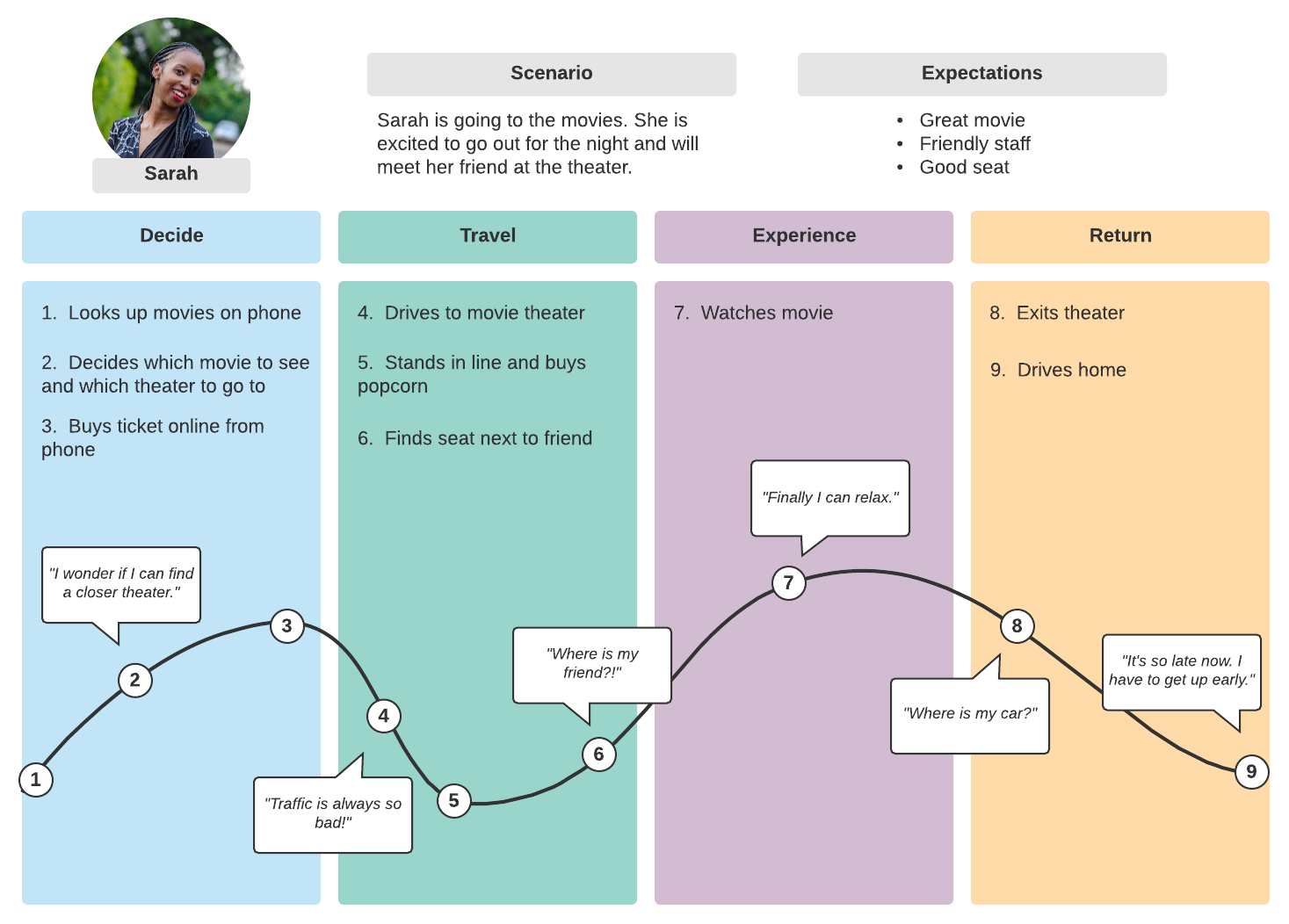
![Customer Journey Map (2023): How-to & Examples [+ Template]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Customer-Journey-1.png)
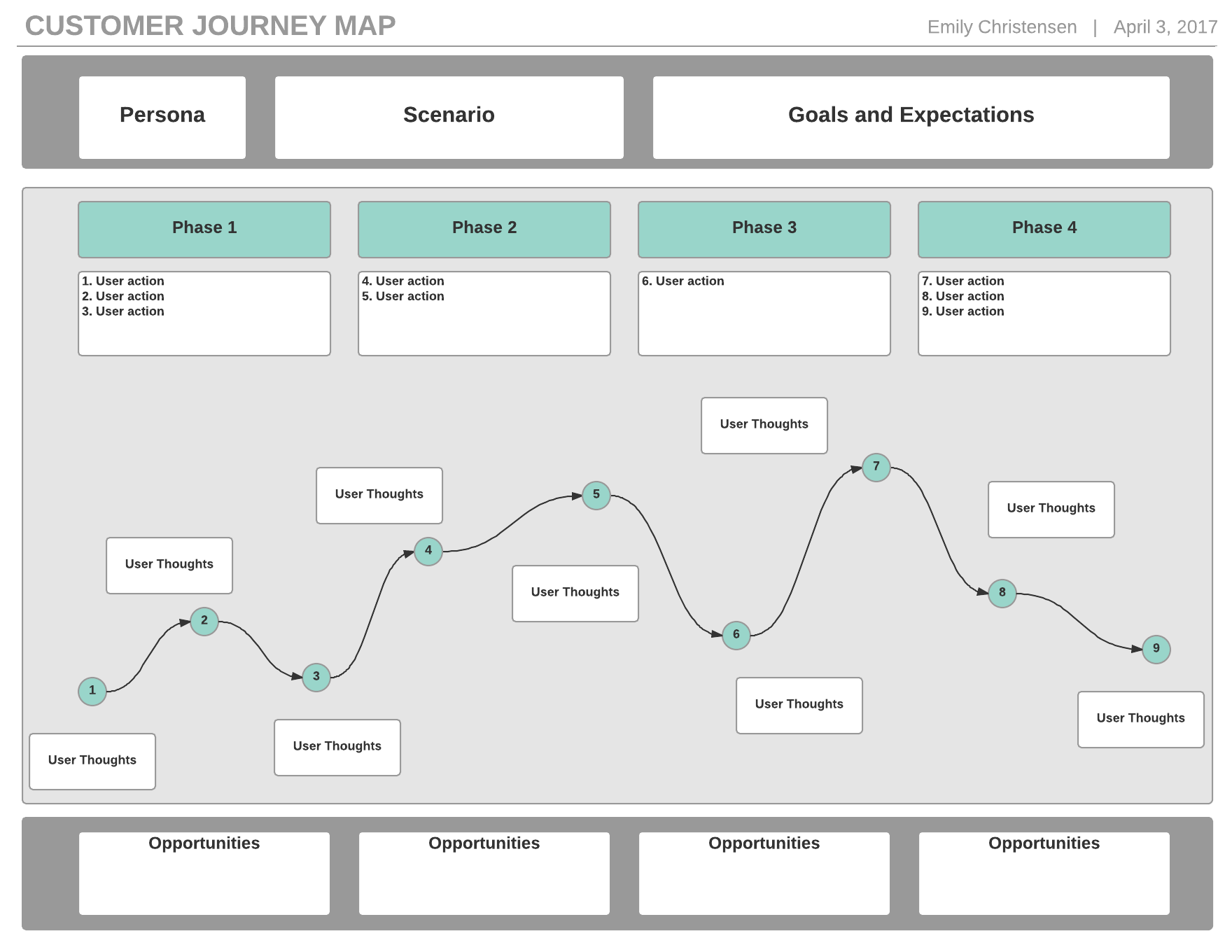


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Customer Journeys: A Comprehensive Guide to Rider Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!