Mapping the Flow: Understanding Lava Flows on the Big Island of Hawaii
Related Articles: Mapping the Flow: Understanding Lava Flows on the Big Island of Hawaii
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Flow: Understanding Lava Flows on the Big Island of Hawaii. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Flow: Understanding Lava Flows on the Big Island of Hawaii

The Big Island of Hawaii, the youngest and largest island in the Hawaiian archipelago, is a dynamic landscape sculpted by volcanic activity. Its iconic shield volcanoes, Kilauea and Mauna Loa, are responsible for the constant reshaping of the island’s surface, with lava flows playing a crucial role in this ongoing process.
Maps of lava flows on the Big Island serve as invaluable tools for understanding the island’s geological history, predicting future eruptions, and managing the risks associated with volcanic activity. These maps provide a visual representation of the distribution and extent of past lava flows, offering insights into the behavior of the volcanoes and the potential impact of future eruptions on infrastructure, communities, and the environment.
Understanding Lava Flow Maps
Lava flow maps are typically created using a combination of field observations, aerial imagery, satellite data, and historical records. They depict the boundaries of past lava flows, often categorized by the type of lava and the eruption that produced it.
Key Features of Lava Flow Maps:
- Lava Flow Units: Maps distinguish different lava flows based on their age, composition, and source. Each unit represents a distinct eruption event, providing a timeline of volcanic activity.
- Flow Direction: Arrows or lines indicate the direction of lava flow during an eruption, revealing the path of the molten rock.
- Flow Length and Width: The maps illustrate the extent of each lava flow, providing information about the volume of erupted material and the potential impact on the surrounding landscape.
- Flow Features: Maps may include features like lava tubes, fissures, and craters, which contribute to understanding the dynamics of lava flow.
- Elevation Contours: Elevation contours can be incorporated to depict the topography and potential pathways of future lava flows.
Importance of Lava Flow Maps:
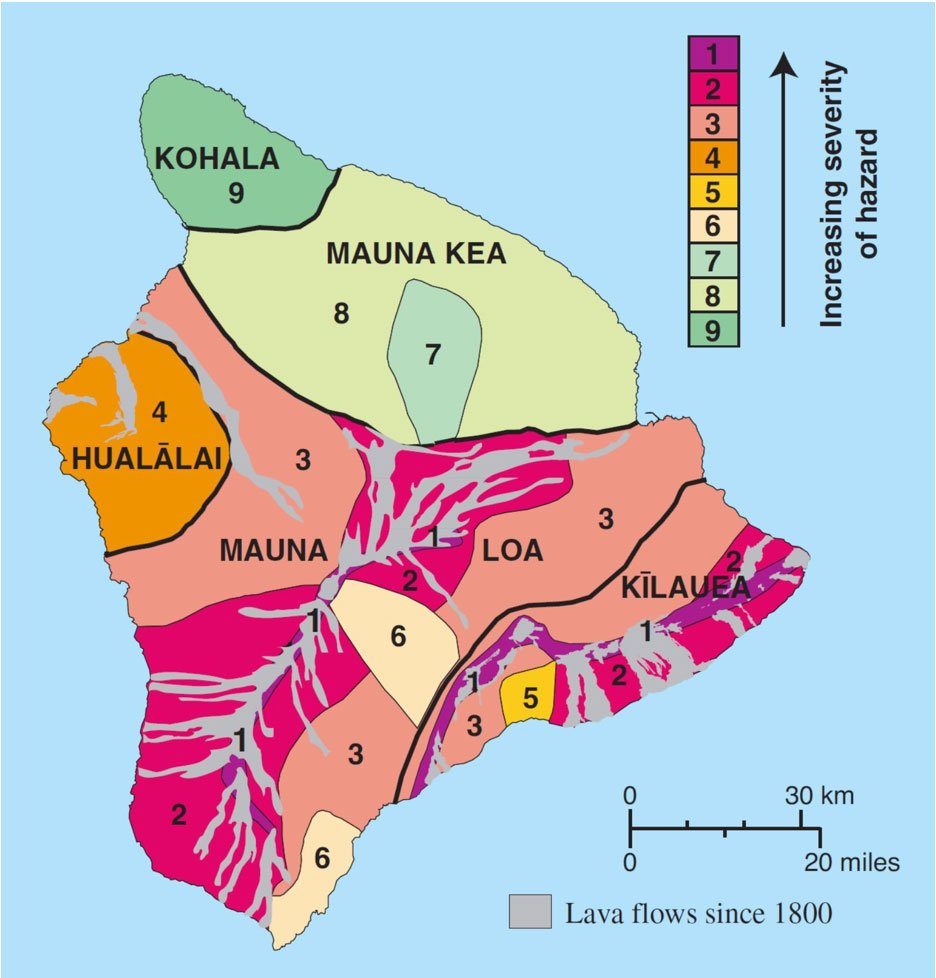
- Hazard Assessment: Maps provide critical information for hazard assessment and risk management. They help identify areas most vulnerable to future lava flows, informing land-use planning, evacuation strategies, and infrastructure development.
- Historical Insights: Lava flow maps serve as a record of past volcanic activity, revealing the evolution of the island’s landscape and the frequency and intensity of eruptions.
- Scientific Research: Maps are essential for scientists studying volcanism, providing data on lava flow dynamics, eruption characteristics, and the interaction of lava with the environment.
- Environmental Monitoring: Lava flow maps contribute to environmental monitoring by highlighting areas affected by volcanic activity and aiding in the assessment of ecological impacts.
- Community Awareness: Maps can raise public awareness about volcanic hazards, promoting preparedness and informing decision-making related to safety and risk mitigation.
Examples of Lava Flow Maps on the Big Island:
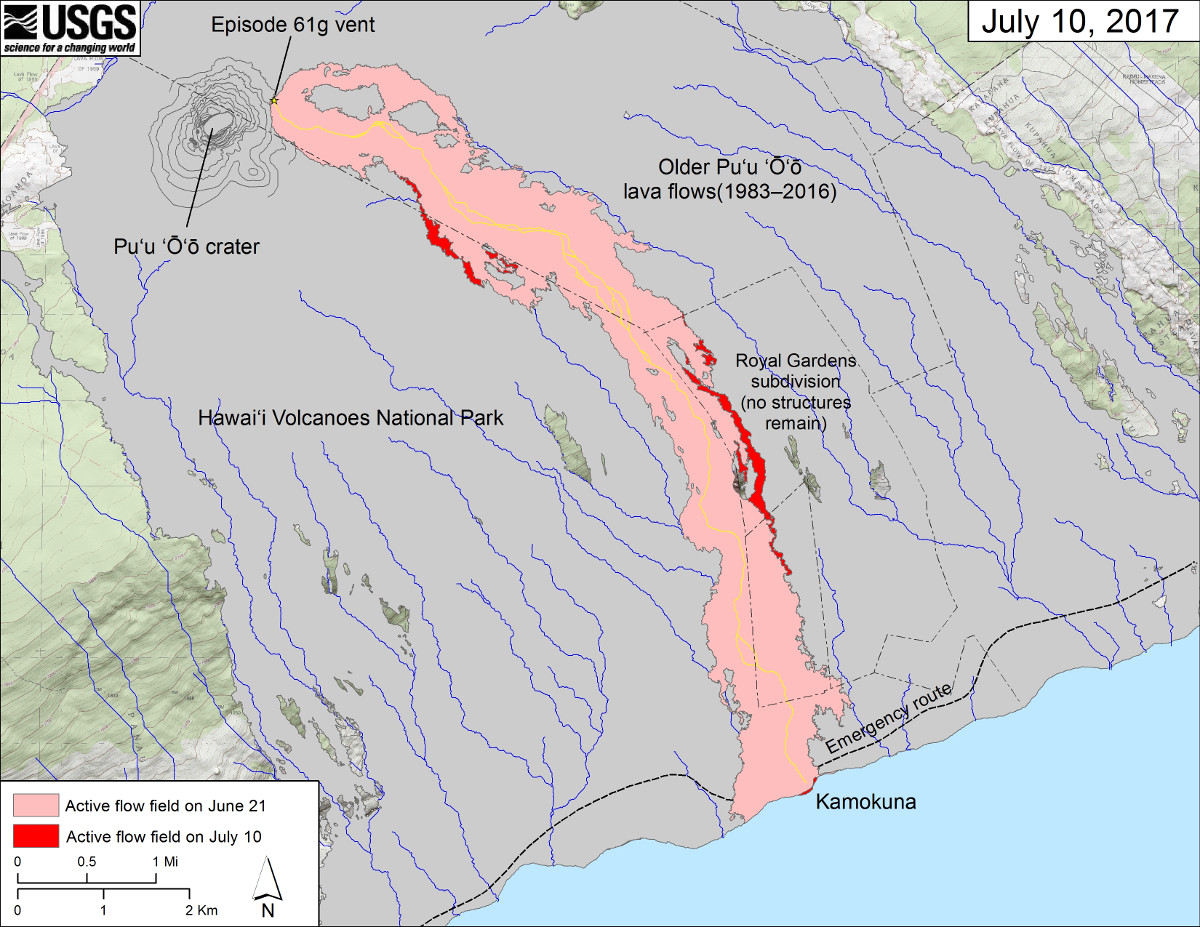
- USGS Lava Flow Maps: The United States Geological Survey (USGS) maintains comprehensive lava flow maps for Kilauea and Mauna Loa, providing updated information on recent eruptions and historical flows.
- Hawaii Volcanoes National Park Maps: The park’s maps highlight areas of volcanic activity, including active lava flows, craters, and volcanic vents, aiding visitor safety and education.
- University Research Maps: Universities and research institutions often create detailed maps focused on specific aspects of lava flow behavior, contributing to scientific understanding.
FAQs about Lava Flow Maps:
Q: How are lava flow maps updated?
A: Lava flow maps are constantly updated through field observations, aerial and satellite imagery, and analysis of volcanic activity. The USGS and other organizations maintain active monitoring programs to track eruptions and adjust maps accordingly.
Q: Can lava flow maps predict future eruptions?
A: While lava flow maps cannot predict the exact timing or location of future eruptions, they provide valuable information about potential eruption zones and the likely paths of lava flows. This information helps with preparedness and risk mitigation.
Q: Are lava flow maps accurate?
A: Lava flow maps are created using the best available data and scientific methods, but they are not perfect. The complexity of volcanic activity and the dynamic nature of lava flows can lead to some uncertainty. However, maps provide a valuable representation of the potential hazards associated with eruptions.
Q: How can I access lava flow maps for the Big Island?
A: Lava flow maps are readily available online through the USGS website, the Hawaii Volcanoes National Park website, and various university research portals.
Tips for Using Lava Flow Maps:
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare maps from different organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of lava flow history and potential hazards.
- Understand Map Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and legends used on lava flow maps to interpret the information correctly.
- Consider Elevation: Factor in elevation contours to assess the potential pathways of lava flows and areas at risk.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest updates from the USGS and other relevant organizations regarding volcanic activity and changes in lava flow maps.
Conclusion:
Lava flow maps are indispensable tools for understanding the dynamic landscape of the Big Island of Hawaii. By providing a visual representation of past volcanic activity, they offer crucial insights into the behavior of volcanoes, aiding in hazard assessment, risk management, and scientific research. These maps are essential for safeguarding communities, protecting infrastructure, and managing the impacts of volcanic eruptions on the environment. As the Big Island continues to be shaped by volcanic forces, lava flow maps will remain vital resources for understanding and adapting to the island’s unique and ever-evolving landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Flow: Understanding Lava Flows on the Big Island of Hawaii. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!