Equal Area Maps: Preserving Proportions and Unveiling Global Truths
Related Articles: Equal Area Maps: Preserving Proportions and Unveiling Global Truths
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Equal Area Maps: Preserving Proportions and Unveiling Global Truths. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Equal Area Maps: Preserving Proportions and Unveiling Global Truths
The world we inhabit is a sphere, yet the maps we use to represent it are flat. This fundamental difference presents a significant challenge: how to accurately depict a three-dimensional surface on a two-dimensional plane without distorting its features. Equal area maps, also known as equivalent maps, address this challenge by prioritizing the preservation of area. These maps ensure that the relative sizes of geographical features are maintained, providing a more truthful representation of the Earth’s surface compared to other map projections.
Understanding the Distortion Dilemma
All map projections, by their very nature, introduce distortion. This is because the Earth’s curved surface cannot be perfectly flattened without stretching or shrinking certain areas. Different projections prioritize different aspects, such as preserving shapes (conformal projections), distances (equidistant projections), or directions (azimuthal projections). Equal area projections, however, prioritize the preservation of area.
The Significance of Area Preservation
Preserving area is crucial for various applications, particularly when analyzing spatial data. Equal area maps are essential for:
- Accurate Representation of Global Phenomena: When studying population density, resource distribution, or environmental impacts, it is critical to ensure that areas are represented proportionally. Equal area maps prevent misinterpretations that can arise from distorted projections.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing the sizes of different countries or regions requires an accurate representation of their relative areas. Equal area maps provide a reliable basis for such comparisons, avoiding misleading conclusions drawn from distorted maps.
- Cartographic Accuracy: Equal area maps are vital for tasks like calculating land area, estimating resource availability, and planning infrastructure projects. By ensuring that areas are accurately represented, these maps provide the foundation for informed decision-making.
- Visual Communication: While equal area maps may not always be visually appealing, they offer a clear and accurate representation of the world, promoting a better understanding of global relationships and spatial patterns.
Common Types of Equal Area Projections
Several equal area projections exist, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most commonly used include:
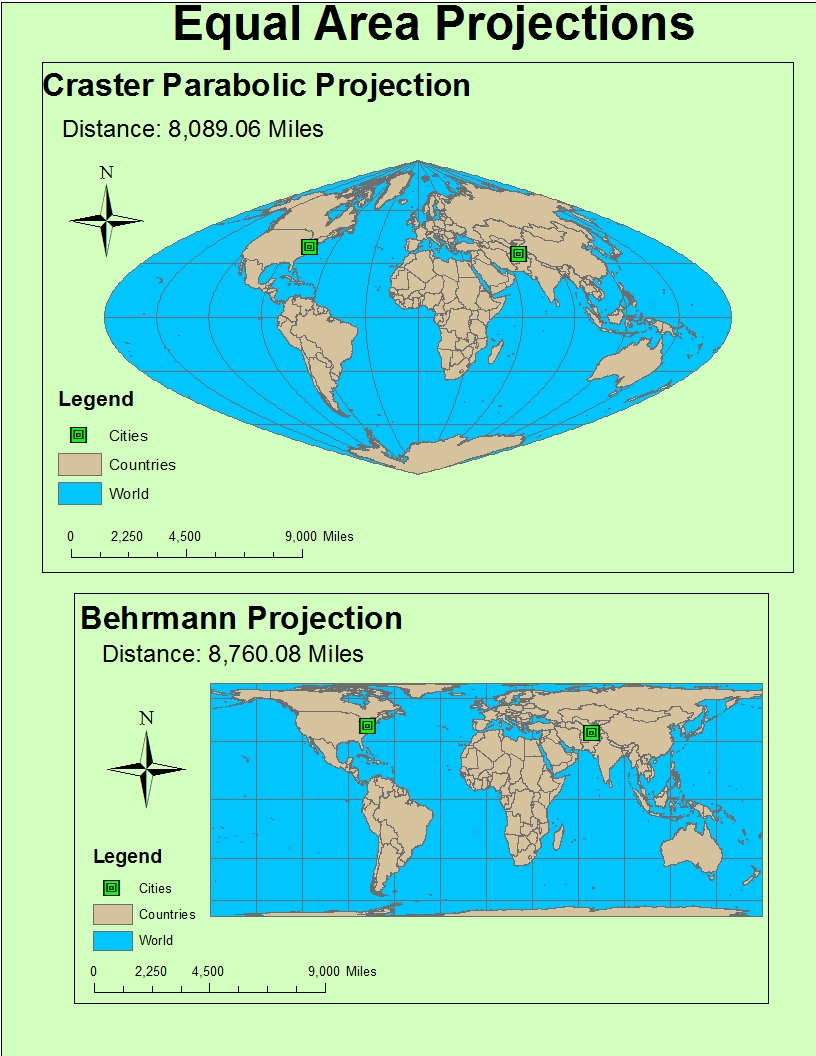
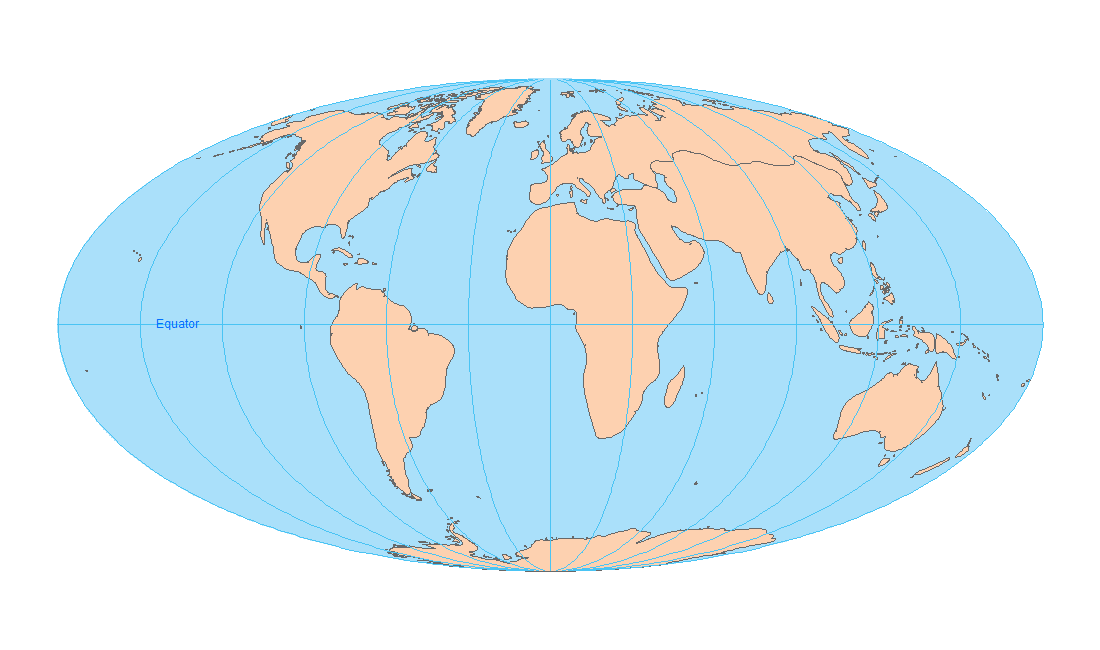
- Mollweide Projection: This projection is known for its distinctive oval shape and its ability to preserve area while minimizing distortion in the mid-latitudes. It is often used for global maps and atlases.
- Lambert Azimuthal Equal Area Projection: This projection is centered on a specific point, with all points equidistant from the center having the same area. It is commonly used for mapping specific regions or continents.
- Albers Equal Area Conic Projection: This projection is designed for mapping regions that extend longitudinally, such as the United States. It uses a conical shape to preserve area while minimizing distortion.
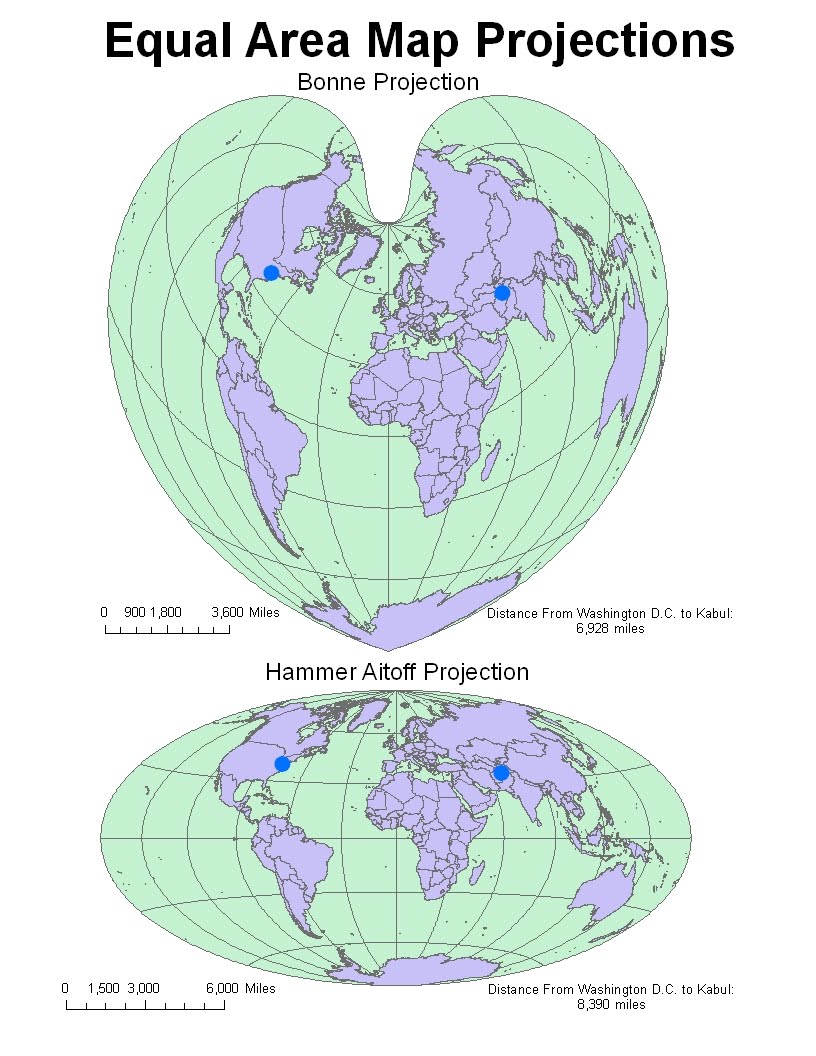
- Bonne Projection: Similar to the Albers projection, the Bonne projection uses a conical shape to preserve area. However, it features curved parallels and straight meridians, making it visually distinct.
The Trade-offs of Equal Area Projections
While equal area projections excel at preserving area, they come with some inherent limitations:
- Distortion of Shapes: To maintain accurate area representation, equal area projections often distort shapes, particularly towards the poles. This can make countries or continents appear elongated or compressed.
- Complex Visual Representation: Some equal area projections, such as the Mollweide, can have an unconventional visual appearance, potentially leading to confusion or misinterpretation for viewers accustomed to more familiar projections.
FAQs about Equal Area Maps
1. What is the difference between equal area maps and other map projections?
Equal area maps prioritize the preservation of area, ensuring that the relative sizes of geographical features are maintained. Other projections may prioritize different aspects, such as shape, distance, or direction, leading to distortions in area.
2. Are equal area maps always the best choice?
While equal area maps are essential for tasks involving area measurement and comparison, they may not be the best choice for every application. If preserving shape or direction is paramount, other projections may be more suitable.
3. Can equal area maps be used for navigation?
Equal area maps are not generally recommended for navigation as they can distort distances and directions, making it difficult to accurately determine routes.
4. Why are there so many different types of equal area projections?
Different equal area projections are designed to minimize distortion in specific areas or for particular applications. The choice of projection depends on the specific needs of the user.
5. How can I tell if a map is an equal area projection?
Look for a label or description indicating that the projection is equal area or equivalent. Additionally, the map should preserve the relative sizes of geographical features, with areas represented proportionally.
Tips for Using Equal Area Maps
- Consider the purpose of the map: Determine whether preserving area is the primary concern. If so, an equal area projection is likely the best choice.
- Choose the appropriate projection: Different equal area projections have different strengths and weaknesses. Select a projection that minimizes distortion in the region of interest.
- Be aware of potential distortions: While equal area maps preserve area, they may distort shapes. Understand the limitations of the chosen projection.
- Use multiple maps: Combining different projections can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the data. For example, an equal area projection for area analysis and a conformal projection for shape analysis.
Conclusion
Equal area maps play a vital role in understanding the world around us. By preserving area, they provide a more accurate representation of global phenomena, facilitating informed decision-making in various fields. While they may not be the perfect solution for every mapping need, their ability to accurately represent relative sizes makes them indispensable tools for cartographers, researchers, and anyone seeking a truthful depiction of the Earth’s surface. Recognizing the importance of area preservation and utilizing equal area maps effectively can lead to a deeper understanding of our planet and its complexities.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Equal Area Maps: Preserving Proportions and Unveiling Global Truths. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!