China’s Position on the World Map: A Giant in the East
Related Articles: China’s Position on the World Map: A Giant in the East
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to China’s Position on the World Map: A Giant in the East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
China’s Position on the World Map: A Giant in the East
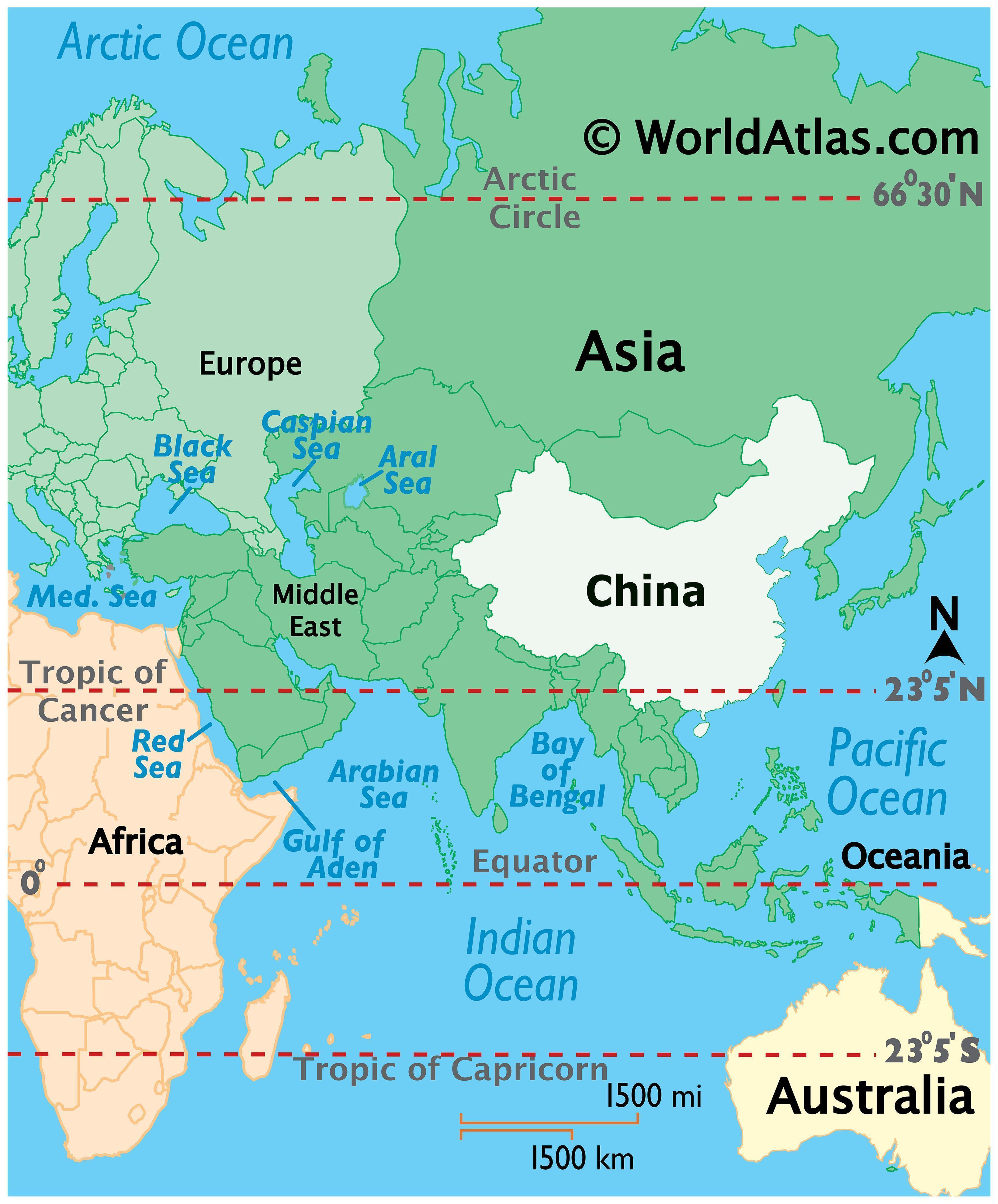
China, the world’s most populous nation, occupies a prominent position in East Asia. Situated on the eastern edge of the Eurasian continent, it stretches across a vast expanse of land, encompassing diverse landscapes and climates. Its geographical location has significantly shaped its history, culture, and global influence.
A Land of Contrasts:
China’s geographical diversity is striking. From the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas in the west to the fertile plains of the Yangtze River Delta in the east, the country exhibits a wide range of physical features. It boasts towering mountains, vast deserts, fertile plains, and extensive coastlines. This geographical variation has led to the development of distinct regional cultures and economies.
Strategic Location:
China’s location at the crossroads of East Asia grants it immense strategic importance. It shares borders with 14 countries, including Russia, India, Vietnam, and North Korea. This proximity has historically fostered both cooperation and conflict, making China a key player in regional politics and security.
Maritime Influence:
With a coastline stretching over 14,500 kilometers, China boasts access to the Pacific Ocean and the South China Sea. These waterways have served as vital trade routes for centuries, connecting China to the rest of the world. China’s maritime influence has grown significantly in recent years, with its expanding naval presence and growing economic interests in the region.
Global Economic Powerhouse:
China’s geographical location has played a crucial role in its economic rise. Its vast landmass provides abundant natural resources, while its proximity to major markets in Asia and beyond has facilitated trade and investment. China’s economic success has propelled it to the position of the world’s second-largest economy, with its manufacturing prowess and technological advancements impacting global markets.
Cultural Significance:
China’s rich history and cultural heritage are deeply intertwined with its geographical location. Ancient civilizations flourished along the Yellow River, laying the foundation for Chinese culture and traditions. The country’s vast territory has allowed for the development of diverse regional cultures, each with its unique customs, languages, and artistic expressions.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its geographical advantages, China faces several challenges. Its vast population and rapid economic growth put immense pressure on its natural resources and environment. The country’s mountainous terrain and complex geological conditions pose challenges to infrastructure development and resource management. However, China’s geographical location also presents opportunities for regional cooperation and global engagement.
FAQs on China’s Position:
Q: What are the major geographical features of China?
A: China’s geography is characterized by diverse landscapes, including towering mountains (the Himalayas, the Kunlun Mountains), vast deserts (the Taklamakan Desert, the Gobi Desert), fertile plains (the North China Plain, the Yangtze River Delta), and extensive coastlines.
Q: What are the key neighboring countries of China?
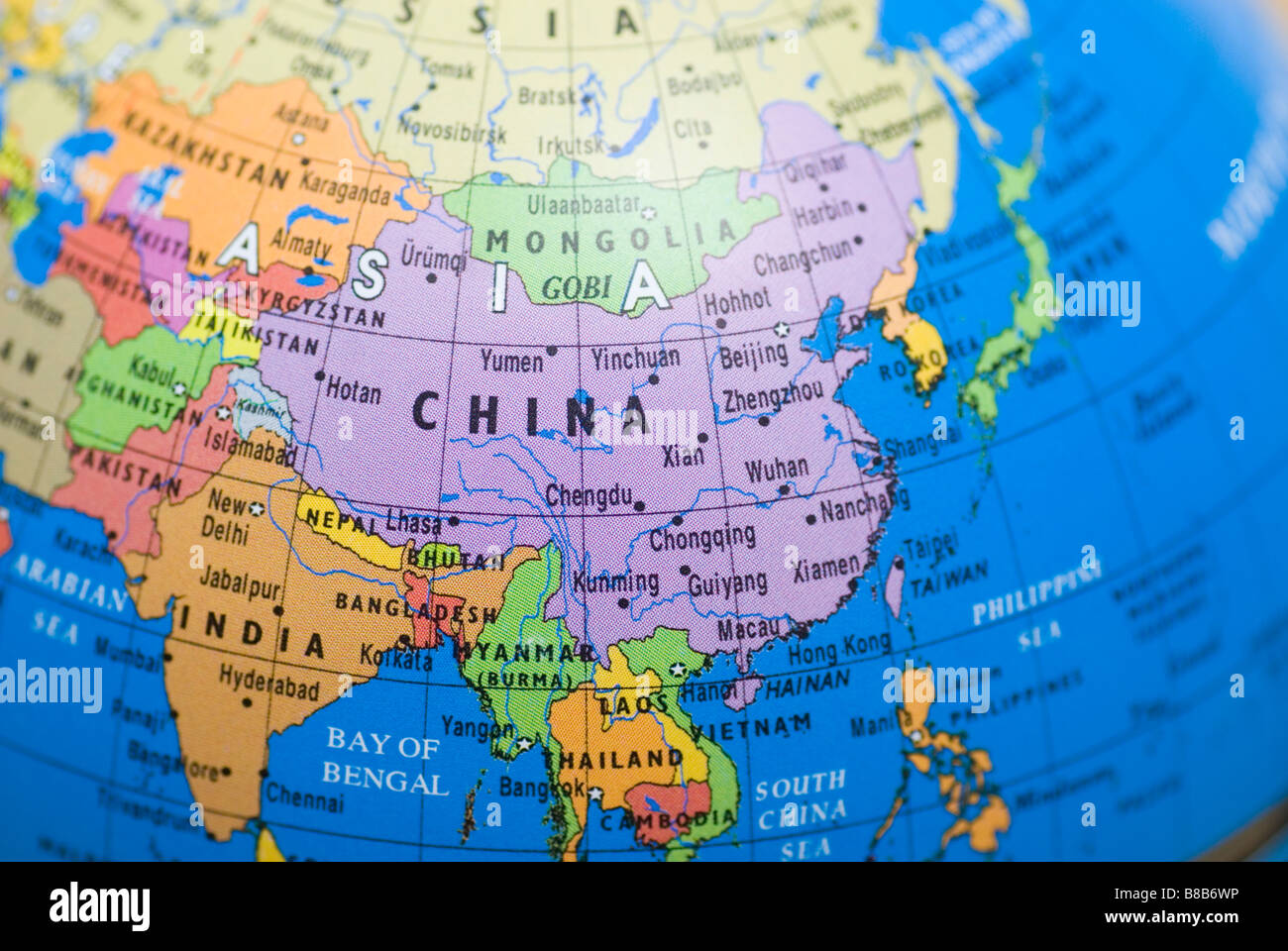
A: China shares borders with 14 countries: Russia, Mongolia, North Korea, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, India, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan.
Q: How does China’s location affect its economic development?
A: China’s geographical location has been a major factor in its economic rise. Its vast landmass provides abundant natural resources, while its proximity to major markets in Asia and beyond has facilitated trade and investment.
Q: What are the challenges faced by China due to its geographical location?
A: China’s geographical location poses challenges such as environmental pressures, resource scarcity, infrastructure development, and natural disasters like earthquakes and floods.
Q: How is China’s geographical location shaping its global influence?
A: China’s strategic location, its growing economic power, and its expanding maritime presence have all contributed to its increasing global influence.
Tips for Understanding China’s Geography:
- Use a world map: Visualizing China’s position on a world map is essential for understanding its geographical context.
- Explore regional maps: Studying regional maps of East Asia can help you understand China’s relationships with neighboring countries and its role in the region.
- Research key geographical features: Learn about China’s major mountains, rivers, deserts, and coastal regions to grasp its geographical diversity.
- Connect geography to history and culture: Understand how China’s geographical location has influenced its history, culture, and development.
Conclusion:
China’s position on the world map is a testament to its geographical and geopolitical significance. Its vast landmass, diverse landscapes, strategic location, and growing economic power make it a key player in the global arena. Understanding China’s geography is crucial for comprehending its historical trajectory, its current challenges, and its future prospects. As China continues to rise on the world stage, its geographical location will continue to shape its destiny.


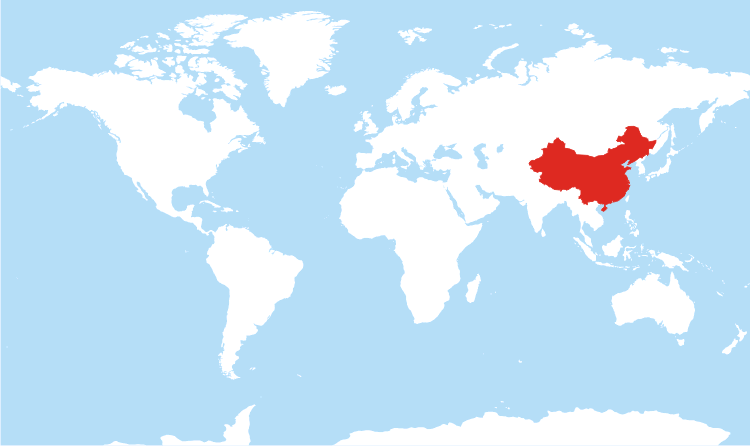
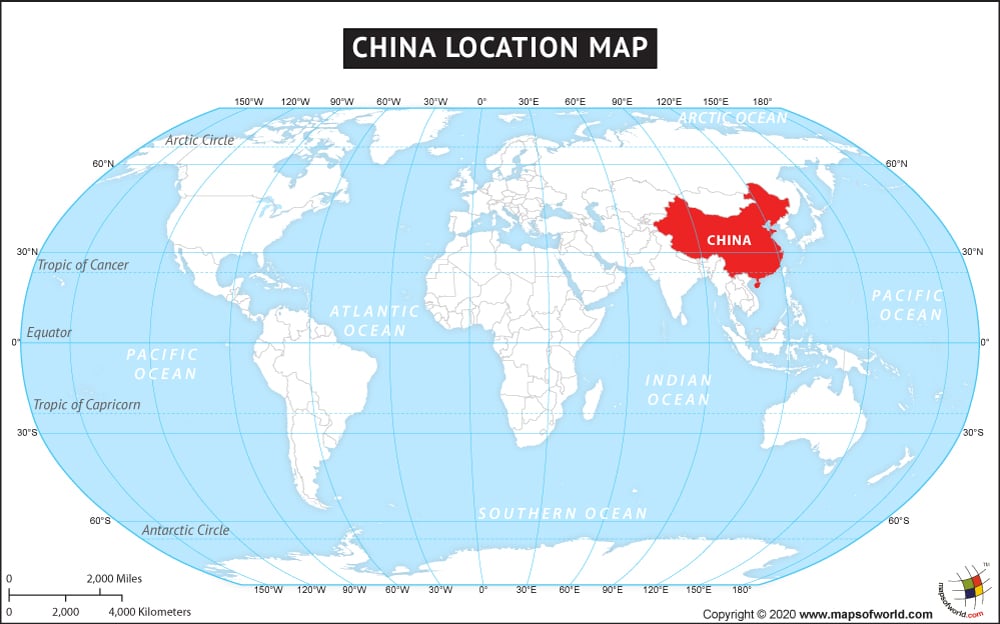
_(W3).svg/1280px-China_in_the_world_(undisputed)_(W3).svg.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into China’s Position on the World Map: A Giant in the East. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!