Charting the Course: Understanding National Roadmaps and Their Significance
Related Articles: Charting the Course: Understanding National Roadmaps and Their Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Course: Understanding National Roadmaps and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Course: Understanding National Roadmaps and Their Significance

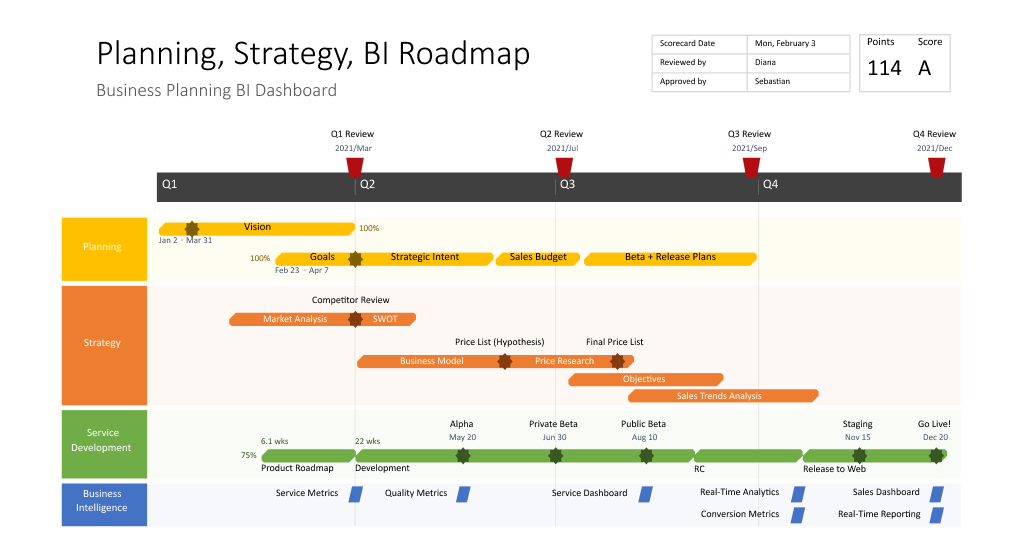
A national roadmap is a strategic document that outlines a nation’s vision, goals, and action plan for achieving a specific objective or set of objectives. It serves as a comprehensive guide, providing a clear direction and framework for coordinated efforts across various sectors and stakeholders. National roadmaps are essential tools for navigating complex challenges and achieving ambitious aspirations, be it in the realm of economic development, technological advancement, or social progress.
The Core Components of a National Roadmap
A well-structured national roadmap typically encompasses the following key elements:
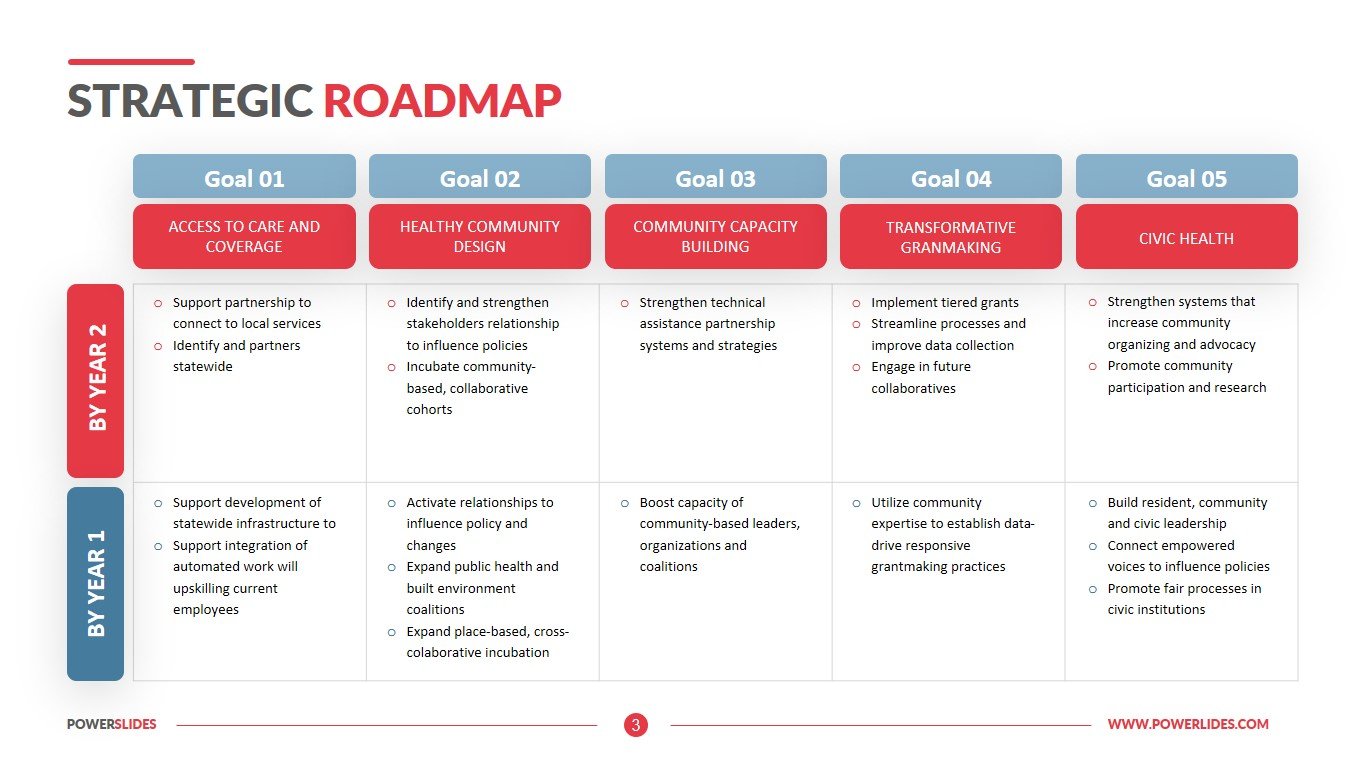
- Vision and Objectives: A clear articulation of the desired future state and the specific goals to be achieved. These objectives should be measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Contextual Analysis: A thorough assessment of the current situation, including strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis), as well as an understanding of the relevant global and regional trends.
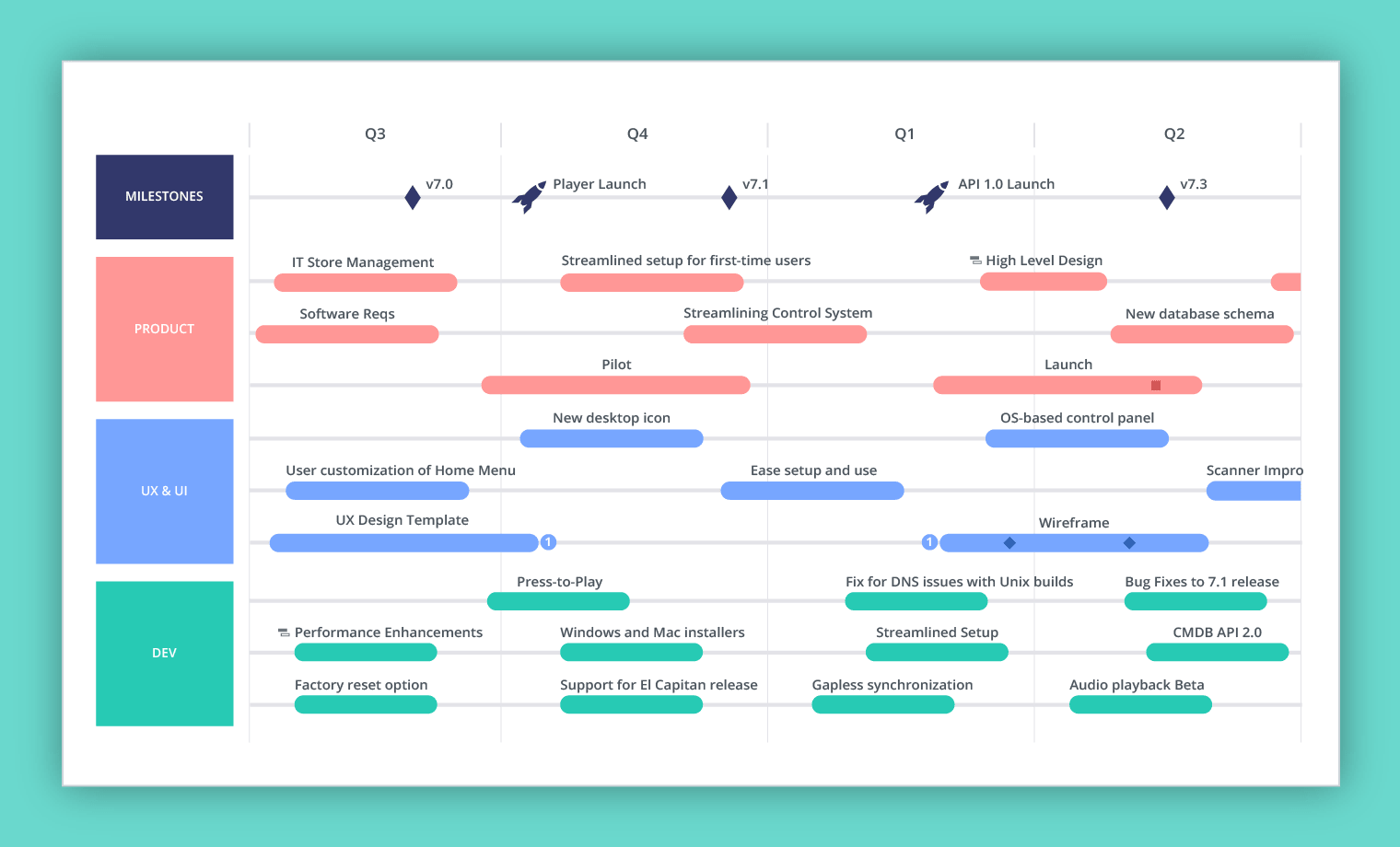
- Strategic Actions: A detailed plan outlining the specific actions, initiatives, and programs required to achieve the stated objectives. This includes timelines, responsible entities, and resource allocation.
- Performance Indicators and Monitoring: Measurable indicators and a robust monitoring system to track progress towards achieving the roadmap’s goals. This allows for regular evaluation, adjustments, and course correction as needed.
- Stakeholder Engagement: A collaborative process involving all relevant stakeholders, including government agencies, private sector entities, civil society organizations, and individuals. This ensures buy-in, ownership, and effective implementation.
The Importance of National Roadmaps
National roadmaps play a crucial role in driving national development and progress. They offer numerous benefits, including:
- Clarity of Direction: Roadmaps provide a clear and shared vision for the future, aligning efforts and resources towards a common goal. This eliminates ambiguity and fosters a sense of purpose among stakeholders.
- Strategic Alignment: They ensure that different sectors and initiatives are aligned with the overall national strategy, maximizing impact and minimizing duplication of efforts.
- Resource Optimization: Roadmaps facilitate efficient allocation of resources by prioritizing key activities and ensuring that investments are targeted towards achieving desired outcomes.
- Accountability and Transparency: They establish clear performance indicators and monitoring mechanisms, enabling accountability for progress and promoting transparency in decision-making.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Roadmaps foster collaboration among diverse stakeholders, promoting dialogue, knowledge sharing, and joint action towards achieving common goals.
- Increased Investment and Innovation: A well-defined roadmap can attract domestic and foreign investment, stimulate innovation, and create a conducive environment for economic growth.
- Improved Public Perception: A transparent and well-communicated roadmap can build trust and confidence among the public, fostering a sense of shared ownership and support for national goals.
Examples of National Roadmaps
National roadmaps are used across a wide range of sectors and areas of focus. Some notable examples include:
- Economic Development: Roadmaps for economic diversification, industrial development, or promoting entrepreneurship.
- Technological Advancement: Roadmaps for digital transformation, artificial intelligence adoption, or renewable energy transition.
- Social Progress: Roadmaps for improving education, healthcare, or social inclusion.
- Environmental Sustainability: Roadmaps for climate change mitigation, biodiversity conservation, or sustainable resource management.
- National Security: Roadmaps for cybersecurity, defense modernization, or disaster preparedness.
FAQs about National Roadmaps
1. What is the difference between a national roadmap and a national strategy?
While both terms are often used interchangeably, a national strategy is a broader, overarching document that defines the overall direction and goals for a nation. A national roadmap, on the other hand, is a more specific and actionable plan that outlines the steps and initiatives to achieve the objectives set out in the strategy.
2. How are national roadmaps developed and implemented?
The development and implementation of a national roadmap typically involve a multi-stage process:
- Needs Assessment: Identifying the key challenges and opportunities that need to be addressed.
- Vision and Goal Setting: Defining the desired future state and setting specific, measurable goals.
- Strategic Planning: Developing a detailed plan outlining the actions, initiatives, and programs required to achieve the goals.
- Resource Allocation: Securing the necessary financial, human, and technical resources for implementation.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Executing the plan, tracking progress, and making adjustments as needed.
- Evaluation and Review: Regularly assessing the effectiveness of the roadmap and making necessary revisions to ensure alignment with evolving needs and circumstances.
3. Who are the key stakeholders involved in national roadmap development and implementation?
The key stakeholders in national roadmap development and implementation typically include:
- Government Agencies: Ministries, departments, and regulatory bodies responsible for relevant sectors.
- Private Sector Entities: Businesses, industries, and associations representing the private sector.
- Civil Society Organizations: Non-governmental organizations, community groups, and advocacy groups.
- Academic Institutions: Universities, research centers, and think tanks.
- International Organizations: Multilateral institutions, development agencies, and foreign governments.
4. What are the challenges associated with developing and implementing national roadmaps?
Developing and implementing national roadmaps can be challenging, with obstacles such as:
- Lack of Political Will: Insufficient commitment from leadership to prioritize the roadmap’s objectives and provide necessary support.
- Limited Resources: Insufficient financial, human, and technical resources to implement the roadmap’s initiatives.
- Coordination and Collaboration: Difficulties in coordinating efforts among different stakeholders and agencies.
- Lack of Capacity: Insufficient skills and expertise within government agencies and implementing organizations.
- Public Awareness and Engagement: Difficulties in raising public awareness and securing buy-in for the roadmap’s objectives.
Tips for Effective National Roadmap Development and Implementation
- Involve all stakeholders: Engage all relevant stakeholders in the development and implementation of the roadmap to ensure buy-in and ownership.
- Focus on realistic and achievable goals: Set realistic and achievable goals that are aligned with the nation’s capabilities and resources.
- Develop a robust monitoring and evaluation system: Establish clear performance indicators and a robust monitoring system to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
- Communicate effectively: Clearly communicate the roadmap’s vision, goals, and progress to all stakeholders, including the public.
- Be adaptable and responsive: Be prepared to adapt the roadmap to changing circumstances and evolving priorities.
- Seek external expertise and support: Leverage expertise from international organizations, development partners, and other countries with experience in similar areas.
Conclusion
National roadmaps are essential tools for navigating complex challenges and achieving ambitious aspirations. They provide a clear direction, align efforts, optimize resources, and promote accountability. By effectively developing and implementing national roadmaps, nations can chart a course towards a brighter future, achieving sustainable development, economic prosperity, and social progress.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Course: Understanding National Roadmaps and Their Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!