A Journey Through Italy’s Political Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance
Related Articles: A Journey Through Italy’s Political Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Italy’s Political Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Italy’s Political Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance
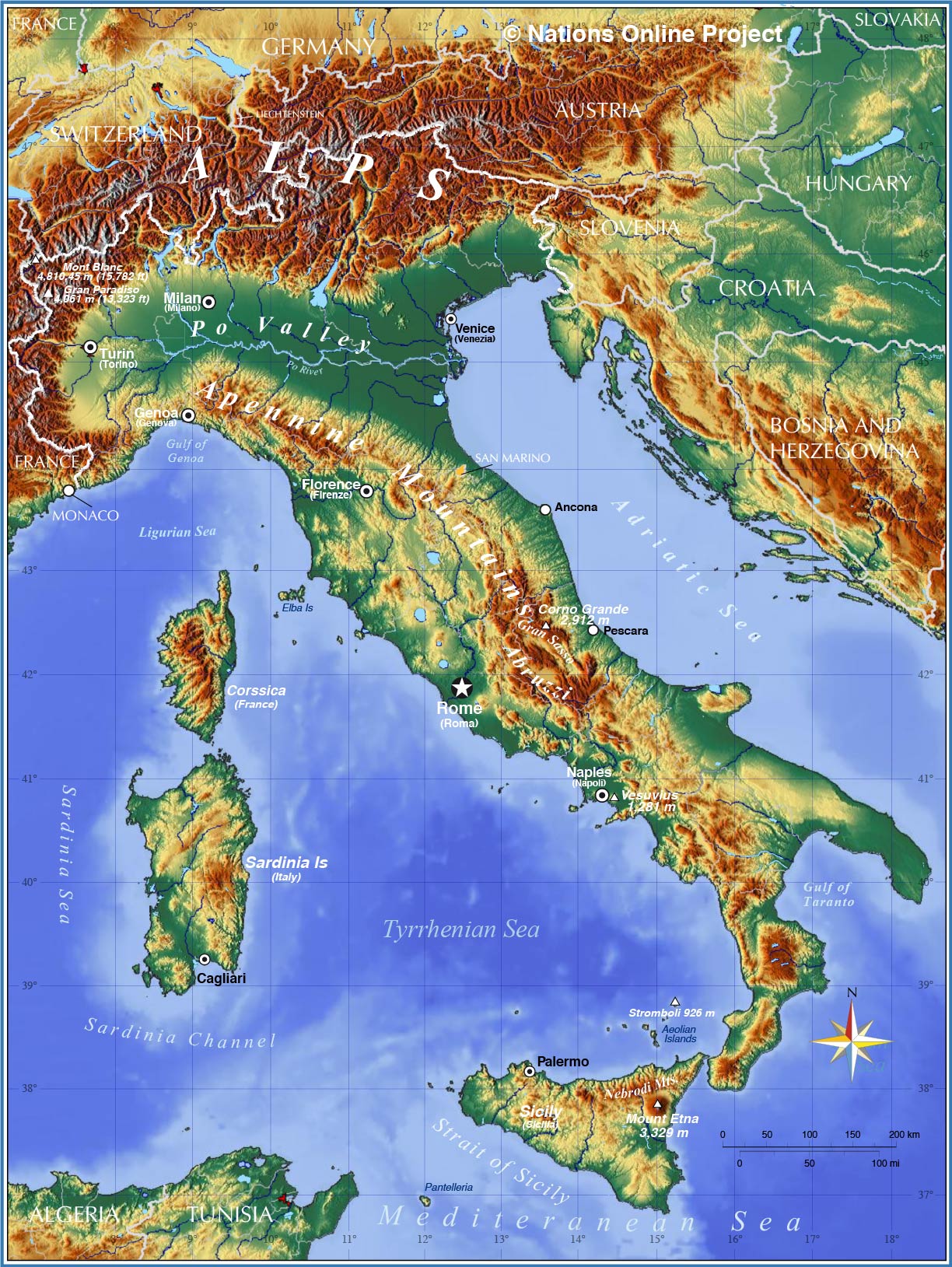
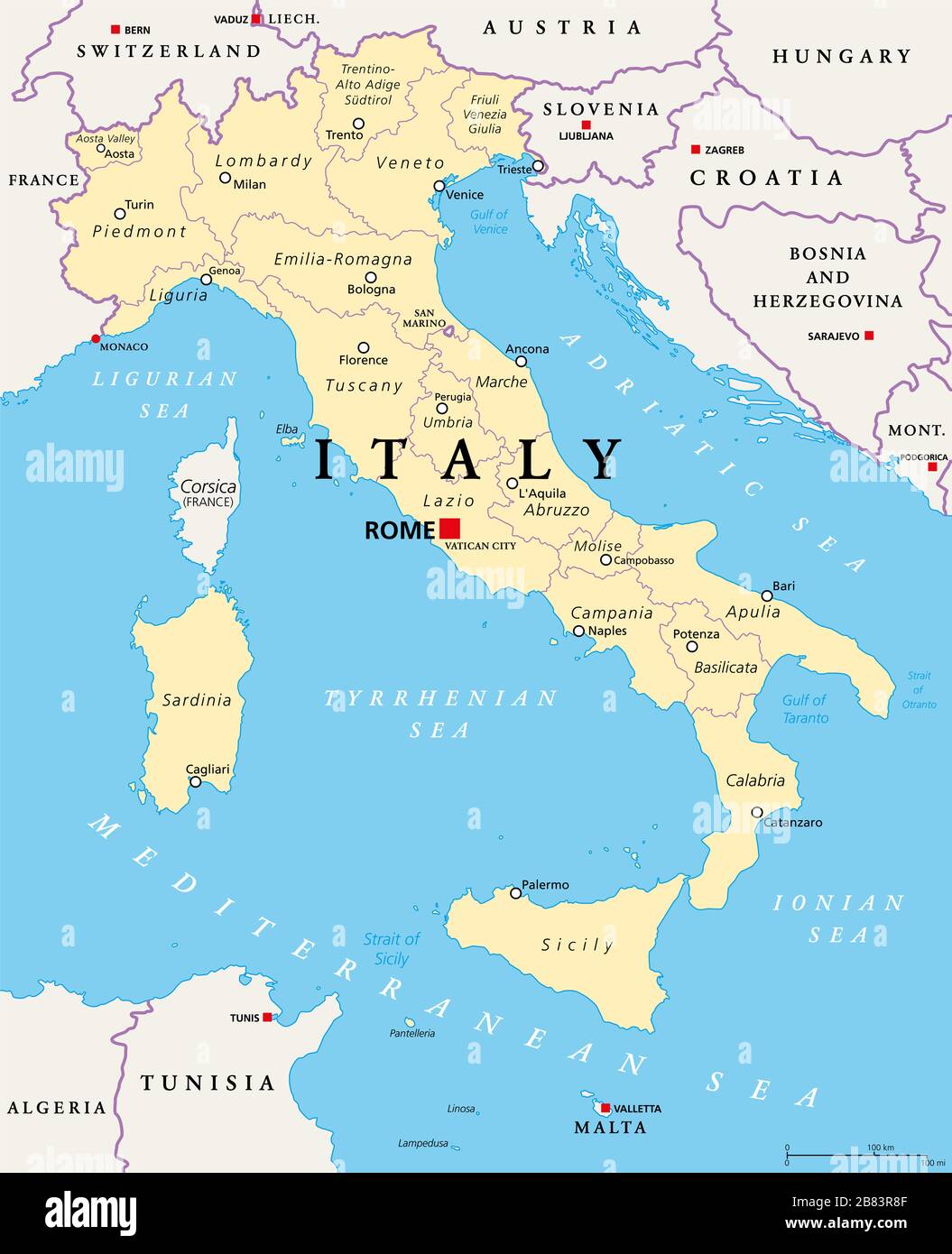
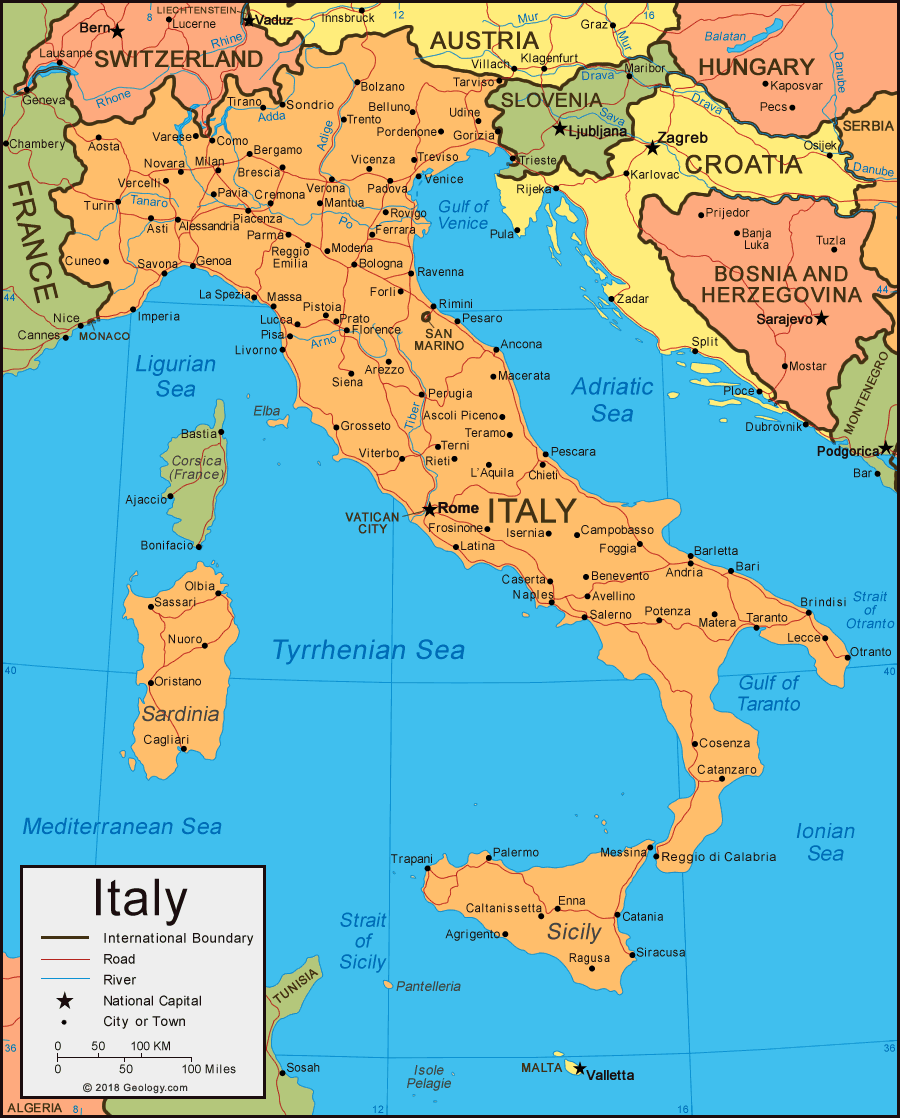
Italy, a nation steeped in history and culture, boasts a complex political map that reflects its rich tapestry of regions, identities, and administrative structures. Understanding this map is essential for comprehending the country’s diverse governance, economic development, and social dynamics. This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of Italy’s political landscape, delving into its regional divisions, historical context, and the significance of its political map.
Regional Divisions and Administrative Structure:
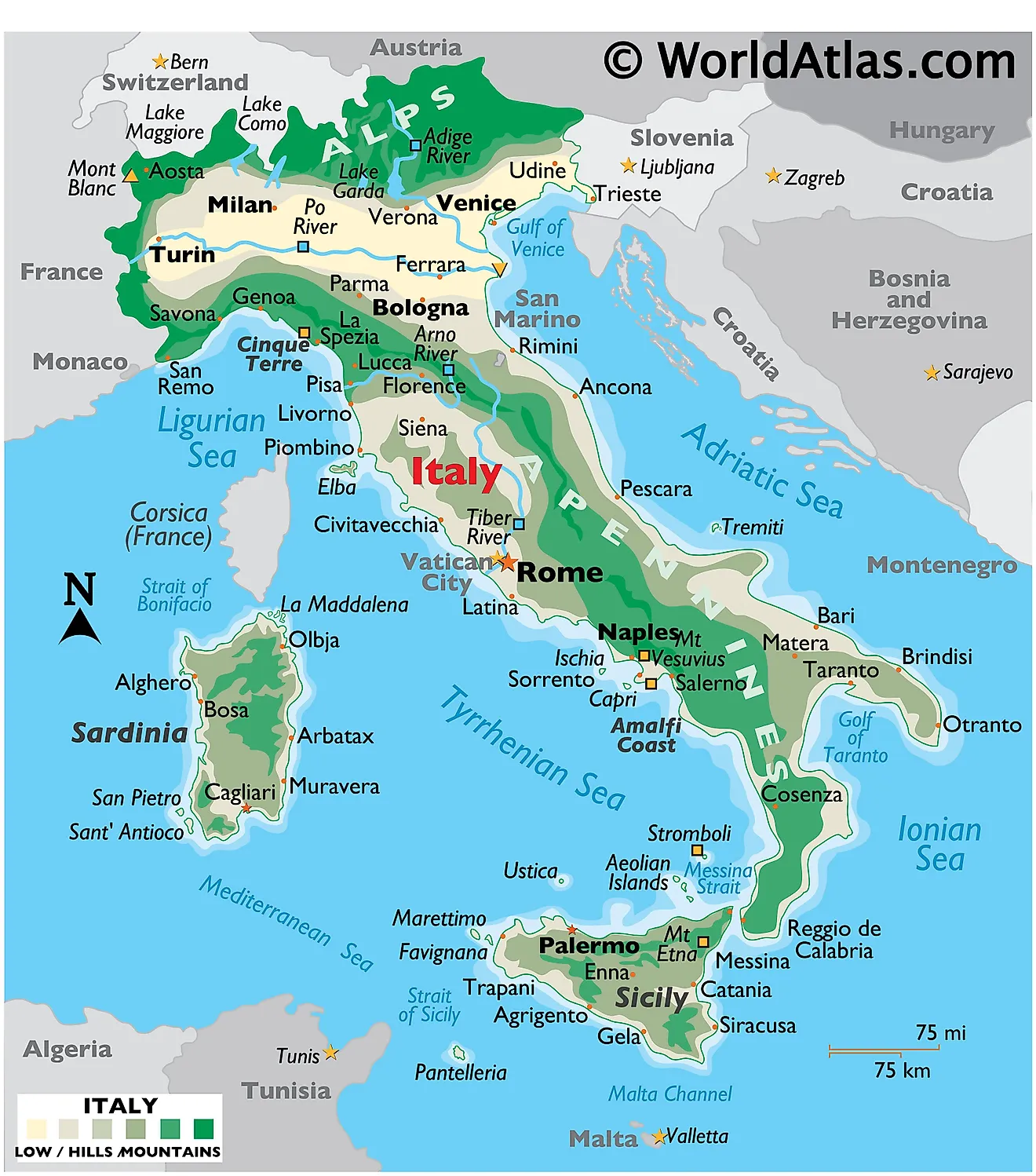
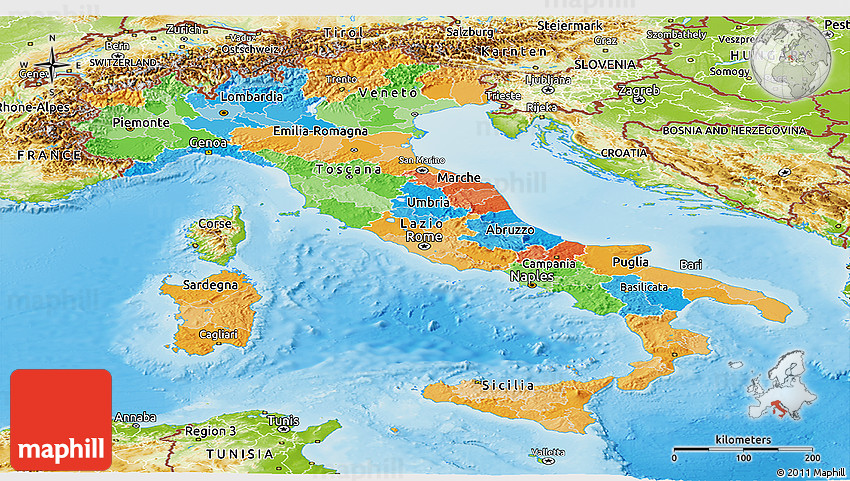
Italy’s political map is divided into 20 regions, each with its own distinct identity and administrative structure. These regions can be further categorized into:
- Ordinary Regions: These are the most common type, comprising 15 regions with elected regional councils and presidents. These regions have autonomy in areas such as education, healthcare, and cultural policies. Examples include Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, and Tuscany.
-
Autonomous Regions: These regions enjoy special status due to their distinct linguistic, cultural, or historical heritage. They have a higher degree of autonomy compared to ordinary regions. Italy has five autonomous regions:
- Valle d’Aosta: A small region in the northwestern Alps with French as an official language.
- Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol: A bilingual region in the Alps, with Italian and German as official languages.
- Friuli-Venezia Giulia: A region in northeastern Italy with a strong Slovene minority.
- Sicily: An island region with a unique history and culture.
- Sardinia: Another island region with a distinct language and cultural heritage.
Historical Context and Evolution:
The current political map of Italy is the product of a long and complex historical process. The unification of Italy in the 19th century brought together diverse regions with distinct identities and traditions. This led to a centralizing tendency in governance, with power concentrated in Rome. However, the desire for greater regional autonomy has been a recurring theme in Italian politics.
The post-World War II period witnessed the emergence of regionalism as a significant political force. The Italian Constitution of 1948 recognized the principle of regional autonomy, paving the way for the creation of the current regional system. The decentralization process, however, has been gradual and uneven, with varying degrees of autonomy granted to different regions.
The Importance of Italy’s Political Map:
Understanding Italy’s political map is crucial for several reasons:
- Regional Diversity: The map highlights the vast diversity of Italy’s regions, each with its own unique cultural heritage, economic structure, and political landscape. This diversity shapes the nation’s political discourse, economic development, and social fabric.
- Political Decentralization: The map reflects the ongoing process of political decentralization in Italy. The regional system allows for a more flexible and responsive governance, catering to the specific needs and aspirations of different regions.
- Economic Development: Regional autonomy plays a significant role in economic development. Regions have the ability to tailor policies to their specific economic needs, attracting investments and promoting innovation.
- Cultural Identity: The map underscores the importance of regional cultural identities. The recognition of linguistic and cultural minorities in autonomous regions contributes to the preservation and promotion of Italy’s diverse cultural heritage.
- Political Stability: The regional system contributes to political stability by providing a platform for regional voices and concerns. This can help to mitigate the risk of separatism and promote national unity.
FAQs about Italy’s Political Map:
1. What is the significance of the autonomous regions in Italy?
Autonomous regions enjoy a higher degree of autonomy than ordinary regions, reflecting their distinct linguistic, cultural, or historical heritage. They have greater control over areas like education, healthcare, and cultural policies, fostering the preservation of their unique identities.
2. How does the regional system impact Italian politics?
The regional system introduces a layer of complexity to Italian politics. Regional elections and party politics play a significant role in national politics, as regional parties and movements can exert influence on national policy-making.
3. What are the challenges facing the regional system in Italy?
Challenges include balancing regional autonomy with national unity, ensuring equitable resource distribution, and addressing disparities in economic development between different regions.
4. How does the political map of Italy compare to other European countries?
Italy’s regional system is a relatively decentralized model compared to other European countries like France and Spain. It reflects a balance between centralized governance and regional autonomy, reflecting the country’s historical and cultural complexities.
5. What are the future prospects for the regional system in Italy?
The future of the regional system depends on various factors, including political will, economic conditions, and social demands. The ongoing debate about regional autonomy and the potential for further decentralization will continue to shape Italy’s political landscape.
Tips for Understanding Italy’s Political Map:
- Explore Regional Identities: Delve into the cultural, linguistic, and historical characteristics of different regions to gain a deeper understanding of their unique identities.
- Study Regional Elections: Pay attention to regional elections and the influence of regional parties on national politics.
- Analyze Economic Data: Compare economic indicators across different regions to understand the impact of regional autonomy on economic development.
- Engage with Local Media: Consult local newspapers and websites to get insights into regional issues and perspectives.
- Travel and Experience: Visiting different regions provides firsthand experience of their unique cultures and political realities.
Conclusion:
Italy’s political map is a testament to the country’s complex history, diverse regional identities, and ongoing evolution of governance. Understanding this map is essential for comprehending the nation’s political dynamics, economic development, and social fabric. By recognizing the importance of regional autonomy and the challenges it presents, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of Italian politics and its impact on the country’s future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Italy’s Political Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!