A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Michigan-Wisconsin Border
Related Articles: A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Michigan-Wisconsin Border
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Michigan-Wisconsin Border. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Michigan-Wisconsin Border

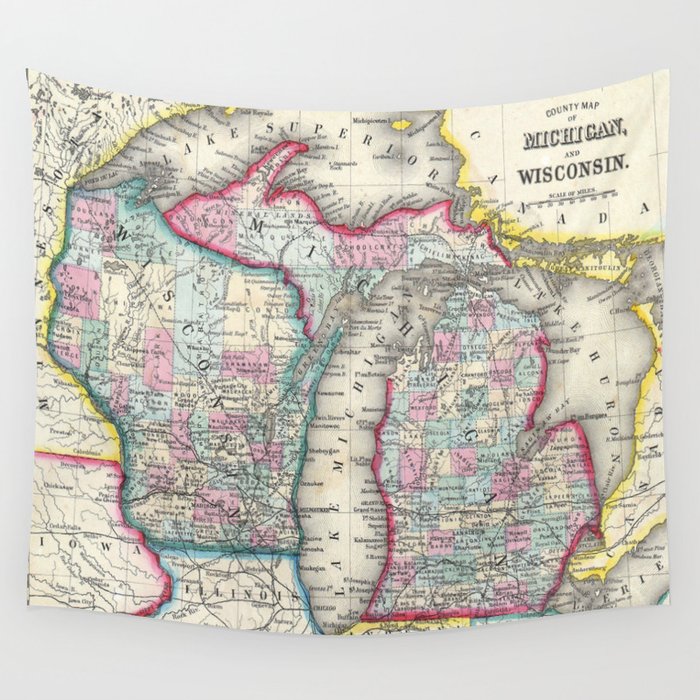
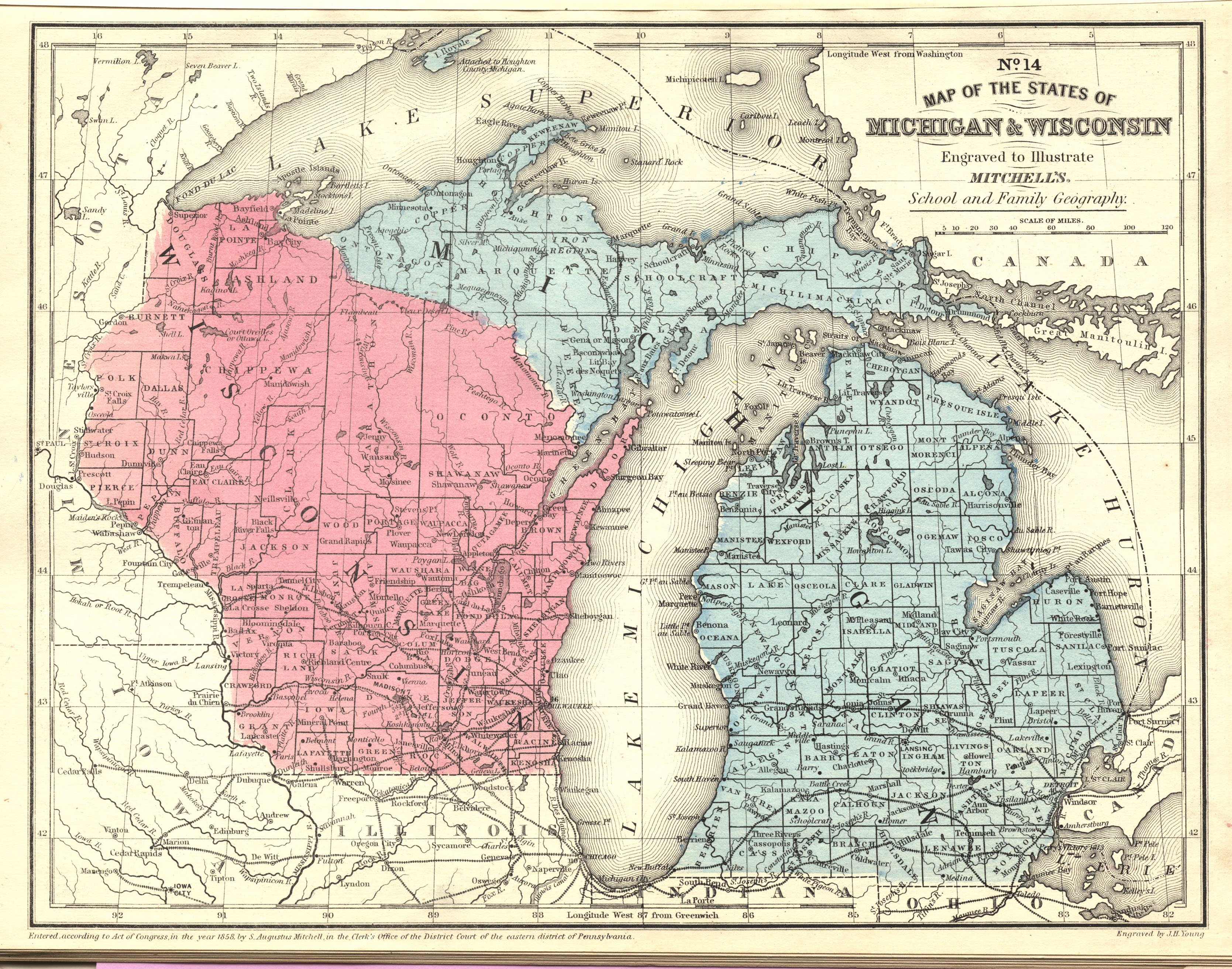
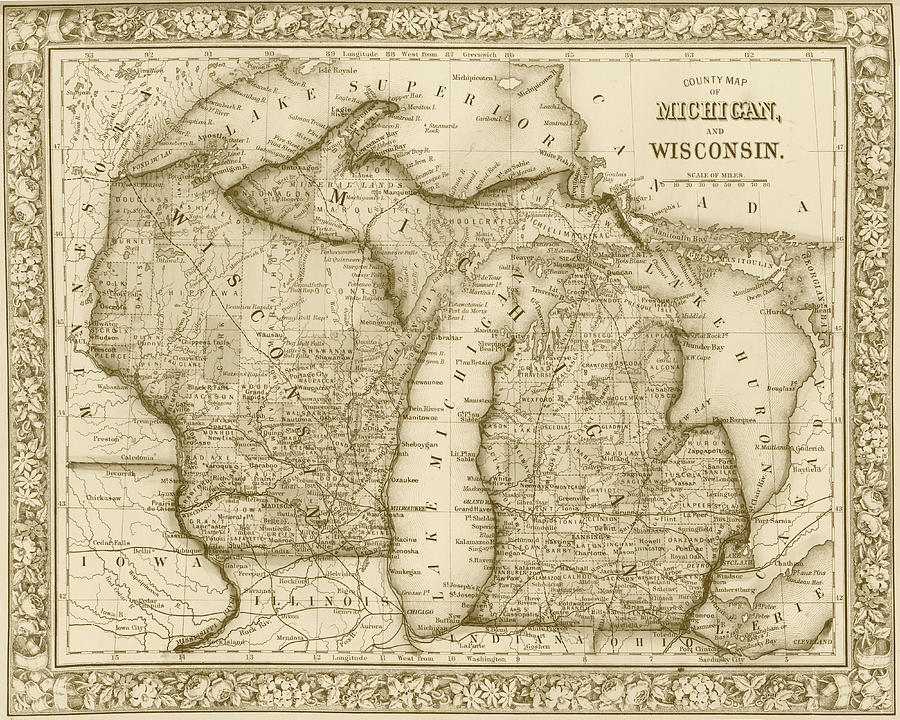
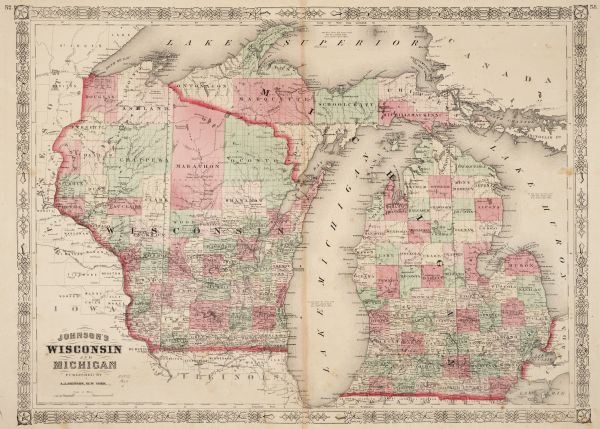
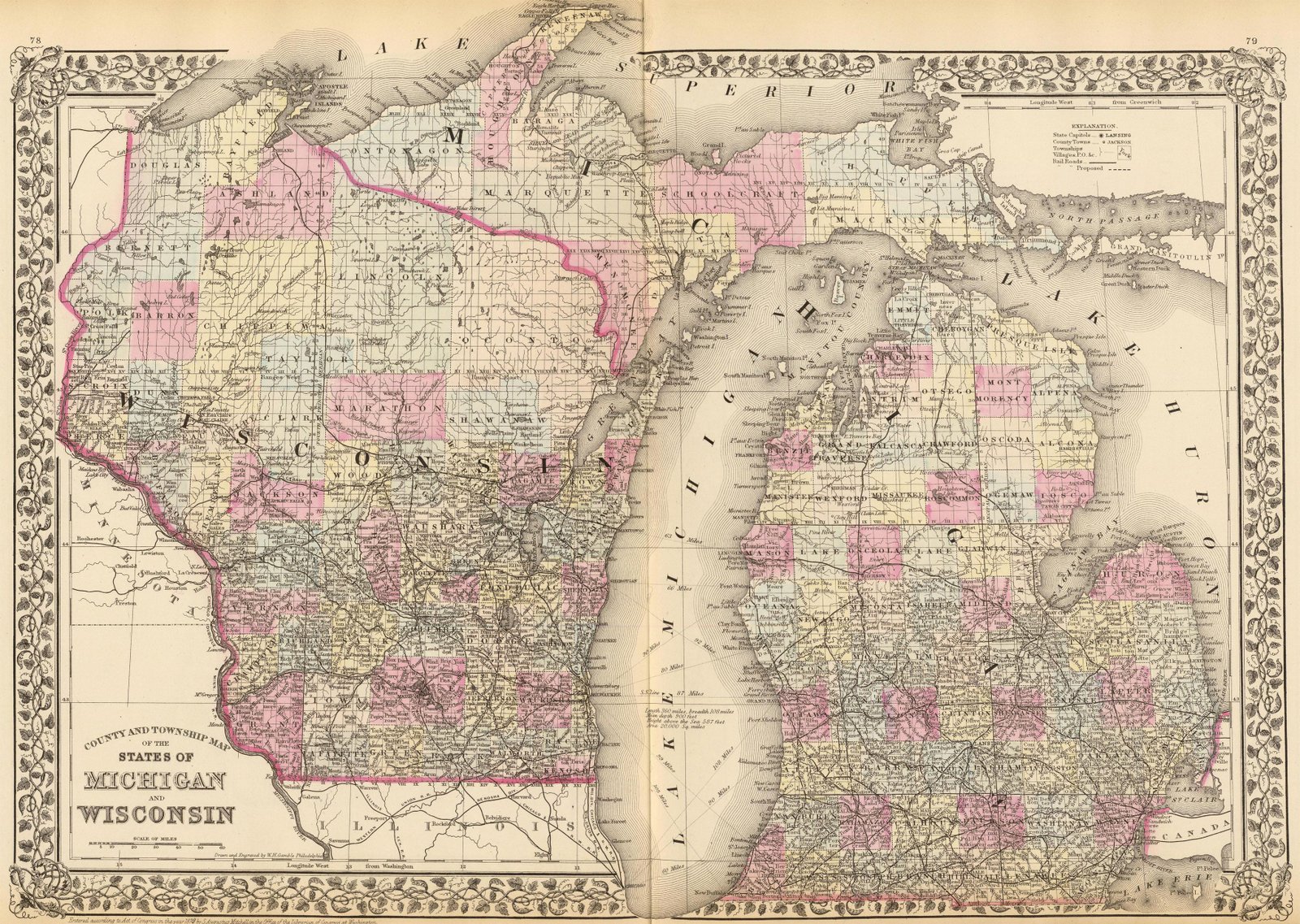
The border between Michigan and Wisconsin, a geographical tapestry woven from lakes, rivers, and shared history, is a fascinating study in regional interaction. It is a boundary that is both physically defined and culturally nuanced, shaping the landscapes, economies, and identities of both states. Understanding this border requires exploring its physical features, the historical forces that shaped it, and the contemporary dynamics that continue to influence its significance.
A Border Defined by Water:
The Michigan-Wisconsin border is primarily defined by water bodies, with the vast expanse of Lake Michigan forming its western edge. This shared waterway serves as a natural boundary, shaping the coastline of both states and influencing their maritime history, economies, and recreational opportunities. The border then weaves inland, following the courses of several rivers, including the Menominee River, the Sturgeon Bay Ship Canal, and the Peshtigo River. These waterways not only delineate the physical boundary but also connect the two states, facilitating trade, transportation, and cultural exchange.
Historical Crossroads:
The history of the Michigan-Wisconsin border is interwoven with the history of the Great Lakes region, marked by Indigenous presence, European exploration, and the westward expansion of the United States. The region was initially inhabited by various Indigenous tribes, including the Menominee, the Ojibwe, and the Potawatomi, who lived in harmony with the land and its resources. European exploration began in the 17th century, with French fur traders establishing trading posts along the Great Lakes. The arrival of European settlers in the 19th century led to the displacement of Indigenous populations and the establishment of formal state boundaries.
The Treaty of Fort Laramie in 1851 played a crucial role in defining the modern Michigan-Wisconsin border. The treaty established the current boundary, which followed the natural features of the landscape, including the Menominee River and Lake Michigan. This treaty, however, also marked a turning point in the relationship between the United States government and Indigenous tribes, leading to the dispossession of their lands and the forced relocation of many tribes.
Contemporary Dynamics:
Today, the Michigan-Wisconsin border remains a dynamic and evolving region, influenced by various contemporary factors. The shared economy of the two states is deeply interconnected, with industries such as tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing crossing state lines. The Great Lakes, a vital resource for both states, continue to be a source of economic activity, recreation, and environmental concerns. The border region also faces challenges related to population growth, infrastructure development, and the preservation of natural resources.
The Importance of the Border:
The Michigan-Wisconsin border is more than just a geographical line; it represents a unique cultural and economic nexus. It is a region where the shared history of two states, the beauty of the Great Lakes, and the dynamism of contemporary life converge. Understanding this border is crucial for appreciating the complex relationship between these two states, the challenges they face, and the opportunities they share.
FAQs about the Michigan-Wisconsin Border:
1. What is the length of the Michigan-Wisconsin border?
The Michigan-Wisconsin border is approximately 450 miles long, extending from the southern tip of Lake Michigan to the northern tip of the Upper Peninsula.
2. What are the major cities located on the Michigan-Wisconsin border?
Major cities located on the Michigan-Wisconsin border include Green Bay, Wisconsin; Milwaukee, Wisconsin; and Traverse City, Michigan.
3. What is the significance of the Menominee River to the Michigan-Wisconsin border?
The Menominee River serves as a natural boundary for a significant portion of the Michigan-Wisconsin border. It is an important source of water, recreation, and economic activity for both states.
4. What are the main industries that operate along the Michigan-Wisconsin border?
The main industries operating along the Michigan-Wisconsin border include tourism, agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation.
5. What are the environmental challenges facing the Michigan-Wisconsin border region?
The Michigan-Wisconsin border region faces various environmental challenges, including water pollution, invasive species, and climate change.
Tips for Exploring the Michigan-Wisconsin Border:
1. Visit the Door County Peninsula: This picturesque peninsula in Wisconsin offers stunning views of Lake Michigan, charming towns, and abundant recreational opportunities.
2. Explore the Mackinac Bridge: This iconic bridge connects the Upper and Lower Peninsulas of Michigan, offering breathtaking views of the Straits of Mackinac.
3. Visit the Apostle Islands National Lakeshore: Located in northern Wisconsin, this national lakeshore features rugged islands, pristine waters, and diverse wildlife.
4. Experience the Door County Maritime Museum: This museum in Sturgeon Bay, Wisconsin, showcases the rich maritime history of the Great Lakes region.
5. Hike the North Country Trail: This long-distance trail traverses the Michigan-Wisconsin border, offering scenic views and challenging hiking opportunities.
Conclusion:
The Michigan-Wisconsin border is a fascinating testament to the interplay of geography, history, and culture. It is a region where the past and present converge, shaping the lives of residents and visitors alike. By understanding the physical features, historical forces, and contemporary dynamics that define this border, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of the Great Lakes region and the enduring significance of its natural and human landscapes.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Michigan-Wisconsin Border. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!