A Frozen Landscape: Uncovering the Secrets of Ice Age North America
Related Articles: A Frozen Landscape: Uncovering the Secrets of Ice Age North America
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Frozen Landscape: Uncovering the Secrets of Ice Age North America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Frozen Landscape: Uncovering the Secrets of Ice Age North America

The North America we know today is a far cry from the frigid expanse it was during the Pleistocene Epoch, commonly known as the Ice Age. This period, spanning from roughly 2.6 million to 11,700 years ago, witnessed the dramatic advance and retreat of massive ice sheets that reshaped the continent’s geography, climate, and ultimately, the trajectory of life.
Mapping the Ice Age:
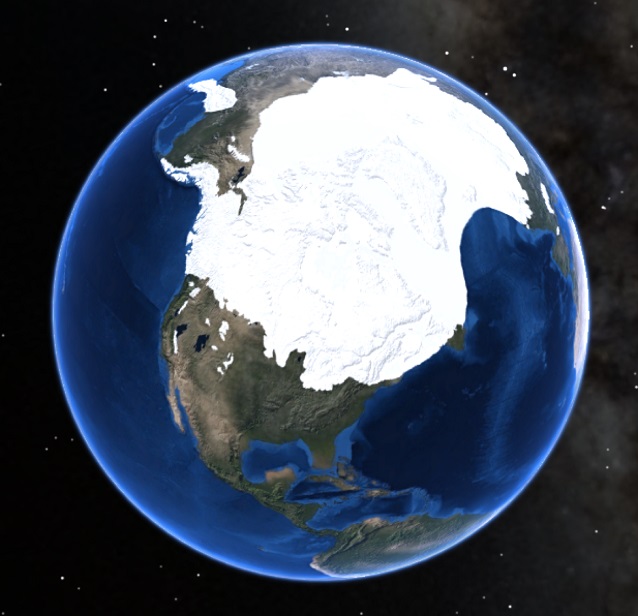
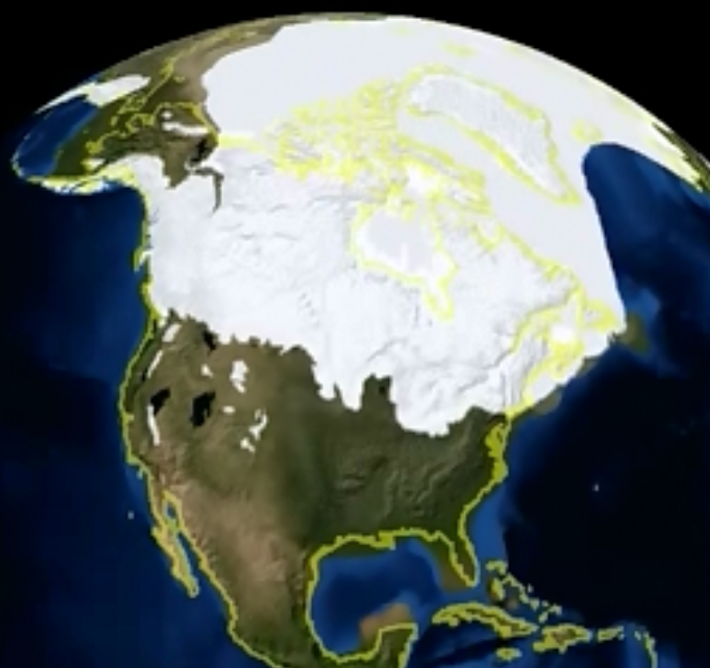
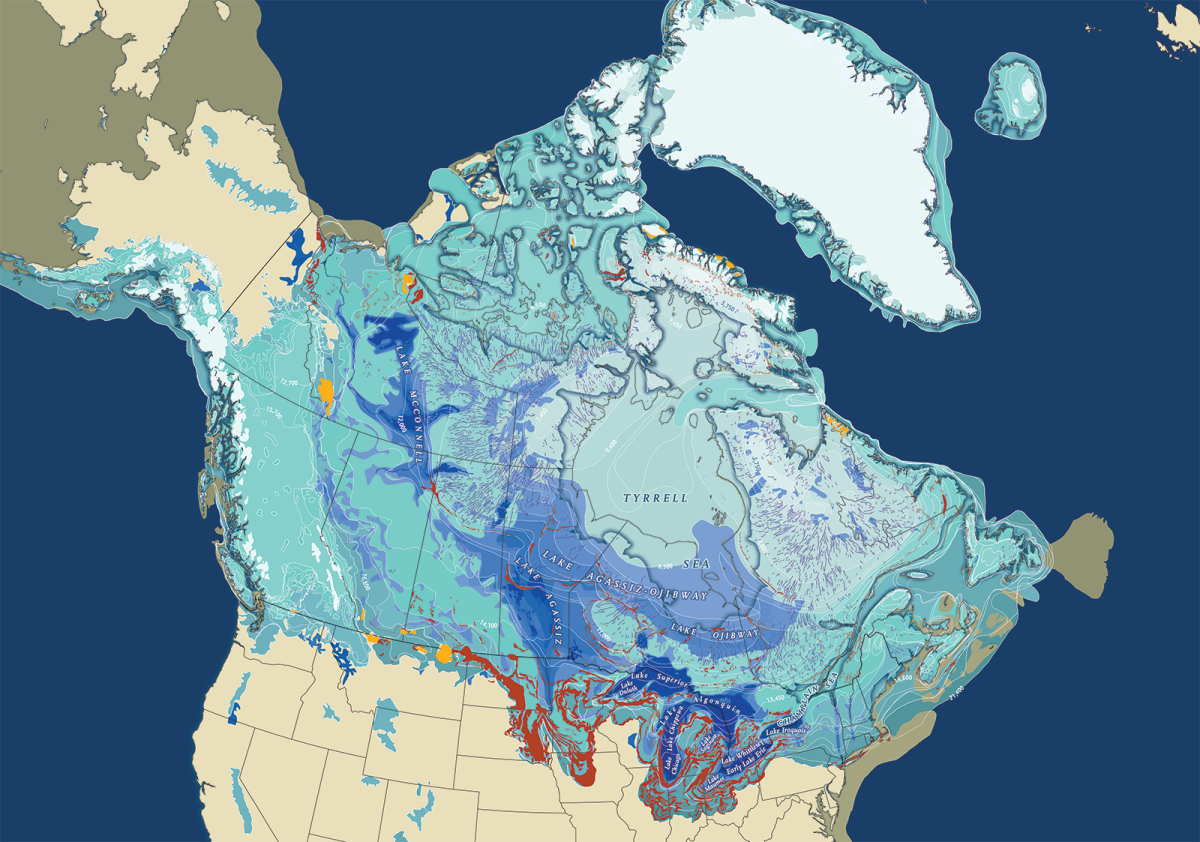
Visualizing the vastness and impact of these glaciers is made possible through Ice Age North America maps. These maps, meticulously crafted by scientists using geological evidence, provide a detailed picture of the ice sheets’ extent, their movement, and the profound changes they wrought upon the landscape.
The Ice Sheets: Giants of the Pleistocene
During the Ice Age, vast sheets of ice, known as continental glaciers, spread across North America, reaching their maximum extent around 20,000 years ago. These glaciers, originating in the north, pushed southward, covering much of Canada and parts of the United States. The Laurentide Ice Sheet, the largest of them all, stretched from the Arctic Ocean to the Ohio River Valley, while the Cordilleran Ice Sheet covered much of the western mountains.
The Impact of Glaciation:
The presence of these massive ice sheets profoundly altered the landscape of North America:
- Erosion and Deposition: The sheer weight of the glaciers carved out valleys, sculpted mountains, and deposited vast amounts of sediment, creating the characteristic features of the Great Lakes region, the Finger Lakes of New York, and the vast plains of the Midwest.
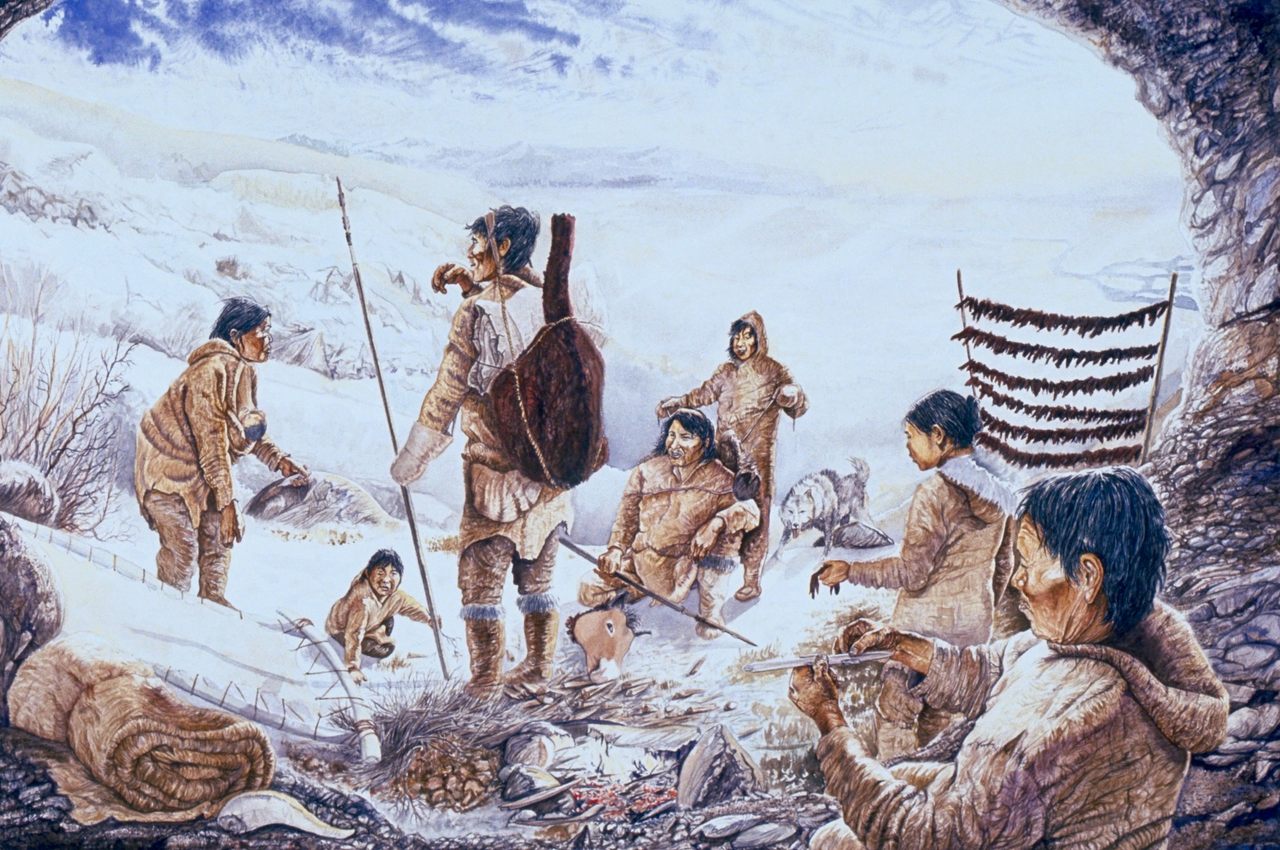
- Sea Level Changes: As water was locked up in the ice sheets, global sea levels dropped significantly, exposing vast stretches of land that are now submerged. This led to the formation of land bridges, such as Beringia, connecting Asia and North America, facilitating the migration of early humans and animals.
- Climate Shifts: The presence of ice sheets significantly altered regional and global climate patterns, leading to colder temperatures, increased snowfall, and changes in precipitation patterns.
Beyond the Ice:
Beyond the immediate impact of the glaciers, the Ice Age left a lasting legacy on North America:
- Soil Formation: The glaciers’ retreat deposited rich glacial till, a mixture of rock, clay, and sand, which formed the fertile soils that support agriculture in many parts of the continent.
- Water Resources: The glaciers carved out depressions that filled with meltwater, creating the Great Lakes, a vital source of freshwater and a cornerstone of the North American economy.
- Biodiversity: The Ice Age saw the emergence of new species, the extinction of others, and the migration of animals across the continent, shaping the biodiversity we see today.
Unveiling the Past: The Importance of Ice Age Maps
Ice Age North America maps are invaluable tools for understanding the past and present of the continent. They provide insights into:
- Geological History: Maps reveal the extent and movement of glaciers, helping scientists understand the processes that shaped the landscape.
- Climate Change: By studying the advance and retreat of glaciers, researchers can gain insights into past climate fluctuations and their impact on the environment.
- Human Migration: Maps help trace the migration routes of early humans and animals across the continent, shedding light on the peopling of North America.
- Resource Management: Understanding the distribution of glacial deposits helps in the management of water resources, soil fertility, and mineral resources.
FAQs about Ice Age North America Maps:
1. What are Ice Age North America maps based on?
Ice Age maps are created using a variety of geological evidence, including:
- Glacial Deposits: The presence of glacial till, erratics (rocks transported by glaciers), and striations (scratches on bedrock) indicate the extent and direction of ice flow.
- Landforms: Features like U-shaped valleys, cirques (bowl-shaped depressions), and moraines (deposits of rock and sediment) are characteristic of glacial activity.
- Paleoclimate Data: Analyses of sediment cores, tree rings, and ice cores provide information about past climate conditions.
2. How accurate are Ice Age North America maps?
The accuracy of Ice Age maps depends on the availability and quality of data. While maps provide a general picture of glacial extent, the exact boundaries and details can vary based on ongoing research and data refinement.
3. How do Ice Age maps help us understand climate change today?
Studying past glacial cycles provides valuable insights into the Earth’s climate system. By analyzing the factors that caused glacial advance and retreat, scientists can better understand the mechanisms of climate change and predict its potential impact on future environments.
4. What are some of the key features shown on Ice Age North America maps?
Key features include:
- The Laurentide and Cordilleran Ice Sheets: The major ice sheets that covered much of North America.
- Glacial Retreat Routes: The paths taken by retreating glaciers, often marked by moraines and outwash plains.
- Land Bridges: Areas of exposed land, like Beringia, that connected continents during periods of low sea level.
- Key Glacial Features: U-shaped valleys, cirques, and other landforms created by glacial activity.
Tips for Understanding Ice Age North America Maps:
- Pay attention to scale: The vastness of the ice sheets can be difficult to grasp. Consider the scale of the map and the actual size of the features shown.
- Look for key features: Identify the major ice sheets, glacial retreat routes, and other significant landforms.
- Consider the time frame: Different maps may represent different periods of glacial advance and retreat. Pay attention to the time frame covered by each map.
- Relate the map to modern geography: Try to visualize how the landscape of North America has been shaped by glacial activity.
Conclusion:
Ice Age North America maps are invaluable tools for understanding the continent’s geological history, climate change, and the evolution of life. They reveal a dramatic and dynamic past, offering insights into the forces that shaped the landscape we inhabit today. By studying these maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and the profound impact of climate change on the planet.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Frozen Landscape: Uncovering the Secrets of Ice Age North America. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!